Foreign Tax Identifying Number
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the Foreign Tax Identifying Number (FTIN), a crucial aspect of international tax compliance and business operations. FTINs are unique identifiers assigned to individuals and entities engaged in cross-border transactions, playing a vital role in tax reporting and due diligence processes.
In today's globalized economy, understanding and effectively utilizing FTINs is essential for businesses and individuals alike. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the significance of FTINs, their application, and their role in streamlining international tax obligations.
The Significance of Foreign Tax Identifying Numbers

FTINs serve as a critical tool for tax authorities and businesses to accurately identify and track tax obligations arising from international transactions. They are especially pertinent in the context of cross-border investments, trade, and financial transactions, where the accurate identification of parties involved is essential for tax compliance.
The use of FTINs facilitates efficient tax administration by simplifying the process of collecting and reporting taxes on cross-border transactions. This is particularly beneficial for multinational corporations and individuals with global investment portfolios, as it helps ensure compliance with a range of international tax regulations.
Understanding the FTIN Structure

FTINs are typically country-specific and are issued by the tax authority of the relevant jurisdiction. The structure of an FTIN can vary depending on the country, but they often include a combination of alphanumeric characters, with each character holding a specific meaning.
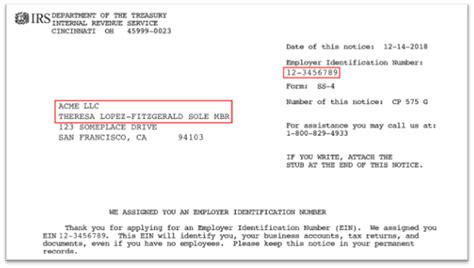
For instance, in the United States, the Foreign Taxpayer Identification Number (FTIN) is also known as the Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN), depending on the individual's status. These numbers are typically 9 digits long and are used for tax reporting purposes by non-resident aliens, foreign corporations, and other entities.
Examples of FTINs by Country
- United States: ITIN (Individual Taxpayer Identification Number) - 9 digits, e.g., 987-65-4321.
- United Kingdom: Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR) - 10 digits, e.g., 1234567890.
- Canada: Business Number (BN) - 9 digits, e.g., 123456789.
- Australia: Australian Business Number (ABN) - 11 digits, e.g., 123-456-789-00.
These examples illustrate the diversity in FTIN structures across different countries, emphasizing the need for businesses and individuals to be well-informed about the specific requirements of each jurisdiction they operate in.
Application and Obtaining an FTIN
The process of applying for an FTIN varies based on the country and the type of entity involved. In most cases, individuals and businesses must complete specific forms and provide supporting documentation to the relevant tax authority.
For instance, in the United States, non-resident aliens and foreign corporations can apply for an ITIN by submitting Form W-7 to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This form requires detailed information about the applicant's identity, foreign status, and reason for needing an ITIN.
Similarly, in the United Kingdom, businesses must apply for a Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR) when they register for Value Added Tax (VAT) or other taxes. The application process involves providing business details and sometimes requires additional verification steps.
Key Considerations for FTIN Applications
- Eligibility: Different countries have specific eligibility criteria for FTIN applications. It’s essential to understand these criteria to ensure a successful application.
- Supporting Documents: Most applications require supporting documents to prove identity, foreign status, or business registration. These can include passports, birth certificates, or business registration certificates.
- Processing Time: The time it takes to obtain an FTIN can vary. Some countries process applications within a few weeks, while others may take several months. It’s crucial to plan accordingly, especially for time-sensitive transactions.
Navigating the FTIN application process can be complex, especially for individuals and businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions. Engaging the services of tax professionals or legal advisors with expertise in international tax matters can be invaluable in ensuring compliance and a smooth application process.
Utilizing FTINs for International Tax Compliance
Once obtained, FTINs become a fundamental tool for international tax compliance. They are used to report income, pay taxes, and demonstrate compliance with local tax regulations.
For instance, businesses engaged in cross-border transactions must report their income and expenses accurately, using their FTINs to identify themselves on tax forms and other documentation. This ensures that the correct tax rates are applied and that the business complies with the tax laws of the relevant jurisdictions.
Similarly, individuals with foreign income or assets may need to use their FTINs when filing tax returns or reporting financial information to their home country's tax authority. This is particularly important for individuals with complex financial situations, such as those with multiple sources of income or assets located in different countries.
The Role of FTINs in Tax Reporting
- Income Reporting: FTINs are used to accurately report income earned in foreign jurisdictions. This ensures that the correct tax treatment is applied and helps prevent double taxation.
- Withholding Tax: In some cases, FTINs are used to facilitate the withholding of tax on cross-border payments. This is particularly relevant for businesses making payments to foreign vendors or contractors.
- Compliance with Tax Treaties: FTINs play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with tax treaties between countries. These treaties often outline specific tax rates and reporting requirements for cross-border transactions.
Effective utilization of FTINs is not only a matter of compliance but also a strategic tool for businesses and individuals to manage their tax obligations efficiently and potentially reduce their tax burden through the application of tax treaties and other tax incentives.
The Future of FTINs and Global Tax Compliance

As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the role of FTINs in global tax compliance is set to expand. With the rise of digital technologies and the growing focus on tax transparency, FTINs are likely to become even more standardized and integrated into international tax systems.
The development of international tax standards, such as the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Project led by the OECD, aims to establish a more uniform approach to tax administration across borders. This initiative, along with others, is likely to influence the structure and application of FTINs, making them an even more critical component of global tax compliance.
Additionally, the growing trend of tax authorities sharing information to combat tax evasion and ensure compliance is likely to further emphasize the importance of accurate FTINs. This sharing of information will make it easier for tax authorities to identify and track cross-border transactions, making FTINs a key tool in maintaining transparency and accountability.
Emerging Trends and Challenges
- Digitalization of Tax Processes: The shift towards digital tax reporting and compliance is likely to streamline the use of FTINs, making them more accessible and easier to manage.
- Data Privacy and Security: With the increased use of FTINs and digital tax reporting, ensuring data privacy and security will become a critical challenge. Tax authorities and businesses will need to implement robust measures to protect sensitive information.
- Tax Treaty Negotiations: As countries continue to negotiate and update tax treaties, the role of FTINs in facilitating compliance with these treaties will become increasingly complex. Businesses and individuals will need to stay updated on these changes to ensure they remain compliant.
The future of FTINs and global tax compliance is undoubtedly exciting, with the potential for significant advancements in standardization, transparency, and efficiency. However, it also presents challenges that will require ongoing attention and adaptation from businesses, individuals, and tax authorities alike.
How do FTINs differ from other tax identification numbers, such as the EIN in the US?
+FTINs are specifically designed for foreign individuals and entities engaged in cross-border transactions. While they serve a similar purpose to domestic tax identification numbers like the EIN, they are tailored to the unique requirements of international tax compliance. FTINs often have different application processes and eligibility criteria, reflecting the specific needs of the foreign jurisdiction.
Are FTINs necessary for all types of cross-border transactions?
+The need for an FTIN can vary depending on the nature and size of the cross-border transaction. Generally, FTINs are required for transactions that involve significant financial value or have tax implications. For instance, businesses making substantial cross-border payments or individuals with substantial foreign income are likely to need an FTIN. However, smaller transactions may not require an FTIN, especially if they fall below certain tax thresholds.
Can FTINs be used for tax planning purposes, or are they solely for compliance?
+FTINs are primarily used for compliance purposes, ensuring that tax obligations arising from cross-border transactions are met. However, they can also be a useful tool for tax planning. By accurately identifying and tracking tax obligations, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their financial strategies and potentially reduce their tax burden. This is particularly relevant in the context of tax treaties and other tax incentives, where FTINs play a critical role in ensuring compliance and accessing tax benefits.