Nebraska Real Estate Taxes
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on Nebraska's real estate taxes, a critical aspect of homeownership in the Cornhusker State. Understanding these taxes is essential for both new and seasoned homeowners, as they can significantly impact your financial planning and property management strategies. Nebraska's unique tax system, known for its progressive nature, offers both challenges and opportunities for property owners. In this article, we'll delve into the specifics of Nebraska real estate taxes, providing you with the knowledge you need to navigate this important financial landscape.
Understanding Nebraska’s Real Estate Tax Structure

Nebraska’s real estate tax system is designed to ensure a fair and equitable distribution of tax burdens across property owners. The state’s approach is characterized by a blend of progressive taxation and local autonomy, with a focus on maintaining a stable revenue stream for essential public services.
Progressive Taxation
At its core, Nebraska’s tax system is progressive, meaning that higher-value properties are taxed at a higher rate than lower-value properties. This approach aims to ensure that those with greater financial means contribute more to the state’s revenue, fostering a more equitable distribution of tax responsibilities.
The progressive nature of Nebraska's tax system is evident in its valuation methodology. Properties are assessed based on their actual value, and tax rates are applied progressively as property values increase. This means that homeowners with higher-valued properties will generally pay a higher tax rate than those with lower-valued properties.
Local Autonomy
One of the unique aspects of Nebraska’s tax system is the degree of local autonomy granted to counties and municipalities. Each county in Nebraska has the authority to set its own tax rate, within certain state-mandated limits. This local control allows for a more tailored approach to taxation, considering the specific needs and circumstances of each community.
Local governments have the flexibility to adjust tax rates based on factors such as the cost of providing local services, infrastructure development plans, and economic conditions within their jurisdictions. This local control ensures that tax revenues are directed towards the specific needs of each community, fostering a sense of local ownership and accountability.
Taxable Value and Assessment
In Nebraska, real estate taxes are levied based on the taxable value of a property, which is determined through a process known as assessment. The assessment process involves evaluating the property’s fair market value, taking into account factors such as location, size, condition, and recent sales data of comparable properties.
Once the fair market value is determined, it is multiplied by an assessment percentage, which varies depending on the type of property. For residential properties, the assessment percentage is typically 100%, meaning the taxable value is the same as the property's fair market value. However, for commercial and agricultural properties, the assessment percentage can be lower, resulting in a lower taxable value.
Calculating Real Estate Taxes in Nebraska

Calculating real estate taxes in Nebraska involves a multi-step process that takes into account various factors, including the property’s taxable value, the tax rate set by the local government, and any applicable exemptions or credits.
Step 1: Determining Taxable Value
As mentioned earlier, the taxable value of a property is determined through the assessment process. This value is then subject to certain adjustments, such as exemptions and credits, which can reduce the taxable value.
One common exemption in Nebraska is the homestead exemption, which provides a reduction in taxable value for homeowners who use their property as their primary residence. This exemption helps reduce the tax burden for homeowners and encourages homeownership.
Step 2: Applying the Tax Rate
Once the taxable value is determined, the next step is to apply the tax rate. The tax rate is set by the local government and is typically expressed as a percentage. For example, if the tax rate is set at 1.5%, then for every 100 of taxable value, the property owner would owe 1.50 in taxes.
It's important to note that the tax rate can vary significantly from one county to another, even within the same state. This variation is due to the local autonomy granted to counties in setting their tax rates.
Step 3: Calculating the Tax Bill
To calculate the actual tax bill, the taxable value is multiplied by the tax rate. For instance, if the taxable value of a property is 200,000 and the tax rate is 1.5%, the tax bill would be 3,000 ($200,000 x 0.015). However, it’s worth noting that this calculation is just an estimate, as there may be additional factors, such as special assessments or other local taxes, that can affect the final tax bill.
Tax Payment and Due Dates
In Nebraska, real estate taxes are typically due twice a year, with payment deadlines falling in May and September. However, it’s important to check with your local county treasurer’s office for specific due dates, as they can vary slightly from one county to another.
Property owners have the option to pay their taxes in full by the due date or choose to pay in installments. If paying in installments, the first half is typically due in May, and the second half is due in September. It's crucial to make timely payments to avoid late fees and penalties, which can add to the overall cost of owning a property.
Payment Options
Nebraska offers a variety of payment options to accommodate different preferences and circumstances. Property owners can pay their taxes in person at the county treasurer’s office, by mail, or online through the county’s website. Some counties even offer the convenience of automatic payments, where the tax amount is automatically deducted from the property owner’s account on the due date.
Tax Relief Programs
Nebraska recognizes the importance of providing tax relief to certain groups of property owners, especially those who may be facing financial challenges or who are on fixed incomes. As such, the state offers several tax relief programs to ease the burden of real estate taxes.
Homestead Exemption
The homestead exemption is a key tax relief program in Nebraska. As mentioned earlier, this exemption reduces the taxable value of a property for homeowners who use it as their primary residence. The exemption amount varies depending on the county and the homeowner’s age, with older homeowners often eligible for larger exemptions.
Property Tax Credits
Nebraska also provides property tax credits to eligible homeowners. These credits can reduce the amount of taxes owed and are typically based on income and property value. For example, homeowners with limited income and moderate property values may qualify for a property tax credit, which can significantly reduce their tax burden.
Senior Citizen Exemption
Nebraska offers a special exemption for senior citizens, who often face fixed incomes and rising property values. This exemption provides a reduction in the taxable value of the property, helping to ease the financial burden of real estate taxes for older homeowners.
Challenges and Opportunities
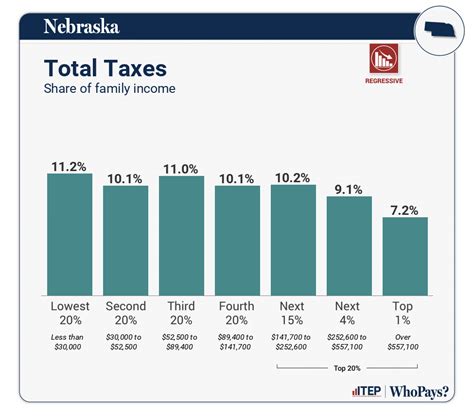
While Nebraska’s real estate tax system is designed to be fair and equitable, it is not without its challenges. One of the main challenges faced by property owners is the potential for significant tax increases due to rising property values. As property values increase, so does the taxable value, leading to higher tax bills.
However, the progressive nature of Nebraska's tax system also presents opportunities. For homeowners with higher-value properties, the progressive tax rates mean that their tax burden is spread across a larger base, making it more manageable. Additionally, the local autonomy in setting tax rates allows for flexibility and adaptability to the unique needs of each community.
Strategies for Managing Real Estate Taxes
To effectively manage real estate taxes in Nebraska, homeowners can employ several strategies. First, staying informed about local tax rates and any changes that may impact their property is crucial. Property owners should regularly review their tax assessments and ensure they accurately reflect the property’s value.
Second, taking advantage of tax relief programs, such as the homestead exemption and property tax credits, can significantly reduce the tax burden. It's important for homeowners to research and understand the eligibility criteria for these programs and apply accordingly.
Lastly, seeking professional advice from tax consultants or financial advisors can provide valuable insights and strategies for managing real estate taxes. These professionals can help property owners navigate the complex tax landscape, optimize their tax positions, and plan for future tax liabilities.
The Impact of Real Estate Taxes on Property Ownership
Real estate taxes play a significant role in the overall cost of owning a property in Nebraska. For homeowners, these taxes represent a substantial financial obligation that must be factored into their long-term financial planning. The impact of real estate taxes can be felt not only in the immediate tax payments but also in the overall affordability of homeownership.
Affordability and Financial Planning
High real estate taxes can significantly impact the affordability of homeownership, especially for those on fixed incomes or with limited financial resources. In some cases, the tax burden can be so substantial that it discourages potential homeowners from entering the market or forces current homeowners to consider selling their properties.
To ensure the long-term financial viability of homeownership, it is essential for homeowners to carefully consider the impact of real estate taxes when planning their budgets and financial strategies. This includes factoring in not only the initial purchase price of the property but also the ongoing tax obligations that come with ownership.
The Role of Real Estate Taxes in Community Development
Real estate taxes are a critical source of revenue for local governments in Nebraska, funding essential public services such as education, infrastructure, and public safety. The tax revenue collected is used to support community development initiatives, improve local infrastructure, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
As such, real estate taxes are not merely a financial obligation for homeowners but also a crucial investment in the community. By paying their fair share of taxes, homeowners contribute to the collective well-being of their communities, ensuring that essential services are adequately funded and that local development projects can be realized.
Balancing Act: Managing Real Estate Taxes and Community Development
While real estate taxes are necessary for community development, it is important for local governments to strike a balance between generating sufficient revenue and ensuring that the tax burden remains manageable for homeowners. This delicate balance requires careful consideration of tax rates, assessment methodologies, and the availability of tax relief programs.
Local governments must continually evaluate their tax policies to ensure they are fair, equitable, and sustainable. This includes regularly reviewing tax rates, assessing the impact of property value fluctuations, and making adjustments as needed to maintain a stable and predictable tax environment for homeowners.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
The landscape of real estate taxes in Nebraska is subject to change, influenced by various factors such as economic conditions, political decisions, and community needs. As such, it is important for homeowners to stay informed about potential changes to the tax system that may impact their financial obligations.
Economic Factors and Tax Policy
Economic conditions play a significant role in shaping real estate tax policies. During periods of economic growth, property values tend to rise, leading to increased taxable values and potentially higher tax burdens for homeowners. Conversely, during economic downturns, property values may decline, resulting in lower taxable values and reduced tax obligations.
Local governments must carefully navigate these economic cycles, ensuring that tax policies remain fair and sustainable. This may involve adjusting tax rates or implementing temporary tax relief measures to support homeowners during challenging economic times.
Political Decisions and Tax Reform
Political decisions at the state and local levels can also significantly impact real estate tax policies. Changes in leadership or shifts in political priorities may lead to tax reform initiatives aimed at addressing specific concerns or achieving particular policy objectives.
Homeowners should stay engaged with local politics and be aware of any proposed tax reforms that may affect their financial obligations. Participating in public consultations and expressing their views can help shape the tax policies that impact their communities.
Community Needs and Local Initiatives
Real estate taxes are a critical tool for local governments to address community needs and support local initiatives. As such, changes in community demographics, infrastructure requirements, or public service demands may prompt adjustments to tax policies.
For instance, growing communities may require additional funding for infrastructure development or public services, leading to potential increases in real estate taxes. Conversely, mature communities with stable populations may experience a shift in tax priorities, focusing on maintaining existing services rather than expanding them.
Conclusion
Nebraska’s real estate tax system is a complex but essential component of homeownership in the state. Understanding the tax structure, calculation process, and available relief programs is crucial for homeowners to effectively manage their financial obligations and contribute to their communities.
While real estate taxes can present challenges, especially in the form of rising property values, the progressive nature of Nebraska's tax system and the local autonomy in setting tax rates provide opportunities for homeowners to navigate these challenges effectively. By staying informed, taking advantage of tax relief programs, and seeking professional advice, homeowners can ensure they are well-prepared to meet their tax obligations and contribute to the continued development and prosperity of their communities.
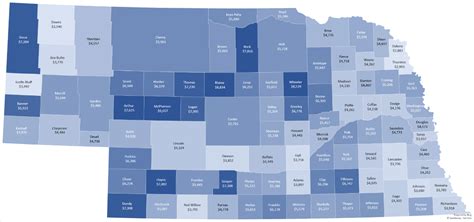
What is the average real estate tax rate in Nebraska?
+The average real estate tax rate in Nebraska can vary significantly from one county to another. As of [current year], the average tax rate across the state is approximately [average tax rate]%. However, it’s important to note that this is just an average, and individual counties may have higher or lower tax rates.
How often are real estate taxes assessed in Nebraska?
+Real estate taxes in Nebraska are typically assessed annually. The assessment process involves evaluating the property’s fair market value and determining its taxable value. This process ensures that the taxes are based on the current value of the property.
Are there any ways to reduce my real estate tax bill in Nebraska?
+Yes, there are several ways to potentially reduce your real estate tax bill in Nebraska. These include taking advantage of tax relief programs such as the homestead exemption, applying for property tax credits based on income and property value, and ensuring that your property assessment accurately reflects the current market value.
What happens if I fail to pay my real estate taxes in Nebraska?
+Failing to pay your real estate taxes in Nebraska can result in serious consequences. Late payments may incur penalties and interest, and if the taxes remain unpaid, the county may place a lien on the property. In extreme cases, the property could be subject to a tax sale to recover the outstanding taxes.
How can I stay informed about changes to real estate tax policies in Nebraska?
+To stay informed about changes to real estate tax policies in Nebraska, it’s important to regularly check the websites of your local county treasurer’s office and the Nebraska Department of Revenue. These sources provide up-to-date information on tax rates, assessment processes, and any proposed or enacted tax reforms.