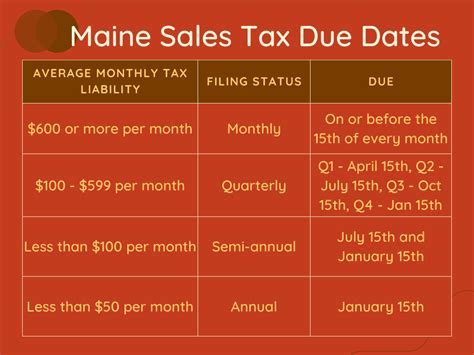
Ohio County Income Tax Rates

Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the income tax rates in Ohio's counties. This article will delve into the intricacies of the state's tax system, providing you with a clear understanding of how much you might owe in taxes based on your residence. Ohio's tax structure is unique, with each county setting its own local income tax rates, adding an extra layer of complexity to the process.
Unraveling Ohio’s County Income Tax Landscape

Ohio’s income tax system is a fascinating study in diversity and complexity. Unlike many other states, Ohio does not impose a uniform income tax rate across its borders. Instead, each of Ohio’s 88 counties is granted the autonomy to establish its own local income tax rates, creating a unique and varied tax landscape.
This decentralized approach to taxation has led to a wide range of tax rates across the state, from as low as 0% to as high as 2.75%, depending on the county in which you reside. This variation is a reflection of the state's commitment to local control and decision-making, ensuring that tax revenues are directed towards the specific needs and priorities of each community.
The Mechanics of Ohio’s County Income Taxes
Ohio’s county income taxes are typically levied as a flat percentage of your taxable income. This means that, regardless of your income level, the tax rate remains the same. However, it’s important to note that not all counties in Ohio impose a local income tax. Currently, 52 of Ohio’s 88 counties have implemented a local income tax, while the remaining counties rely solely on state and federal taxes.
For those counties that do levy a local income tax, the rates can vary significantly. Some counties opt for a single flat rate, while others employ a graduated tax system, where the tax rate increases as your income rises. This complexity arises from the fact that each county's tax structure is tailored to its unique financial needs and the preferences of its residents.
| County | Income Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Adams | 1.25% |
| Allen | 1.8% |
| Ashland | 0.8% |
| Ashtabula | 1.5% |
| Athens | 1.35% |
| Auglaize | 1.25% |
| Belmont | 1.5% |
| ... | ... |
This table provides a glimpse into the diverse tax rates across Ohio's counties. As you can see, there's a wide range of rates, from as low as 0.5% to as high as 2.75%. This variability underscores the importance of understanding your local tax landscape when planning your finances.
The Impact of County Income Taxes on Your Wallet
Understanding Ohio’s county income tax rates is not just an academic exercise; it has a direct and tangible impact on your personal finances. For instance, let’s consider the difference in tax liability between two residents, John and Jane, who earn the same annual income but live in different counties.
John, a resident of Franklin County, which has an income tax rate of 2.5%, would owe $2,500 in local income taxes on an annual income of $100,000. On the other hand, Jane, a resident of Summit County, with an income tax rate of 1.5%, would owe only $1,500 on the same income.
This example highlights how the county you reside in can significantly influence your tax liability. It's a critical factor to consider when making decisions about where to live and work, especially for those with higher incomes or those planning for long-term financial goals.
Navigating Ohio’s Tax System: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we’ve explored the basics of Ohio’s county income tax system, let’s delve into a practical guide on how to navigate this complex landscape.
Step 1: Identify Your County’s Tax Rate
The first step in understanding your tax liability is to identify the income tax rate for your county. You can easily find this information on your county’s official website or by contacting the local tax authority. Alternatively, there are numerous online resources and tax guides that provide detailed information on county tax rates.
For instance, the Ohio Department of Taxation maintains a comprehensive list of county tax rates, which is updated regularly. This list provides a quick and easy way to check the tax rate for your county and can be a valuable resource for tax planning.
Step 2: Calculate Your Taxable Income
Once you know your county’s tax rate, the next step is to determine your taxable income. This is the amount of your income that is subject to taxation, after allowable deductions and exemptions have been applied.
In Ohio, taxable income is typically calculated by subtracting your standard or itemized deductions, personal exemptions, and any other allowable deductions from your gross income. The Ohio Department of Taxation provides detailed guidelines on how to calculate your taxable income, ensuring you can accurately assess your tax liability.
Step 3: Apply the Tax Rate
With your taxable income calculated, you can now apply your county’s income tax rate to determine your tax liability. Simply multiply your taxable income by the tax rate to arrive at the amount you owe in local income taxes.
For example, if your taxable income is $50,000 and your county's tax rate is 1.5%, your local income tax liability would be $750. This calculation provides a clear understanding of the direct financial impact of your county's tax rate on your personal finances.
Step 4: Consider Tax Credits and Deductions
While the above steps provide a basic understanding of your tax liability, it’s important to remember that there are often additional tax credits and deductions that can reduce the amount of tax you owe. These can include tax credits for dependents, education, or certain types of income, as well as deductions for medical expenses, charitable contributions, or business-related expenses.
Consulting with a tax professional or utilizing tax preparation software can help you identify and apply these credits and deductions, ensuring you pay no more in taxes than is absolutely necessary.
The Future of Ohio’s County Income Taxes
As we look to the future, it’s clear that Ohio’s county income tax system will continue to evolve in response to the changing economic and social landscape. The ongoing debate around tax policy, both at the state and local levels, reflects a dynamic and responsive system that adapts to the needs of its residents.
One potential area of change is the consideration of a uniform state income tax, which could simplify the tax landscape for Ohio residents. While this proposal has been debated in the past, it remains a topic of discussion among policymakers and stakeholders. A move towards a state-wide flat tax could significantly reduce the complexity of Ohio's tax system, making it more straightforward for residents to understand and navigate.
Additionally, as the state continues to grow and develop, we can expect to see further refinement and adjustment of county tax rates. This could include counties raising or lowering their rates to align with their economic goals or to maintain competitiveness with neighboring counties.
In conclusion, Ohio's county income tax rates present a unique and dynamic aspect of the state's tax system. By understanding these rates and the factors that influence them, residents can make informed decisions about their financial planning and contribute to the economic vitality of their communities.
How often do Ohio’s county income tax rates change?
+
Ohio’s county income tax rates can change annually or more frequently, depending on the county. These changes are often made to align with the county’s budgetary needs and economic goals.
Are there any counties in Ohio that do not impose a local income tax?
+
Yes, currently, there are 36 counties in Ohio that do not levy a local income tax. These counties rely solely on state and federal taxes for their revenue.
What happens if I work in a different county than where I live?
+
If you work in a different county than where you live, you may be subject to income tax in both counties. However, many counties have reciprocity agreements, which allow you to be taxed only in your resident county. It’s important to check with both counties to understand your specific tax obligations.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available for Ohio residents?
+
Yes, Ohio offers various tax credits and incentives, such as the Homestead Exemption, which provides a tax credit for homeowners aged 65 and older or permanently disabled, and the Earned Income Tax Credit, which benefits low- to moderate-income workers and families.