General Excise Tax Hawaii
General Excise Tax: Understanding Hawaii’s Unique Tax System

In the picturesque state of Hawaii, a vibrant economy thrives amidst its stunning natural landscapes. At the heart of Hawaii's financial landscape lies the General Excise Tax (GET), a critical component of the state's tax structure. This article delves into the intricacies of Hawaii's GET, shedding light on its unique features, impact, and significance for both residents and businesses.
Unraveling Hawaii’s General Excise Tax

The General Excise Tax in Hawaii is a broad-based tax applied to most business activities within the state. Unlike traditional sales taxes, GET is levied on the privilege of doing business rather than the sale of specific goods or services. This fundamental difference sets Hawaii’s tax system apart from many other states in the US.
Implemented in 1942, the GET has evolved into a cornerstone of Hawaii's revenue generation, contributing significantly to the state's fiscal health and public services. The tax is administered by the Department of Taxation, which ensures compliance and provides guidance to taxpayers.
Key Characteristics of Hawaii’s GET
Hawaii’s General Excise Tax is characterized by several distinct features:
- Base Tax Rate: The standard GET rate is currently set at 4%, which is applied to most transactions. This base rate has remained relatively stable over the years, providing a consistent revenue stream for the state.
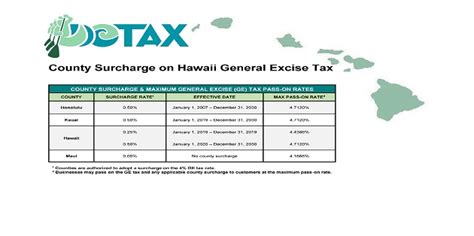
- Surcharge and Special Rates: In addition to the base rate, certain activities and industries are subject to surcharges or special rates. For instance, wholesale businesses pay a 0.5% surcharge, while hotels and resorts incur a 10.25% rate, including the Transient Accommodation Tax (TAT). These variations cater to specific sectors’ revenue contributions.
- Service and Retail Sectors: GET is applicable to a wide range of services and retail sales. From professional services like legal and medical practices to retail stores and online transactions, the tax is integral to various business operations.
- Contractor Excise Tax: A notable aspect of Hawaii’s tax system is the Contractor Excise Tax, which applies to construction-related activities. Contractors must pay a 4.166% tax on their construction contracts, impacting the building and development industry.
Hawaii's GET, with its comprehensive coverage, ensures that a broad spectrum of economic activities contribute to the state's revenue.
The Impact on Businesses and Residents
The General Excise Tax influences the financial landscape for both businesses and individuals in Hawaii:
- Businesses: Companies operating in Hawaii must navigate the complexities of GET, ensuring compliance with tax regulations. This includes understanding the tax rate applicable to their specific industry and accurately calculating and remitting the tax.
- Consumers: Residents and visitors to Hawaii indirectly bear the GET through the prices of goods and services they purchase. While the tax is not visible on individual items like a sales tax, it is embedded in the overall cost, affecting consumers’ purchasing power.
- Economic Development: GET plays a crucial role in supporting Hawaii’s economic development. The revenue generated funds essential public services, infrastructure projects, and social programs, contributing to the overall well-being of the state.
Performance and Revenue Analysis
A closer look at Hawaii’s GET revenue reveals some intriguing insights:
| Fiscal Year | General Excise Tax Revenue (in millions) |
|---|---|
| 2021-2022 | 2,938.8</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2020-2021</td> <td>2,232.4 |
| 2019-2020 | $3,175.5 |
The data highlights the significant contribution of GET to Hawaii's fiscal revenue. Despite a dip in revenue during the COVID-19 pandemic (2020-2021), the tax system has proven resilient, demonstrating its importance as a stable revenue source.
Future Implications and Tax Reform
As Hawaii’s economy evolves, discussions surrounding tax reform and the future of GET are gaining traction. Key considerations include:
- Tax Simplification: There are ongoing efforts to simplify the tax system, making it more accessible and understandable for businesses and taxpayers. Streamlining processes and reducing administrative burdens are key priorities.
- Revenue Stability: Hawaii’s reliance on GET as a primary revenue source prompts considerations of diversifying the tax base. Exploring alternative revenue streams ensures a more balanced and resilient fiscal foundation.
- Tourism’s Impact: With tourism being a significant driver of GET revenue, managing the industry’s fluctuations becomes crucial. Striking a balance between promoting tourism and ensuring sustainable revenue generation is a delicate task.
The future of Hawaii's tax system is poised for evolution, aiming to adapt to the changing economic landscape while maintaining fiscal stability.
Conclusion
Hawaii’s General Excise Tax is a unique and integral part of the state’s financial ecosystem. As a broad-based tax, GET contributes significantly to Hawaii’s economic vitality, supporting public services and infrastructure. Understanding its complexities and implications is vital for businesses and residents alike.
As Hawaii charts its economic course, the evolution of its tax system will undoubtedly shape the state's future. By staying informed and engaged, stakeholders can actively contribute to the ongoing dialogue surrounding tax reform and economic prosperity.
What is the difference between Hawaii’s GET and a traditional sales tax?
+
Hawaii’s GET differs from a traditional sales tax as it is levied on the privilege of doing business rather than the sale of goods or services. This means that GET is applicable to a wider range of activities, making it a more comprehensive tax system.
How does GET impact small businesses in Hawaii?
+
Small businesses in Hawaii must navigate the complexities of GET, ensuring compliance with tax regulations. The tax can impact their operating costs and pricing strategies, requiring careful consideration and planning.
What are the benefits of Hawaii’s GET for the state’s economy?
+
GET provides a stable and reliable revenue stream for Hawaii’s economy, funding essential public services and infrastructure. It contributes to economic development and supports the state’s fiscal health.