Kansas Real Estate Taxes

Welcome to the ultimate guide on understanding Kansas real estate taxes. This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of property taxation in the Sunflower State, offering a detailed analysis of the tax structure, assessment process, and strategies to navigate this essential aspect of homeownership.
Unraveling the Kansas Real Estate Tax System
The real estate tax system in Kansas is a crucial component of the state’s revenue generation, playing a significant role in funding various public services and infrastructure. Understanding this system is essential for both new and existing homeowners, as it directly impacts their financial obligations and planning.
The Tax Assessment Process
In Kansas, real estate taxes are primarily assessed at the county level, with each county having its own assessor’s office responsible for determining property values. The assessment process involves several key steps:
- Appraisal: County assessors use a combination of market data, sales comparisons, and other valuation methods to appraise the value of each property.
- Equalization: To ensure fairness, the State Board of Tax Appeals (BOTA) equalizes property values across counties, adjusting for any significant discrepancies.
- Notice of Value: Property owners receive a Notice of Value, detailing the assessed value of their property. This notice serves as a basis for tax calculations.
- Appeals: Property owners have the right to appeal their assessed value if they believe it is inaccurate. The appeals process typically involves a review by the county appraisal board.
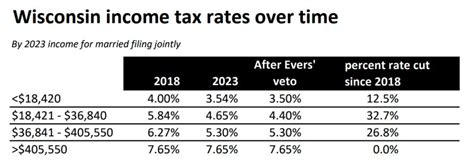
Tax Rates and Calculations
The tax rate in Kansas is expressed as a mill levy, which represents the number of dollars in tax per $1,000 of assessed value. This rate is determined by various taxing entities, including school districts, cities, counties, and special assessment districts. The mill levy is then applied to the assessed value of the property to calculate the annual tax amount.
| County | Mill Levy | Average Tax Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Johnson | 105.69 | 1.06 |
| Sedgwick | 98.91 | 0.99 |
| Wyandotte | 105.86 | 1.06 |
| Shawnee | 100.50 | 1.01 |
Property Tax Exemptions and Credits
Kansas offers several exemptions and credits to reduce the tax burden for certain property owners. These include:
- Homestead Exemption: This exemption provides a tax reduction for owner-occupied residences. The exemption amount varies by county but can significantly lower the taxable value of a property.
- Senior Citizen Exemption: Senior citizens who meet certain income requirements may qualify for an additional exemption, further reducing their taxable value.
- Veteran’s Exemption: Kansas honors its veterans by offering an exemption for those who served in the military, depending on their disability status and length of service.
- Tax Credits: The state also provides various tax credits, such as the Mortgage Credit Certificate (MCC) program, which offers a federal income tax credit based on a portion of the mortgage interest paid.
Strategies for Managing Real Estate Taxes

Understanding the real estate tax landscape in Kansas is just the first step. Here are some strategies to help homeowners manage their tax obligations effectively:
Stay Informed and Engage
Staying informed about tax rates, assessments, and exemptions is crucial. Attend local government meetings, especially those related to tax policies and budgets. Engage with your county assessor’s office to understand the assessment process and your property’s valuation.
Appeal Your Assessment
If you believe your property’s assessed value is too high, consider appealing. Gather evidence, such as recent sales of similar properties, to support your case. The appeals process can be complex, so consulting a professional tax advisor or attorney may be beneficial.
Utilize Exemptions and Credits
Take advantage of the exemptions and credits available to you. Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria and understand the application process. These benefits can significantly reduce your tax liability.
Consider Long-Term Planning
Real estate taxes are an ongoing expense. Consider tax implications when making long-term financial plans, such as retirement planning or investing in real estate. Strategies like refinancing or adjusting your mortgage term can impact your tax deductions and overall financial health.
The Impact of Real Estate Taxes on Property Ownership
Real estate taxes are an essential consideration for anyone buying or owning property in Kansas. These taxes directly affect a homeowner’s financial planning and overall cost of living. Understanding the tax system and staying proactive can help homeowners manage their obligations effectively.
Case Study: Impact on Home Buyers
Let’s consider the experience of a hypothetical family, the Johnsons, who recently moved to Kansas. The Johnsons purchased a home in Johnson County, attracted by the excellent school system and thriving community. However, they were surprised to learn that their annual real estate taxes amounted to nearly $4,000, which was a significant portion of their monthly budget.
By understanding the tax system and staying engaged with local government, the Johnsons were able to navigate this challenge. They successfully appealed their assessment, reducing their taxable value and, consequently, their tax burden. Additionally, they took advantage of the homestead exemption, further lowering their taxes.
Future Implications and Outlook
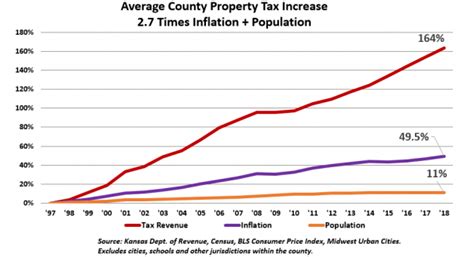
The real estate tax system in Kansas is constantly evolving, influenced by economic trends, population growth, and government policies. While the state’s tax structure is generally considered stable, homeowners should stay vigilant for any changes that may impact their tax obligations.
One potential area of concern is the state's reliance on property taxes to fund public education. As the cost of education rises, there may be increased pressure on property owners to contribute more through taxes. However, the state's commitment to equalization and exemptions suggests a continued focus on fairness and accessibility.
Conclusion: Navigating Kansas’ Real Estate Tax Landscape
In conclusion, understanding and effectively managing real estate taxes is a critical aspect of property ownership in Kansas. By staying informed, engaging with local government, and utilizing available exemptions and credits, homeowners can navigate this complex landscape with confidence. The real estate tax system, while intricate, is a vital component of the state’s economy and public services, and its impact on individuals and communities is significant.
What is the average annual real estate tax rate in Kansas?
+The average annual real estate tax rate in Kansas varies by county, with some counties having rates as low as 0.70% and others as high as 1.40%. It’s important to check with your specific county’s assessor’s office for an accurate rate.
How often are property assessments conducted in Kansas?
+Property assessments in Kansas are typically conducted every two years, with the assessed value used as the basis for tax calculations. However, counties have the authority to assess properties annually if they choose.
Are there any online tools to estimate my real estate taxes in Kansas?
+Yes, several online tools are available to estimate your real estate taxes based on your property’s location and assessed value. These tools can provide a quick estimate, but it’s always recommended to consult official sources for accurate information.