Illinois Sales Tax Rate
Illinois, a vibrant state in the Midwest region of the United States, has a robust sales tax system that plays a crucial role in its economic landscape. The sales tax rate in Illinois is a dynamic aspect of the state's revenue generation strategy, and it has evolved over the years to meet the diverse needs of its population and businesses. This article delves into the intricacies of the Illinois sales tax rate, exploring its history, current structure, variations across counties, and its impact on the state's economy.
The Evolution of Illinois Sales Tax Rates
The journey of Illinois’ sales tax rates began in 1933, when the state introduced its first sales tax as a means to bolster revenue during the Great Depression. The initial rate was set at 2%, a modest figure compared to the complex structure we see today. Over the decades, the sales tax rate has undergone several revisions, reflecting the changing economic needs and priorities of the state.
One significant milestone in the evolution of Illinois sales tax rates was the introduction of the Local Government Sales Tax in 1967. This reform allowed counties and municipalities to levy their own sales taxes, providing them with a direct source of revenue. This move not only increased the overall sales tax rate but also introduced a layer of complexity, as tax rates started to vary across different regions within the state.
In recent years, the Illinois sales tax rate has seen further adjustments, with the state grappling with budgetary challenges and economic downturns. The Illinois Personal and Corporate Income Tax increases in 2011 and 2017, for instance, put less pressure on the sales tax to contribute to state revenue, leading to a relatively stable sales tax rate in the past decade.
Understanding the Current Illinois Sales Tax Rate
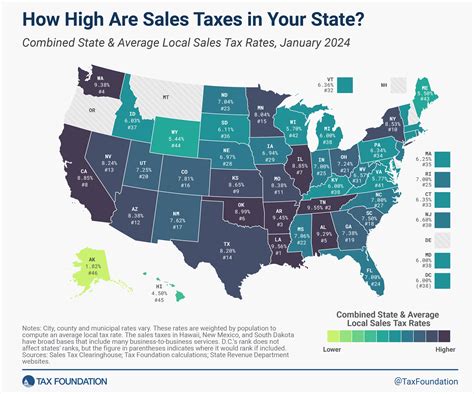
As of my last update in January 2023, the statewide sales tax rate in Illinois stands at 6.25%, a figure that has remained constant since 2010. This rate applies to the sale of most goods and some services within the state. However, it’s important to note that this is just the base rate, and actual sales tax rates can vary significantly depending on the specific location within Illinois.
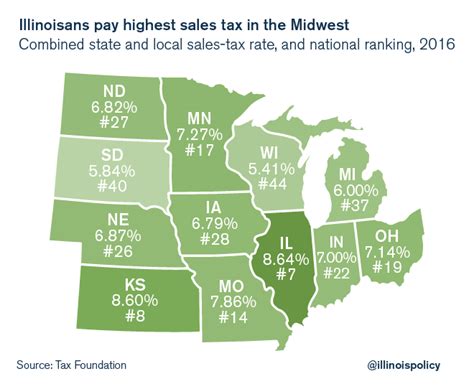
Illinois operates a multitiered sales tax system, where the state tax is supplemented by additional local taxes. This means that the total sales tax rate can range from 6.25% to over 10% depending on the county and municipality where the sale takes place. These additional taxes are often used to fund specific local initiatives or services, such as transportation projects or public safety improvements.
| County | Additional Local Taxes | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Cook County | 1.25% | 7.5% |
| Will County | 1.75% | 8% |
| Lake County | 1.5% | 7.75% |
| DuPage County | 1.75% | 8% |
| Kane County | 1.25% | 7.5% |
For instance, in Cook County, which includes the city of Chicago, the additional local tax rate is 1.25%, resulting in a total sales tax rate of 7.5%. On the other hand, Will County, located south of Chicago, imposes an additional local tax of 1.75%, leading to a total sales tax rate of 8%. These variations in sales tax rates across counties can have a significant impact on consumer spending patterns and business strategies within the state.
Impact on Illinois’ Economy and Businesses
The Illinois sales tax rate has a profound impact on the state’s economy and the businesses operating within its borders. For consumers, a higher sales tax rate can lead to increased costs for goods and services, potentially influencing purchasing decisions and consumer behavior. On the other hand, businesses, especially those in the retail and hospitality sectors, must carefully consider these tax rates when setting their pricing strategies and planning their operations.
From a broader economic perspective, the sales tax revenue generated in Illinois contributes significantly to the state's overall budget. In fiscal year 2021, sales tax revenue accounted for 26.7% of the state's total general revenue, highlighting its importance as a source of funding for various state programs and services.
Future Prospects and Potential Changes
Looking ahead, the future of Illinois’ sales tax rate remains a topic of discussion and speculation. With ongoing economic challenges and the state’s complex fiscal situation, there is a possibility of future adjustments to the sales tax rate. Some economists and policymakers have proposed reforms to simplify the sales tax system, potentially standardizing rates across the state to reduce administrative complexities and enhance tax fairness.
Additionally, with the rise of e-commerce and the changing landscape of consumer behavior, the Illinois Department of Revenue has been actively working to ensure that sales taxes are accurately collected and remitted for online sales. This includes implementing the Wayfair decision, which requires out-of-state sellers to collect and remit sales tax for goods sold to Illinois residents, even without a physical presence in the state.
What is the purpose of sales tax in Illinois?
+Sales tax in Illinois is a critical source of revenue for the state and local governments. It helps fund essential public services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and public safety initiatives.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Illinois?
+Yes, Illinois has designated sales tax holidays where certain items are exempt from sales tax for a limited period. These holidays often coincide with major shopping events like back-to-school season or the holidays.
How do online sales impact the Illinois sales tax rate?
+The rise of e-commerce has led to increased scrutiny and enforcement of sales tax collection for online sales. Illinois has implemented measures to ensure that online sellers collect and remit sales tax, even if they don’t have a physical presence in the state.