Goods And Services Tax Exemptions

The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive indirect tax system that has revolutionized the tax structure in many countries. While GST aims to simplify taxation, it also introduces certain exemptions and special provisions to accommodate various sectors and industries. These exemptions play a crucial role in ensuring a balanced and fair tax regime, benefiting specific goods, services, and entities. In this article, we delve into the world of GST exemptions, exploring their significance, types, and their impact on businesses and consumers alike.
Understanding GST Exemptions
GST exemptions refer to the specific goods, services, or entities that are excluded from the purview of GST taxation. These exemptions are strategically designed to promote certain economic activities, support vulnerable sectors, and maintain social equity. By granting exemptions, governments can encourage the growth of specific industries, protect essential services, and alleviate financial burdens on specific groups.
The decision to exempt certain goods or services from GST is a delicate balance between revenue generation and social welfare. Governments carefully consider various factors, including economic implications, consumer welfare, and international trade practices, when formulating exemption policies. These exemptions can vary widely across different countries, reflecting their unique economic and social priorities.
Types of GST Exemptions

GST exemptions can be broadly categorized into three main types: zero-rated supplies, exempt supplies, and specific exemptions.
Zero-Rated Supplies
Zero-rated supplies are goods or services that are exempt from GST but still attract a tax rate of zero. In this case, the supplier can claim a refund for the input tax paid on purchases related to the zero-rated supply. This type of exemption is often applied to exports, international trade, and certain essential services.
For instance, in many countries, exports are zero-rated to encourage international trade and maintain competitiveness in the global market. Similarly, certain healthcare services, education, and financial services may be zero-rated to ensure access to these essential services without the burden of taxes.
Exempt Supplies
Exempt supplies are goods or services that are completely exempt from GST, and no tax is charged on their supply or purchase. Suppliers of exempt supplies are not eligible to claim input tax credits, as they do not pay any GST on their inputs. This type of exemption is typically applied to socially important goods and services.
Examples of exempt supplies include basic food items, healthcare products, educational materials, and certain charitable activities. By exempting these items, governments aim to ensure that essential goods and services remain affordable for all segments of society.
Specific Exemptions
Specific exemptions are targeted towards particular sectors, goods, or services, and are granted based on unique circumstances or strategic considerations. These exemptions are often temporary and may be subject to specific conditions or criteria.
For example, certain agricultural products may be granted specific exemptions to support the farming industry and promote food security. Similarly, exemptions may be provided for renewable energy initiatives, research and development activities, or specific infrastructure projects to encourage sustainable development.
Impact of GST Exemptions
GST exemptions have a significant impact on businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. Here are some key implications:
Benefits for Businesses
GST exemptions can provide significant advantages to businesses operating in specific sectors. By exempting certain goods or services, businesses can reduce their tax liabilities, improve cash flow, and enhance their competitive edge. This is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that often face financial constraints.
Additionally, zero-rated supplies allow businesses to recover input tax, ensuring a more efficient tax system. This encourages businesses to focus on their core activities rather than navigating complex tax regulations.
Consumer Welfare
GST exemptions directly impact consumer welfare by making essential goods and services more affordable. By exempting basic necessities, governments ensure that low-income households can access these items without bearing the burden of taxation. This promotes social inclusivity and reduces the regressive nature of indirect taxes.
Furthermore, zero-rated supplies for exports enhance the competitiveness of domestic products in the global market, benefiting consumers both domestically and internationally.
Revenue Generation and Economic Growth
While GST exemptions may result in a reduction of tax revenue for governments, they play a strategic role in promoting economic growth. By exempting certain sectors, governments can stimulate specific industries, attract investments, and create employment opportunities. This balanced approach ensures that the tax system supports overall economic development.
Case Study: GST Exemptions in the Healthcare Sector
To illustrate the practical implications of GST exemptions, let’s explore a case study focusing on the healthcare sector. Healthcare is a critical sector that often receives special consideration in GST frameworks.
In many countries, healthcare services and medical supplies are exempt from GST to ensure affordable and accessible healthcare for all. This exemption covers a wide range of services, including hospital stays, medical consultations, diagnostic tests, and the supply of essential medicines.
| Healthcare Category | GST Exemption Status |
|---|---|
| Hospitalization Services | Exempt |
| Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation | Exempt |
| Diagnostic Services (e.g., X-rays, MRI) | Exempt |
| Prescription Drugs | Exempt |
| Medical Devices (e.g., pacemakers, insulin pumps) | Exempt |
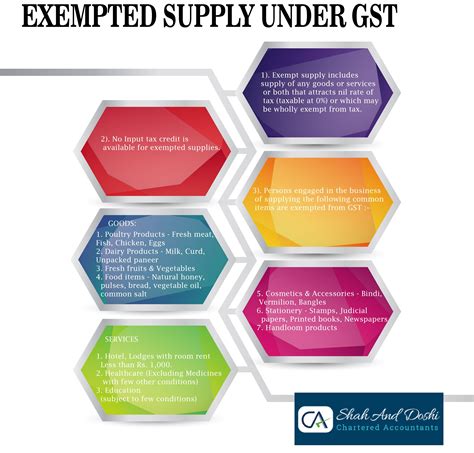
By exempting these healthcare services and supplies, governments prioritize the well-being of their citizens and reduce the financial barriers associated with medical treatment. This exemption ensures that individuals can access necessary healthcare services without facing additional tax burdens.
Impact on Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and pharmaceutical companies, benefit from the GST exemption. They can pass on the savings to patients, making healthcare more affordable. Additionally, the exemption allows these providers to focus on delivering quality healthcare without the administrative burden of GST compliance.
Future Implications and Challenges

GST exemptions, while beneficial, also present certain challenges and considerations for policymakers and businesses alike. As the economic landscape evolves, governments must continuously evaluate and adapt their exemption policies.
Dynamic Economic Environment
The dynamic nature of the economy necessitates regular reviews of GST exemption lists. As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, certain sectors may require additional support or revised exemption policies. Governments must stay agile to ensure that exemptions remain relevant and effective.
Administrative Complexity
GST exemptions can introduce administrative complexities for businesses and tax authorities. Businesses need to understand the specific criteria and conditions associated with each exemption to ensure compliance. Tax authorities, on the other hand, must effectively monitor and enforce these exemptions to prevent tax evasion.
International Trade and Harmonization
In a globalized world, international trade considerations play a crucial role in formulating GST exemption policies. Countries must harmonize their exemption policies with international trade agreements to avoid trade barriers and maintain competitiveness. This balance is essential to ensure that domestic industries are not disadvantaged in the global market.
Conclusion
GST exemptions are a critical component of any tax system, offering a delicate balance between revenue generation and social welfare. By strategically exempting certain goods, services, and entities, governments can promote economic growth, support vulnerable sectors, and ensure social inclusivity. The case study on healthcare exemptions demonstrates the practical impact of these policies, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
However, the challenges associated with GST exemptions, such as administrative complexities and dynamic economic environments, cannot be overlooked. Policymakers must remain vigilant in their efforts to refine and adapt exemption policies to meet the evolving needs of their economies. As the world continues to evolve, GST exemptions will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping tax systems and driving economic development.
How do GST exemptions impact small businesses?
+GST exemptions can significantly benefit small businesses by reducing their tax liabilities and improving cash flow. This support is crucial for the growth and sustainability of small enterprises.
Are there any drawbacks to GST exemptions for governments?
+While GST exemptions promote specific sectors and social welfare, they can result in reduced tax revenue for governments. Balancing revenue generation with social objectives is a key challenge for policymakers.
How often are GST exemption policies reviewed and updated?
+GST exemption policies are typically reviewed periodically, often annually or bi-annually, to ensure they remain aligned with economic trends and social priorities. Regular reviews are essential to adapt to changing market dynamics.