Nebraska State Income Tax

Welcome to an in-depth exploration of Nebraska's state income tax system. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the tax laws and regulations that govern the citizens and businesses of the Cornhusker State. With a unique tax structure and a range of deductions and credits available, Nebraska offers a complex yet intriguing system for taxpayers. Let's delve into the specifics and uncover the ins and outs of Nebraska's state income tax.
Understanding Nebraska's Tax Landscape

Nebraska operates under a progressive income tax system, which means that as your income increases, so does the tax rate applied to your earnings. This system ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a greater proportion of their earnings to the state's revenue. The state's tax laws are designed to balance the needs of its residents and businesses while maintaining a competitive environment for economic growth.
The tax year in Nebraska aligns with the federal tax year, running from January 1st to December 31st. This simplifies the tax filing process for individuals and businesses, as they can utilize their federal tax information when preparing their state returns.
Nebraska's Department of Revenue plays a crucial role in administering and enforcing the state's tax laws. They provide resources and guidance to taxpayers, ensuring compliance and facilitating a smooth tax filing process. Their website offers a wealth of information, including tax forms, publications, and helpful tools to assist residents in understanding their tax obligations.
Tax Rates and Brackets
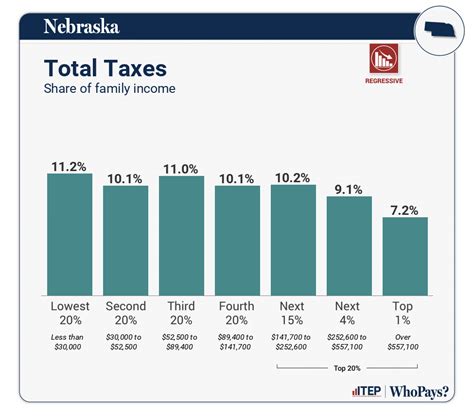
Nebraska employs a three-bracket income tax system, with rates varying depending on an individual's or couple's taxable income. These brackets are designed to ensure fairness and progressivity in the tax system. As of the 2023 tax year, the tax rates in Nebraska are as follows:
| Tax Rate | Applicable Income Range |
|---|---|
| 2.46% | $0 - $30,350 (Single) or $0 - $60,700 (Married Filing Jointly) |
| 4.80% | $30,351 - $60,700 (Single) or $60,701 - $121,400 (Married Filing Jointly) |
| 6.84% | Over $60,700 (Single) or Over $121,400 (Married Filing Jointly) |

These tax rates are applied to taxable income, which is calculated after deductions and exemptions are taken into account. The brackets are designed to provide a progressive tax system, where higher incomes are taxed at a higher rate, ensuring fairness and a balanced approach to revenue collection.
Comparative Analysis
Nebraska's tax rates are relatively moderate when compared to other states. For instance, some states like California and New York have much higher tax rates for top earners, while others like Florida and Texas have no income tax at all. Nebraska's system aims to strike a balance, offering a competitive environment for businesses while ensuring sufficient revenue for state operations.
Deductions and Credits
Nebraska offers a range of deductions and credits to ease the tax burden on its residents. These deductions and credits can significantly reduce the amount of tax owed, providing much-needed relief to taxpayers.
Standard Deduction
Nebraska allows taxpayers to claim a standard deduction, which reduces the taxable income. As of the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction amounts are as follows:
| Filing Status | Standard Deduction Amount |
|---|---|
| Single | $3,800 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $7,600 |
| Head of Household | $5,700 |
The standard deduction is a valuable tool for taxpayers, as it simplifies the tax filing process and provides a basic level of tax relief. However, some taxpayers may benefit more from itemizing their deductions, especially if they have significant medical expenses, charitable contributions, or other eligible deductions.
Itemized Deductions
Nebraska allows taxpayers to itemize their deductions, which can provide additional tax savings. Some common itemized deductions include:
- Medical and dental expenses exceeding 7.5% of adjusted gross income
- State and local taxes paid, including property taxes
- Charitable contributions to qualifying organizations
- Home mortgage interest
- Casualty and theft losses
By itemizing deductions, taxpayers can reduce their taxable income further, potentially resulting in a lower tax bill. However, it's important to note that itemizing deductions may not always be beneficial, especially if the standard deduction provides a larger tax benefit.
Credits
Nebraska offers a variety of tax credits to assist residents and promote certain activities or behaviors. Some notable credits include:
- The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), which provides a refundable credit for low- to moderate-income workers.
- The Child and Dependent Care Credit, which helps offset the costs of childcare for working parents.
- The Credit for College Tuition and Fees, which assists Nebraska residents in paying for higher education expenses.
- The Renewable Energy Production Tax Credit, encouraging the development and use of renewable energy sources.
These credits can significantly reduce a taxpayer's liability, making them an important consideration when preparing tax returns. It's crucial to understand the eligibility requirements and guidelines for each credit to ensure proper utilization.
Filing and Payment Options
Nebraska offers several convenient methods for taxpayers to file their state income tax returns and make payments. These options include:
- Online filing through the Nebraska Department of Revenue's website, which provides a secure and efficient way to file returns and make payments.
- Paper filing, where taxpayers can mail their completed tax forms and payment to the Department of Revenue.
- Electronic funds transfer (EFT), which allows taxpayers to pay their taxes directly from their bank account.
- Credit card payments, accepted by the Department of Revenue for a small convenience fee.
Taxpayers can choose the method that best suits their needs and preferences. The online filing option is particularly popular, as it provides a user-friendly interface and real-time updates on the status of the tax return.
Due Dates and Penalties
Nebraska's income tax returns are due on the same date as federal returns, typically April 15th of the following year. However, if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the due date is extended to the next business day. It's important for taxpayers to be aware of these due dates to avoid late filing penalties and interest charges.
Late filing penalties in Nebraska can be significant, with a base penalty of 5% of the tax due for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest accrues on any unpaid tax balances, with a rate that varies based on federal short-term interest rates.
Taxpayer Resources and Support

The Nebraska Department of Revenue provides extensive resources and support to taxpayers. Their website offers a wealth of information, including tax forms, publications, and helpful guides. Taxpayers can find answers to common questions, understand their rights and responsibilities, and access important tax deadlines.
For those seeking additional assistance, the Department of Revenue offers a taxpayer assistance program. This program provides personalized support to taxpayers, helping them navigate the tax system, understand their obligations, and resolve any issues they may encounter. The program is designed to ensure that taxpayers have the resources they need to comply with Nebraska's tax laws.
Online Tools and Resources
Nebraska's Department of Revenue website is a valuable resource for taxpayers. It provides access to a range of online tools and resources, including:
- Tax calculators, which help taxpayers estimate their tax liability and understand the impact of different deductions and credits.
- Payment plans, allowing taxpayers to set up installment agreements to pay their taxes over time.
- Amended return filing options, for those who need to make changes to previously filed returns.
- E-signature capabilities, enabling taxpayers to sign and submit their returns electronically.
These online tools enhance the taxpayer experience, providing convenience, efficiency, and a more user-friendly approach to tax filing and management.
Future Implications and Trends
As Nebraska's tax landscape continues to evolve, several trends and potential implications can be observed. One notable trend is the increasing focus on tax fairness and progressivity. Nebraska's tax system is designed to ensure that higher earners contribute a greater share of their income to state revenues, promoting a more equitable distribution of tax burdens.
Additionally, the state is exploring ways to simplify the tax system and reduce compliance costs for taxpayers. This includes efforts to streamline tax forms and processes, making them more user-friendly and efficient. By reducing the complexity of the tax system, Nebraska aims to enhance taxpayer satisfaction and compliance.
Another area of focus is the expansion of tax credits and incentives. Nebraska recognizes the importance of supporting its residents and promoting economic growth. As such, the state is considering the introduction of new credits and incentives to encourage activities such as workforce development, renewable energy adoption, and small business growth. These initiatives aim to create a more competitive and attractive environment for businesses and individuals.
Looking ahead, Nebraska's tax system is expected to remain stable, with a continued focus on fairness, progressivity, and simplicity. The state's commitment to providing taxpayer resources and support, coupled with its efforts to simplify the tax process, positions Nebraska as a leader in tax administration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the deadline for filing Nebraska state income tax returns?
+The deadline for filing Nebraska state income tax returns typically aligns with the federal tax return deadline, which is April 15th of the following year. However, if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the due date is extended to the next business day.
Are there any tax benefits for Nebraska residents who work remotely for out-of-state companies?
+Nebraska has specific rules for remote workers, and the tax implications can vary based on the worker’s residency and the nature of their employment. It’s important for remote workers to consult with a tax professional to understand their tax obligations accurately.
How does Nebraska handle tax refunds?
+Nebraska processes tax refunds promptly, typically within 45 days of receiving a complete and accurate return. Refunds can be issued via direct deposit or check, depending on the taxpayer’s preference.
Are there any tax incentives for starting a business in Nebraska?
+Yes, Nebraska offers a range of tax incentives to support business growth and development. These incentives include tax credits for job creation, research and development, and investment in certain industries. It’s important to consult with a tax professional or the Department of Revenue to understand the specific requirements and benefits.