Hawaii Tax Calculator

The beautiful state of Hawaii is not only a dream destination for many travelers but also a place with a unique tax system that can be intriguing for residents and visitors alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Hawaii's tax structure, providing you with a detailed understanding of how to calculate taxes in this tropical paradise. Whether you're a resident, a business owner, or a curious traveler, this article will equip you with the knowledge to navigate Hawaii's tax landscape with ease.
Unraveling the Hawaii Tax System

Hawaii’s tax system is a blend of various taxes designed to fund the state’s operations and services. While it may seem complex at first glance, breaking it down into components makes it more manageable. Let’s explore the key taxes that make up Hawaii’s revenue stream.
Income Tax: A Key Revenue Source
Like many states, Hawaii imposes an individual income tax on its residents and nonresidents earning income within the state. The Hawaii Department of Taxation oversees the collection and administration of this tax. Here’s a breakdown of the income tax system:
- Tax Rates: Hawaii operates on a progressive tax structure, meaning tax rates increase as your income rises. The state has five income tax brackets, ranging from 1.4% to 11%, ensuring fairness and a balanced approach to taxation.
- Filing Status: Residents and nonresidents can choose between single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, and head of household filing statuses. Each status has its own set of brackets and thresholds.
- Taxable Income: Hawaii defines taxable income as the total income from all sources, including wages, salaries, tips, business income, and investments. However, certain exemptions and deductions can reduce your taxable income.
To illustrate, consider a single taxpayer with a taxable income of $50,000. Using Hawaii's tax brackets for 2023, their tax liability would be calculated as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Income Range | Tax Rate | Tax Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $0 - $4,100 | 1.4% | $57.40 |
| 2 | $4,101 - $10,300 | 3.2% | $198.40 |
| 3 | $10,301 - $30,000 | 5.6% | $1,232 |
| 4 | $30,001 - $100,000 | 7.25% | $2,472.50 |
| 5 | $100,001 and above | 11% | $3,050 |
| Total Tax Liability | $7,010.30 | ||

General Excise Tax: A Broad-Based Levy
In addition to income tax, Hawaii imposes a general excise tax (GET) on most business activities and transactions within the state. This tax is levied on gross income and is often passed on to consumers as part of the sales price. The GET is a key revenue generator for Hawaii, contributing significantly to the state's budget.
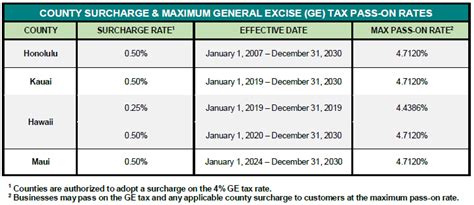
- Tax Rate: The standard GET rate is 4%, but certain activities and industries may have different rates. For example, the GET rate for wholesale and retail sales is 0.5%.
- Filing and Payment: Businesses are responsible for collecting and remitting the GET to the Hawaii Department of Taxation. The frequency of filing and payment depends on the business's size and revenue.
- Exemptions: Some transactions are exempt from GET, including sales of certain foods, prescription drugs, and residential rentals.
Let's say a business has a gross income of $1,000,000 for the year. To calculate the GET liability, we apply the standard 4% rate:
| Gross Income | GET Rate | GET Liability |
|---|---|---|
| $1,000,000 | 4% | $40,000 |
Transient Accommodation Tax: A Tourist-Focused Levy
Hawaii's vibrant tourism industry is a significant contributor to its economy, and the state has a dedicated tax for transient accommodations. The transient accommodation tax (TAT), also known as the hotel room tax, is imposed on the rental of transient accommodations, such as hotels, vacation rentals, and bed-and-breakfasts.
- Tax Rate: The TAT rate varies depending on the location of the accommodation. The standard rate is 10.25%, but counties may impose additional rates. For example, Honolulu has a TAT rate of 14.96%.
- Collection and Remittance: Businesses providing transient accommodations are responsible for collecting the TAT from guests and remitting it to the Hawaii Department of Taxation.
- Exemptions: Certain accommodations, such as long-term rentals (30 days or more), are exempt from the TAT.
If a hotel charges $200 per night for a room and has an occupancy rate of 80%, we can calculate the TAT liability as follows:
| Daily Rate | Occupancy Rate | TAT Rate | TAT Liability per Night |
|---|---|---|---|
| $200 | 80% | 10.25% | $16.40 |
| Total TAT Liability (365 nights) | $6,018 | ||
Real Property Tax: A Foundation for Local Government
Hawaii's real property tax is an essential revenue source for counties, which use it to fund public services and infrastructure. The real property tax is levied on the assessed value of real estate, including land and improvements.
- Assessment: The assessed value of real property is determined by the county assessor based on market conditions and other factors. The assessed value is typically lower than the market value.
- Tax Rates: Counties set their own tax rates, which can vary significantly. The tax rate is applied to the assessed value to calculate the property tax liability.
- Payment: Property owners are responsible for paying their real property taxes. The payment schedule and due dates are set by the county.
As an example, let's consider a residential property with an assessed value of $500,000 in a county with a tax rate of 0.3%. The annual property tax liability would be:
| Assessed Value | Tax Rate | Property Tax Liability |
|---|---|---|
| $500,000 | 0.3% | $1,500 |
Tax Calculation Tools and Resources
Navigating Hawaii's tax system can be simplified with the help of various tools and resources. The Hawaii Department of Taxation provides a wealth of information and guidance to assist taxpayers in understanding their obligations.
Online Tax Calculators
The Hawaii Department of Taxation offers online tax calculators to estimate tax liabilities for various taxes, including income tax, GET, and TAT. These calculators are user-friendly and provide quick estimates based on the information entered.
Tax Forms and Publications
The department also provides a comprehensive collection of tax forms and publications that explain the tax system in detail. These resources cover a wide range of topics, from filing requirements to specific tax credits and deductions.
Taxpayer Assistance
If you have specific questions or need personalized assistance, the Hawaii Department of Taxation offers taxpayer assistance through various channels. You can reach out to their customer service representatives via phone, email, or in-person visits to their offices.
Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with Hawaii’s tax laws is essential to avoid penalties and legal issues. Here are some key considerations for taxpayers and businesses operating in Hawaii.
Filing Deadlines
Hawaii imposes strict filing deadlines for tax returns and payments. Income tax returns, for example, are due by April 20th each year (or the next business day if it falls on a weekend or holiday). Failing to meet these deadlines can result in late fees and penalties.
Tax Registration and Permits
Businesses operating in Hawaii must register with the Hawaii Department of Taxation and obtain the necessary permits and licenses. This includes registering for GET, TAT, and other applicable taxes. Failure to register can lead to significant penalties.
Record Keeping and Audits
Taxpayers and businesses are required to maintain accurate records of their financial transactions and tax obligations. The Hawaii Department of Taxation may conduct audits to ensure compliance. Proper record keeping is crucial for a smooth audit process.
Future Tax Landscape
Hawaii’s tax system is subject to ongoing review and potential changes. As the state’s economy and population evolve, the tax structure may adapt to meet new challenges and opportunities.
Potential Tax Reforms
The Hawaii State Legislature regularly considers tax reform proposals to address issues such as tax fairness, economic growth, and revenue generation. These reforms can impact tax rates, brackets, and exemptions.
Economic Impact of Tourism
Hawaii’s tourism industry plays a crucial role in its economy, and the state carefully manages the tax burden on this sector. As tourism trends change, the state may adjust tax rates and policies to maintain a balance between revenue generation and the industry’s viability.
Digital Economy and Tax Collection
The rise of the digital economy and e-commerce presents new challenges for tax collection. Hawaii, like many states, is exploring ways to tax online transactions and ensure compliance in the digital realm. This includes addressing issues like remote seller taxation and online sales tax collection.
Conclusion: Embracing Hawaii’s Tax System

Hawaii’s tax system, while complex, is a vital component of the state’s economy and governance. Understanding the various taxes and their implications is essential for residents, businesses, and visitors alike. By utilizing the resources and tools provided by the Hawaii Department of Taxation, taxpayers can navigate the system with confidence and ensure compliance.
Whether you're planning a trip to Hawaii or establishing a business in the state, knowledge of the tax landscape is a powerful tool. It empowers you to make informed decisions, calculate your tax liabilities accurately, and contribute to the vibrant economy of this tropical paradise.
What are the tax brackets for Hawaii’s income tax in 2023?
+Hawaii’s income tax brackets for 2023 are as follows: Bracket 1 - 0 to 4,100 (1.4%), Bracket 2 - 4,101 to 10,300 (3.2%), Bracket 3 - 10,301 to 30,000 (5.6%), Bracket 4 - 30,001 to 100,000 (7.25%), and Bracket 5 - $100,001 and above (11%).
How often do businesses need to file and pay the general excise tax (GET)?
+The filing and payment frequency for GET depends on the business’s size and revenue. Monthly, quarterly, or annual filing is common. Larger businesses with higher revenues may be required to file more frequently.
Are there any tax credits or deductions available for Hawaii’s income tax?
+Yes, Hawaii offers various tax credits and deductions to reduce taxable income. These include the personal exemption, standard deduction, and credits for dependents, education, and certain business expenses. It’s essential to review the specific requirements for each credit or deduction.
What is the purpose of the transient accommodation tax (TAT)?
+The TAT is a dedicated tax for the tourism industry in Hawaii. The revenue generated from this tax is used to fund tourism-related projects, infrastructure, and promotional activities. It ensures that the tourism sector contributes to the state’s economy and supports the development of the industry.
How can I register my business for tax purposes in Hawaii?
+To register your business for tax purposes in Hawaii, you need to complete the appropriate forms with the Hawaii Department of Taxation. The registration process may vary depending on the type of business and the taxes involved. It’s advisable to consult the department’s website or seek professional guidance for a smooth registration process.



