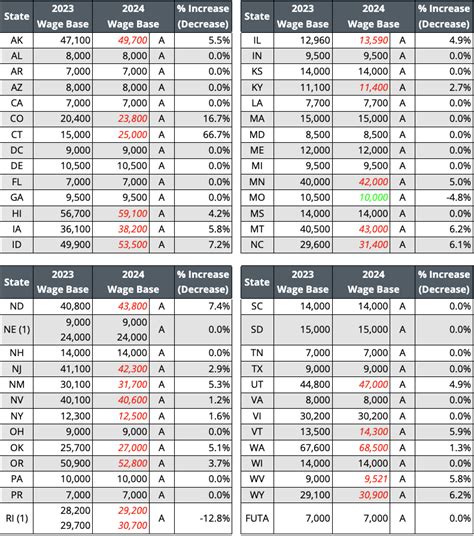
How To Get A Federal Tax Id

Obtaining a Federal Tax Identification Number (also known as an Employer Identification Number or EIN) is a crucial step for businesses and organizations in the United States. An EIN is a unique nine-digit number assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to identify tax-paying entities, and it plays a vital role in various business operations and legal requirements.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the process of obtaining an EIN, exploring the steps, requirements, and considerations to help you navigate the journey smoothly. Whether you're starting a new business or managing an existing one, understanding how to acquire and utilize an EIN is essential for compliance and efficient tax management.
Understanding the Purpose of an EIN
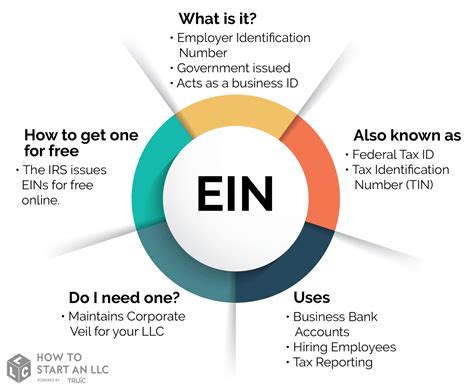
An Employer Identification Number serves as a unique identifier for businesses and organizations in their dealings with the IRS. This number is required for a multitude of purposes, including, but not limited to:
- Filing business tax returns
- Opening a business bank account
- Hiring employees and managing payroll
- Applying for business licenses and permits
- Establishing credit and securing business loans
- Registering for state and local taxes
- Reporting and paying excise taxes
- Completing various IRS forms and applications
An EIN is akin to a Social Security Number for businesses, ensuring accurate record-keeping and compliance with tax laws. It is a critical tool for business owners to manage their financial obligations and maintain a good standing with the IRS.
Who Needs an EIN?

The need for an EIN depends on various factors, including the business structure, ownership, and operations. Here are some scenarios where an EIN is typically required:
Sole Proprietorships
While sole proprietors may use their Social Security Number for certain business activities, an EIN is often recommended for legal and tax purposes. It provides a clear separation between personal and business finances, which can be crucial for liability protection and tax management.
Partnerships and LLCs
Partnerships and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) are typically required to obtain an EIN. This is essential for tax filing, as well as for establishing business bank accounts and managing finances independently from the owners’ personal accounts.
Corporations
Corporations, both C-Corporations and S-Corporations, are legally required to obtain an EIN. This is a fundamental step in the incorporation process and is necessary for all corporate tax filings and business operations.
Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations, including charities, religious organizations, and other tax-exempt entities, must obtain an EIN to apply for tax-exempt status and to comply with reporting requirements.
Trusts and Estates
Trusts and estates that engage in business activities or have income-generating assets may require an EIN for tax purposes. This is particularly important when the trust or estate has employees or needs to file tax returns.
The Application Process
Applying for an EIN is a straightforward process, and the IRS provides several methods to accommodate different business needs and preferences. Here’s an overview of the application methods:
Online Application
The IRS offers an online application process, which is the fastest and most convenient method. It allows applicants to receive their EIN immediately upon successful completion of the application. The online form guides applicants through a series of questions to gather the necessary information.
Fax or Mail Application
For those who prefer a more traditional approach, the IRS provides the option to apply via fax or mail. This method may take longer, typically a few weeks, as the application needs to be processed manually. The IRS provides downloadable forms for this purpose, such as Form SS-4.
Telephone Application
Certain businesses, such as foreign entities or those with special needs, may apply for an EIN over the phone. This option is available for specific cases and requires scheduling an appointment with an IRS representative.
Required Information for Application
To successfully obtain an EIN, applicants must provide specific information to the IRS. Here’s a list of the key details you’ll need to have ready:
- Business Name: The legal name of your business, as it will appear on official documents.
- Business Address: The physical address where your business operates.
- Business Structure: The type of business entity, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, etc.
- Principal Business Activity: A description of your business's primary activities or services.
- Tax Classification: The IRS tax classification for your business, which may be automatically determined based on your business structure.
- Responsible Party: Information about the individual or entity that has control and responsibility over the business's finances and operations. This may include personal details such as name, address, and Social Security Number or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) for individuals.
- Business Start Date: The date your business officially began operations.
- Contact Information: A valid email address and phone number for communication with the IRS.
It's important to ensure that all the information provided is accurate and up-to-date to avoid delays in the application process.
EIN Application for Foreign Entities
Foreign entities, including businesses and organizations based outside the United States, may also need to obtain an EIN for various reasons, such as establishing a US presence, conducting business activities, or investing in US-based entities. The application process for foreign entities has some unique considerations:
- Tax Treaty Exemption: Foreign entities may be eligible for tax treaty benefits, which can reduce or eliminate certain US taxes. To claim these benefits, the entity must provide specific information, including the country of residence and relevant treaty provisions.
- ITIN Requirement: Some foreign individuals may need to obtain an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) if they don't have a Social Security Number. An ITIN is a unique number issued by the IRS to individuals who are not eligible for a Social Security Number but have US tax obligations.
- Foreign Address: Foreign entities must provide their international address, which may require additional details such as city, province, postal code, and country.
- Business Purpose in the US: The IRS will require a clear understanding of the entity's business activities and purpose in the US. This information helps determine the appropriate tax obligations and reporting requirements.
Foreign entities may need to provide additional documentation to support their application, such as proof of business registration in their home country and evidence of US business activities.
Using and Managing Your EIN
Once you have obtained your EIN, it’s essential to understand how to use and manage it effectively. Here are some key considerations:
EIN for Multiple Entities
If you operate multiple businesses or have different entities under your control, you may need separate EINs for each. This ensures accurate tax reporting and compliance for each individual entity.
EIN for Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations must use their EIN for tax-exempt status applications and subsequent tax filings. It’s crucial to maintain accurate records and ensure timely tax reporting to maintain tax-exempt status.
EIN and Business Operations
Your EIN will be used in various aspects of your business operations, including opening bank accounts, establishing credit, and managing payroll. It’s essential to keep your EIN secure and use it responsibly to maintain the integrity of your business operations.
EIN Cancellation and Reactivation
In certain situations, an EIN may be cancelled or become inactive. This can occur if a business ceases operations or if the IRS identifies issues with the EIN. If you need to reactivate an EIN or obtain a new one, the process is similar to the initial application.
Conclusion
Obtaining a Federal Tax Identification Number is a critical step for businesses and organizations in the United States. It provides a unique identifier for tax purposes and facilitates various business operations. By understanding the purpose, requirements, and application process of an EIN, you can ensure compliance and efficient tax management for your business.
Whether you're starting a new venture or managing an existing business, having a clear understanding of your tax obligations and utilizing your EIN effectively will contribute to the success and longevity of your operations.
Can I use my Social Security Number instead of an EIN for my business?
+Using your Social Security Number for business purposes is generally not recommended. While sole proprietors may use their SSN for certain activities, an EIN provides a clear separation between personal and business finances, which is essential for liability protection and tax management.
How long does it take to receive an EIN after applying online?
+When applying online, you will receive your EIN immediately upon successful completion of the application. This is the fastest method and provides instant access to your unique identifier.
Do I need an EIN if I’m a sole proprietor with no employees?
+While not always mandatory, obtaining an EIN for your sole proprietorship is generally recommended. It provides a clear distinction between personal and business finances, simplifies tax reporting, and enhances your business’s professional image.
Can I use the same EIN for multiple businesses I own?
+No, it is not recommended to use the same EIN for multiple businesses. Each business entity should have its own unique EIN to ensure accurate tax reporting and compliance. Using a single EIN for multiple businesses can lead to confusion and potential legal issues.
What happens if I provide incorrect information during the EIN application process?
+Providing incorrect or misleading information during the EIN application can lead to delays or even rejection of your application. It’s crucial to ensure that all the details you provide are accurate and up-to-date. If you realize you’ve made a mistake, you can correct it by reapplying with the correct information.