Nc Tax Rate
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the North Carolina tax landscape, a crucial aspect of doing business and managing personal finances within the state. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the various tax rates and structures implemented by the Tar Heel State, offering valuable insights for businesses, investors, and residents alike.
Unraveling the North Carolina Tax Structure
The tax system in North Carolina is designed to generate revenue for the state’s operations and services while ensuring a fair and competitive business environment. It consists of a range of taxes, each with its own set of rules and rates, influencing the financial strategies of individuals and enterprises operating within the state.
Income Tax: A Snapshot
One of the primary sources of revenue for North Carolina is the personal income tax, which is levied on the taxable income of individuals and businesses. The state operates on a progressive tax structure, meaning the tax rate increases as income rises. Currently, North Carolina has six tax brackets, with rates ranging from 5.25% to 5.75% for individuals and 5.50% for corporations.
| Tax Bracket | Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Up to $21,600 | 5.25% |
| 2 | $21,601 - $43,200 | 5.40% |
| 3 | $43,201 - $86,400 | 5.55% |
| 4 | $86,401 - $153,600 | 5.65% |
| 5 | $153,601 - $256,000 | 5.70% |
| 6 | Above $256,000 | 5.75% |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to periodic adjustments to align with economic conditions and state budget requirements. For businesses, the corporate income tax rate stands at 5.50%, offering a consistent environment for corporate planning.
Sales and Use Tax: A Consumer Perspective
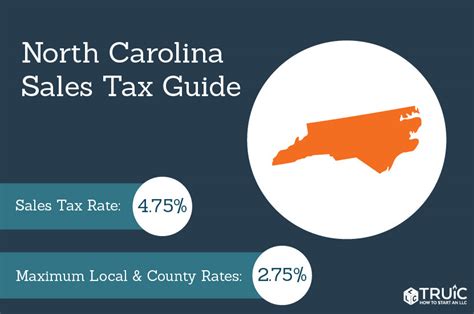
North Carolina levies a statewide sales and use tax on retail sales, leases, and rentals of tangible personal property, as well as certain services. The base rate for sales tax in North Carolina is 4.75%, with local governments having the authority to levy additional taxes, typically up to 2.50%, resulting in a maximum combined rate of 7.25%.
However, it's not a blanket tax. Various goods and services are exempt from sales tax, including prescription drugs, non-prepared food items, and certain manufacturing inputs. Additionally, North Carolina offers tax incentives and rebates for specific industries, encouraging economic development and investment.
Property Tax: Localized Assessment
Property taxes in North Carolina are administered at the county level, resulting in a wide range of rates across the state. The ad valorem property tax is calculated based on the assessed value of the property and the applicable tax rate, which varies depending on the property’s location and use.
The average effective property tax rate in North Carolina stands at 0.79%, ranking it as the 21st highest in the nation. However, this rate can vary significantly, with some counties imposing rates as low as 0.40% and others reaching upwards of 1.40%.
Estate and Inheritance Taxes: A Comparative Analysis
North Carolina does not impose an estate tax, which is a tax on the transfer of an individual’s property at the time of their death. However, it does have an inheritance tax, which is a tax on the beneficiaries of the estate, based on their relationship to the deceased and the value of the inheritance received.
The state's inheritance tax applies only to estates with a value exceeding $5.8 million and has a maximum rate of 19.6%, which is significantly lower than many other states. This absence of an estate tax and the relatively low inheritance tax rate can make North Carolina an attractive jurisdiction for high-net-worth individuals and their heirs.
Other Taxes: A Comprehensive Overview
In addition to the taxes mentioned above, North Carolina imposes various other taxes to fund specific programs and services. These include:
- Fuel Tax: A tax on gasoline and diesel fuel, with rates varying based on the type of fuel and its use.
- Tobacco Tax: A tax on cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products, aimed at discouraging tobacco use and generating revenue for healthcare programs.
- Alcohol Tax: A tax on the sale of alcoholic beverages, with rates dependent on the type of alcohol and its alcohol content.
- Excise Taxes: Taxes on specific goods and services, such as telecommunications services, motor vehicle rentals, and insurance premiums.
Tax Incentives and Relief Programs
North Carolina recognizes the importance of tax incentives in attracting businesses and promoting economic growth. The state offers a range of tax credits and incentives to encourage investment, job creation, and innovation.
Job Development Investment Grant (JDIG)
One of the most significant tax incentives in North Carolina is the Job Development Investment Grant (JDIG). This program provides qualifying companies with performance-based tax relief over a period of 12 years. Companies must meet specific job creation and investment thresholds to be eligible, and the grants are awarded based on a competitive application process.
One North Carolina Fund
The One North Carolina Fund is a discretionary grant program aimed at supporting economic development projects that foster job creation and investment in the state. Grants from this fund are typically used to offset the costs of infrastructure development, workforce training, and other expenses associated with business expansion or relocation.
Enterprise Zones
North Carolina has designated enterprise zones throughout the state, offering a range of tax benefits and incentives to businesses operating within these zones. These benefits can include reduced tax rates, tax credits for job creation, and accelerated depreciation for certain assets.
Film and Entertainment Grants
The state’s film and entertainment industry is supported by a range of tax incentives, including a 25% tax credit for qualified production expenditures. This credit has been instrumental in attracting film and television productions to North Carolina, contributing significantly to the state’s economy.
Historical Rehabilitation Tax Credit
The Historical Rehabilitation Tax Credit program provides a tax credit of up to 20% of qualified rehabilitation expenses for the restoration of historic buildings. This incentive encourages the preservation of historic properties and their adaptive reuse, contributing to the state’s cultural heritage and economic vitality.
Impact on Businesses and Investors
The tax landscape in North Carolina plays a pivotal role in shaping the state’s business environment and investment climate. The combination of a competitive income tax structure, a robust network of tax incentives, and a moderate sales tax rate makes North Carolina an attractive destination for businesses and investors.
For businesses, the availability of tax incentives such as JDIG and the One North Carolina Fund can significantly reduce their tax burden, enhancing their profitability and competitive edge. Additionally, the state's commitment to supporting industries like film and entertainment, as well as historic preservation, demonstrates its willingness to foster diverse economic sectors.
From an investor's perspective, North Carolina's tax structure, coupled with its strong business climate and high quality of life, presents a compelling case. The state's tax incentives, particularly those aimed at job creation and economic development, offer attractive returns on investment, making it a desirable location for capital deployment.
Conclusion: Navigating the Tar Heel State’s Tax Terrain
Understanding the tax structure and incentives in North Carolina is crucial for businesses, investors, and individuals alike. The state’s approach to taxation balances the need for revenue generation with the goal of fostering economic growth and competitiveness.
By offering a progressive income tax structure, a moderate sales tax rate, and a range of targeted tax incentives, North Carolina creates an environment conducive to business success and economic development. Whether you're a business owner looking to expand, an investor seeking opportunities, or an individual planning your financial future, navigating the Tar Heel State's tax terrain can be a rewarding endeavor.
What is the corporate income tax rate in North Carolina?
+The corporate income tax rate in North Carolina is 5.50%.
Are there any tax incentives for renewable energy projects in North Carolina?
+Yes, North Carolina offers tax incentives for renewable energy projects through the Renewable Energy Investment Tax Credit and the Commercial Property Assessed Clean Energy (C-PACE) Program.
What is the average property tax rate in North Carolina?
+The average effective property tax rate in North Carolina is 0.79%, ranking it as the 21st highest in the nation.



