Ky State Income Tax
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Kentucky's State Income Tax. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Kentucky tax system, providing you with an expert analysis of its structure, rates, and implications. Whether you're a resident, a business owner, or simply interested in understanding the financial landscape of the Bluegrass State, this guide will offer valuable insights.
Understanding Kentucky’s State Income Tax Structure
Kentucky operates under a progressive income tax system, which means that the tax rate you pay increases as your income rises. This approach ensures that individuals and businesses with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their earnings towards the state’s revenue. Let’s explore the key components of this system.
Tax Rates and Brackets
Kentucky’s income tax rates are divided into five brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $3,000 | 2% |
| $3,001 - $6,000 | 3% |
| $6,001 - $75,000 | 4% |
| $75,001 - $100,000 | 5% |
| Over $100,000 | 6% |

These rates are applied to your taxable income, which is calculated after various deductions and exemptions are taken into account.
Deductions and Exemptions
Kentucky offers a range of deductions and exemptions to reduce the taxable income of individuals and businesses. Some of the key deductions include:
- Standard Deduction: Kentucky provides a standard deduction for all taxpayers, which helps reduce their taxable income. For the 2022 tax year, the standard deduction is $4,650 for single filers and $9,300 for married couples filing jointly.
- Personal Exemptions: Kentucky allows personal exemptions for each taxpayer and dependent. For the 2022 tax year, the personal exemption amount is $2,000.
- Itemized Deductions: Individuals may choose to itemize their deductions if their total itemized expenses exceed the standard deduction. Common itemized deductions include mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and medical expenses.
Taxable Income Calculation
To calculate your taxable income, you start with your total income from all sources, including wages, salaries, business income, investments, and other earnings. From this amount, you subtract any applicable deductions and exemptions. The result is your taxable income, which is then subjected to the appropriate tax rate based on the income bracket it falls into.
Taxable Entities and Exemptions

Kentucky’s state income tax applies to various entities, including individuals, corporations, partnerships, and trusts. However, there are certain exemptions and special considerations for specific groups.
Individual Taxpayers
All Kentucky residents and non-residents with income sourced from Kentucky are subject to state income tax. This includes wages, salaries, commissions, bonuses, and other forms of compensation. Additionally, Kentucky residents with income from sources outside the state may also need to report and pay taxes on that income.
Corporate Taxation
Kentucky imposes a corporate income tax on businesses operating within the state. The tax rate for corporations is 6% on net income. However, there are various incentives and tax credits available to encourage business growth and investment. These include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investments in renewable energy.
Partnerships and LLCs
Partnerships and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) are not taxed at the entity level in Kentucky. Instead, the income or losses pass through to the individual partners or members, who report and pay taxes on their share of the profits or losses on their personal tax returns.
Tax Exemptions and Credits
Kentucky offers several tax exemptions and credits to promote specific industries and support low-income individuals and families. Some notable exemptions and credits include:
- Homestead Exemption: Kentucky provides a property tax exemption for qualified homeowners. This exemption reduces the assessed value of a primary residence, resulting in lower property taxes.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): The EITC is a refundable tax credit available to low- and moderate-income working individuals and families. It helps reduce the tax burden and provides a financial boost to those who qualify.
- Research and Development Tax Credit: Kentucky offers a tax credit to encourage businesses to invest in research and development activities within the state. This credit can offset a portion of the corporate income tax liability.
Filing and Payment Procedures
Kentucky taxpayers are required to file their state income tax returns annually. The filing deadline is typically aligned with the federal tax deadline, which is usually April 15th. However, in years when April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline may be extended to the next business day.
Filing Options
Kentucky offers several convenient ways to file your state income tax return:
- Online Filing: Kentucky's Department of Revenue provides an online filing system called My Kentucky Tax. This secure platform allows taxpayers to file their returns electronically and receive faster refunds.
- Paper Returns: Taxpayers can also choose to file a paper return by completing Form 740 or Form 740-ES (for estimated tax payments) and mailing it to the appropriate address.
Payment Options
Kentucky accepts various payment methods for income tax liabilities:
- Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT): Taxpayers can authorize an electronic transfer of funds from their bank account to the Department of Revenue. This option is available through the My Kentucky Tax online filing system.
- Credit Card or Debit Card: Kentucky accepts credit and debit card payments for income tax liabilities. A convenience fee may apply for this service.
- Check or Money Order: Taxpayers can send a check or money order payable to the "Kentucky State Treasury" along with their paper return.
Compliance and Enforcement
The Kentucky Department of Revenue is responsible for enforcing state tax laws and ensuring compliance. They have various tools at their disposal to detect and address tax evasion and non-compliance.
Audits and Investigations
The Department of Revenue conducts audits to verify the accuracy of tax returns and ensure compliance with state tax laws. Audits can be random or targeted based on specific indicators of potential non-compliance. During an audit, taxpayers are required to provide documentation and evidence to support the information reported on their tax returns.
Penalties and Interest
Failure to comply with Kentucky’s tax laws can result in penalties and interest charges. Late filing penalties may apply if a taxpayer fails to file their return by the deadline. Similarly, late payment penalties may accrue if taxes are not paid by the due date. Interest may also be charged on any unpaid tax liabilities.
Appeals and Dispute Resolution
Taxpayers who disagree with the findings of an audit or have disputes with the Department of Revenue can initiate an appeals process. This process involves presenting evidence and arguments to an independent administrative law judge. The judge’s decision can be further appealed to the Kentucky Board of Tax Appeals and, ultimately, to the Kentucky Court of Appeals.
Future Outlook and Reforms
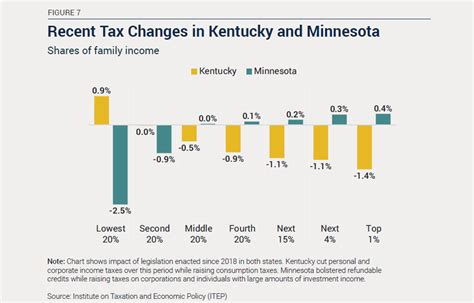
Kentucky’s tax landscape is subject to ongoing discussions and potential reforms. The state’s leadership and tax experts continuously evaluate the effectiveness of the current tax system and explore ways to improve it.
Proposed Reforms
Some of the proposed reforms and initiatives include:
- Flattening the Tax Rate: There have been discussions about simplifying the tax structure by implementing a flat tax rate for all income brackets. This approach aims to reduce the complexity of the current progressive system and provide a more straightforward tax calculation.
- Expanding Tax Credits: Kentucky may explore expanding existing tax credits or introducing new ones to support specific industries, encourage investment, or provide relief to low-income individuals and families.
- Digital Tax Services: The state is likely to continue investing in digital tax services and online platforms to enhance the filing experience for taxpayers and improve efficiency in tax administration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the income tax rate for Kentucky residents in 2023?
+
The income tax rates for Kentucky residents in 2023 remain the same as in previous years. The rates are divided into five brackets: 2% for income up to 3,000, 3% for income between 3,001 and 6,000, 4% for income between 6,001 and 75,000, 5% for income between 75,001 and 100,000, and 6% for income over 100,000.
Are there any special tax incentives for businesses in Kentucky?
+
Yes, Kentucky offers various tax incentives to attract and support businesses. These include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investments in renewable energy. Additionally, there are tax incentives for certain industries, such as manufacturing and tourism.
Can I file my Kentucky state income tax return electronically?
+
Absolutely! Kentucky provides an online filing system called My Kentucky Tax which allows taxpayers to file their returns electronically. This method is secure, convenient, and often results in faster refunds.
What happens if I miss the state income tax filing deadline in Kentucky?
+
Missing the filing deadline may result in late filing penalties. It’s important to note that even if you cannot pay the full amount owed by the deadline, it’s still crucial to file your return on time to avoid additional penalties and interest charges.
Are there any tax exemptions for seniors in Kentucky?
+
Yes, Kentucky provides several tax exemptions and credits for seniors. These include the Homestead Exemption, which reduces the assessed value of a primary residence for property tax purposes, and the Kentucky Senior Citizens Tax Credit, which provides a credit for qualifying seniors.