Pigouvian Tax

The concept of a Pigouvian Tax has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly in discussions surrounding environmental economics and market failures. This tax mechanism, named after the influential British economist Arthur Cecil Pigou, offers a unique approach to addressing externalities and promoting more efficient market outcomes. As the world grapples with pressing environmental challenges, understanding the nuances of Pigouvian Taxation becomes crucial for policymakers, economists, and environmental advocates alike.
Unraveling the Pigouvian Tax: A Mechanism for Market Intervention

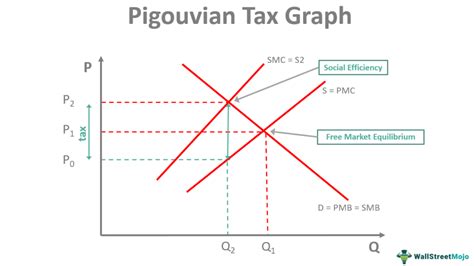
At its core, a Pigouvian Tax is designed to address market failures, specifically those arising from negative externalities. Externalities refer to the costs or benefits that are incurred by parties who did not choose to incur those costs or benefits. Negative externalities occur when an economic activity imposes costs on third parties, often without those parties being compensated. A classic example is the pollution generated by industrial activities, which can harm the environment and public health without the polluters bearing the full cost of these impacts.
Pigou, in his seminal work The Economics of Welfare, proposed that the solution to such market failures lay in taxing the activity that generates the externality. This tax would be set at a level that reflects the social cost of the externality, thus encouraging firms to internalize these costs and adjust their behavior accordingly. By doing so, Pigouvian Taxation aims to restore market efficiency and promote more sustainable and socially optimal outcomes.
Key Principles of Pigouvian Taxation
The effectiveness of a Pigouvian Tax hinges on several critical principles:
- Identification of Externalities: The first step involves identifying the specific negative externality that needs to be addressed. This could range from environmental pollution to congestion or even social costs associated with certain industries.
- Estimation of Social Costs: Once the externality is identified, the next challenge is to estimate the social cost it imposes. This involves a complex process of quantifying the impact on public health, the environment, or other affected areas.
- Tax Rate Determination: The tax rate is then set to equal the estimated social cost. This ensures that the tax reflects the true cost of the externality, providing an incentive for firms to reduce their negative impact.
- Revenue Allocation: The revenue generated from the tax can be used for various purposes. It can be directed towards mitigating the externality's impact, funding environmental initiatives, or even compensating those affected by the externality.
By implementing these principles, Pigouvian Taxation aims to create a more level playing field, ensuring that the costs of economic activities are borne by those who cause them rather than being imposed on society as a whole.
Real-World Applications: A Closer Look at Pigouvian Taxes

The concept of Pigouvian Taxation has found practical applications in various sectors, offering a tangible approach to tackling some of society's most pressing issues.
Environmental Pollution: A Classic Case Study
One of the most well-known applications of Pigouvian Taxation is in addressing environmental pollution. Take, for instance, the case of carbon emissions and climate change. Governments around the world have implemented carbon taxes, aiming to reduce the emissions that contribute to global warming. By taxing carbon-intensive activities, such as fossil fuel use, these taxes encourage firms and individuals to adopt more environmentally friendly practices.
A notable example is the British Columbia Carbon Tax, introduced in 2008. This tax, which starts at $10 per tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent and increases annually, has been effective in reducing emissions without significantly impacting economic growth. The revenue generated from the tax is used to provide tax cuts in other areas, making it a revenue-neutral policy.
| Year | Carbon Tax Rate ($/tonne CO2e) |
|---|---|
| 2008 | $10 |
| ... | ... |
| 2023 | $55 |
In the European Union, the Emissions Trading System (ETS) is another example of a Pigouvian Tax. This cap-and-trade system sets a limit on carbon emissions and allows companies to buy and sell permits to emit carbon dioxide. The price of these permits acts as a tax, incentivizing companies to reduce their emissions and invest in cleaner technologies.
Congestion and Transport
Pigouvian Taxation is also applied to address congestion in urban areas. Congestion charges, like those implemented in London and Singapore, are designed to reduce traffic congestion by charging drivers a fee for entering the city center during peak hours. The revenue generated is often used to improve public transport, further reducing reliance on private vehicles.
Waste Management and Recycling
In the realm of waste management, Pigouvian Taxes can encourage more sustainable practices. Landfill taxes, for instance, are used to discourage the disposal of waste in landfills, promoting recycling and waste reduction initiatives.
The Pros and Cons of Pigouvian Taxation
While Pigouvian Taxation offers a promising approach to addressing market failures, it is not without its challenges and considerations.
Advantages
- Incentivizing Sustainable Behavior: By internalizing the costs of externalities, Pigouvian Taxes encourage firms and individuals to adopt more environmentally and socially responsible practices.
- Revenue Generation: The taxes can generate significant revenue, which can be used to fund environmental initiatives, research, or even compensate those affected by externalities.
- Market Efficiency: By correcting market failures, Pigouvian Taxes contribute to more efficient market outcomes, promoting social welfare.
Challenges and Considerations
- Complexity of Estimation: Accurately estimating the social cost of externalities can be challenging and may require extensive research and modeling.
- Political and Social Acceptance: Implementing Pigouvian Taxes can be met with resistance, as it often requires individuals and firms to pay more for certain activities. Building public support and understanding is crucial.
- Revenue Allocation: Determining how to allocate the revenue generated from Pigouvian Taxes can be complex and may require careful consideration of societal priorities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary objective of a Pigouvian Tax?
+The primary objective of a Pigouvian Tax is to address market failures arising from negative externalities. By taxing the activity that generates the externality, the tax aims to encourage firms and individuals to internalize the costs of their actions, leading to more socially optimal outcomes.
How is the tax rate for a Pigouvian Tax determined?
+The tax rate is set to equal the estimated social cost of the externality. This involves a rigorous process of quantifying the impact of the externality on public health, the environment, or other affected areas.
Can you provide an example of a successful Pigouvian Tax implementation?
+One notable example is the British Columbia Carbon Tax, which has effectively reduced carbon emissions without significantly impacting economic growth. The tax revenue is used to provide tax cuts in other areas, making it a revenue-neutral policy.
What are some challenges associated with Pigouvian Taxation?
+Challenges include the complexity of accurately estimating social costs, potential resistance from the public or industries affected by the tax, and the need for careful consideration when allocating the revenue generated from the tax.
How can Pigouvian Taxation contribute to sustainable development goals?
+By incentivizing more sustainable practices and behaviors, Pigouvian Taxation can play a crucial role in achieving sustainable development goals. It can encourage the adoption of cleaner technologies, promote recycling and waste reduction, and contribute to a more environmentally conscious society.