Nj Tax Forms

In the realm of tax management, understanding the intricacies of various tax forms is paramount. For residents and businesses in the state of New Jersey, navigating the NJ tax forms is a critical aspect of financial compliance and strategic planning. This comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of these forms, offering insights into their purpose, usage, and potential complexities.
The NJ Tax Forms: An Overview

The New Jersey Division of Taxation administers a range of tax forms, each serving a distinct purpose within the state’s fiscal framework. These forms are integral to the collection of revenue, ensuring the state’s financial stability and the provision of essential services.
Form NJ-1040: Individual Income Tax Return
Form NJ-1040 is the primary vehicle for individuals to report their annual income and calculate their state tax liability. This form, akin to its federal counterpart, the 1040, is a detailed roadmap for taxpayers to navigate their income, deductions, and credits.
Key aspects of Form NJ-1040 include:
- Income reporting, encompassing wages, interest, dividends, and other sources.
- Deductions for standard or itemized categories, including medical expenses and state taxes paid.
- A comprehensive schedule for reporting capital gains and losses.
- The option to claim various credits, such as the Child and Dependent Care Credit and the Property Tax Deduction.
Form NJ-1040S: Simplified Resident Income Tax Return
Form NJ-1040S is designed for New Jersey residents with a straightforward tax situation. This simplified form streamlines the tax filing process, making it more accessible for individuals with limited income sources and deductions.
Eligible taxpayers for Form NJ-1040S include:
- Single filers with a gross income below 100,000.</li> <li>Married couples filing jointly with a combined gross income under 200,000.
- Taxpayers with only wage, salary, pension, or annuity income.
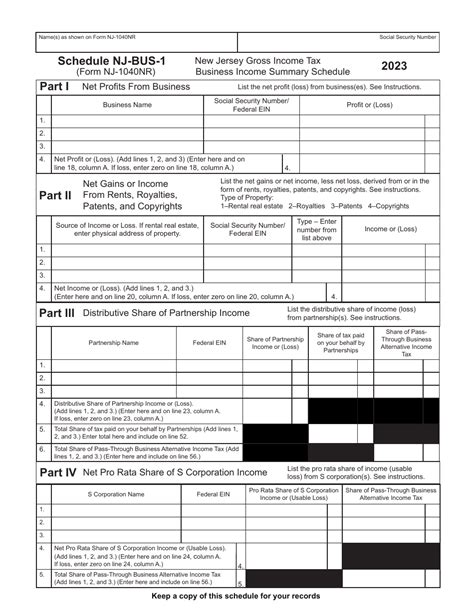
Form NJ-1040NR: Nonresident and Part-Year Resident Income Tax Return
Form NJ-1040NR is for individuals who do not meet the state’s residency requirements but earned income or had a tax liability in New Jersey during the tax year. This form calculates the tax due on income earned or sourced within the state.
Key considerations for Form NJ-1040NR include:
- Determining the portion of income subject to New Jersey tax, which may differ from federal rules.
- Understanding the state’s reciprocity agreements with other states, which can impact tax liability.
- Reporting income from various sources, including wages, business income, and investment gains.
Form NJ-500-X: Corporation Business Tax Return
Form NJ-500-X is the cornerstone for corporations to report their business income and calculate their tax liability in New Jersey. This form is integral to the state’s corporate tax structure and ensures that businesses contribute to the state’s revenue base.
Key components of Form NJ-500-X include:
- Reporting corporate income, including net profits and losses.
- Calculating the Corporation Business Tax, which is based on a corporation’s entire net worth.
- Providing details on business activities, assets, and payroll within the state.
Form NJ-927: Sales and Use Tax Return
Form NJ-927 is the mechanism for businesses to report and remit sales tax collected from customers. This form is a critical part of New Jersey’s sales tax system, ensuring that businesses comply with their tax obligations.
Key aspects of Form NJ-927 include:
- Reporting sales tax collected on taxable goods and services.
- Calculating the amount of tax due, taking into account any applicable exemptions or deductions.
- Remitting the tax to the state on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, depending on the business’s filing frequency.
| Form | Purpose |
|---|---|
| NJ-1040 | Individual Income Tax Return |
| NJ-1040S | Simplified Resident Income Tax Return |
| NJ-1040NR | Nonresident and Part-Year Resident Income Tax Return |
| NJ-500-X | Corporation Business Tax Return |
| NJ-927 | Sales and Use Tax Return |

Navigating the NJ Tax Landscape
Understanding the various NJ tax forms is just the first step in a complex tax journey. The state’s tax system, like many others, is a dynamic and ever-evolving entity, influenced by legislative changes, economic shifts, and legal interpretations.
The Role of Tax Professionals
For individuals and businesses, particularly those with complex financial situations, the guidance of a qualified tax professional can be invaluable. Tax advisors, accountants, and attorneys can provide tailored advice, ensuring compliance and optimizing tax strategies.
Key benefits of engaging tax professionals include:
- Expertise in interpreting complex tax laws and regulations.
- Assistance in identifying eligible deductions and credits.
- Accurate filing to avoid penalties and audits.
- Strategic tax planning to minimize liability and maximize savings.
Staying Informed: Tax Resources and Updates
In the fast-paced world of tax, staying informed is essential. Taxpayers and businesses should leverage a range of resources to stay abreast of the latest developments.
- Official Government Sources: Regularly check the New Jersey Division of Taxation website for updates on tax forms, deadlines, and new legislation.
- Tax News and Blogs: Follow reputable tax news sources and blogs for insights into emerging trends and potential changes.
- Professional Networks: Engage with industry peers and tax professionals to share knowledge and stay informed about best practices.
The Impact of Technology: Tax Software and Online Filing
The advent of digital tax software and online filing platforms has revolutionized the tax landscape. These tools offer enhanced accuracy, convenience, and speed in preparing and filing tax returns.
Key advantages of digital tax solutions include:
- Automated calculations and error-checking to reduce the risk of mistakes.
- Easy access to prior-year returns and historical data.
- Seamless integration with financial institutions for importing data.
- Secure online filing, often with faster processing times.
What are the key differences between Form NJ-1040 and Form NJ-1040S?
+Form NJ-1040 is the standard individual income tax return for New Jersey residents, while Form NJ-1040S is a simplified version designed for taxpayers with simpler financial situations. Form NJ-1040S has fewer lines and is easier to complete, making it suitable for individuals with limited income sources and deductions. It has lower income thresholds and is not suitable for those with more complex financial affairs.
When is the deadline for filing NJ tax returns?
+The deadline for filing New Jersey tax returns typically aligns with the federal deadline, which is usually April 15th of each year. However, it’s crucial to check for any extensions or changes, especially in light of recent tax law modifications.
How often should businesses file Form NJ-927?
+The frequency of filing Form NJ-927, the Sales and Use Tax Return, depends on the business’s sales volume and tax liability. Businesses with higher sales volumes and tax liabilities typically file on a monthly basis, while those with lower volumes may file quarterly or annually. It’s essential for businesses to consult the official guidelines to determine their filing frequency.