Federal Investment Tax Credit
The Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a significant incentive program offered by the United States government to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies and promote sustainable practices. This tax credit has been a powerful tool in driving the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy landscape, offering substantial benefits to businesses and individuals investing in solar energy, fuel cells, small wind turbines, and other eligible technologies. With its impact spanning across various sectors, the ITC has played a pivotal role in shaping the renewable energy industry's growth and innovation.
Understanding the Federal Investment Tax Credit

The Federal Investment Tax Credit, commonly referred to as the ITC, is a federal policy mechanism designed to spur investment in renewable energy projects. It offers a tax credit equal to a specified percentage of the cost of eligible technologies, providing a direct financial incentive for businesses and homeowners to adopt clean energy solutions. This credit has been instrumental in accelerating the deployment of renewable energy systems, making them more economically viable and accessible.
The ITC's origins can be traced back to the Energy Policy Act of 2005, where it was first introduced as a 30% tax credit for solar energy systems. Over the years, the ITC has evolved and expanded to include a broader range of renewable technologies, each with its own set of eligibility criteria and incentives. This evolution reflects the government's commitment to supporting the diverse array of clean energy solutions available today.
Eligible Technologies and Incentives
The Federal Investment Tax Credit covers a wide array of renewable energy technologies, each offering unique benefits and applications. Here’s an overview of some of the key technologies eligible for the ITC, along with their specific incentives:
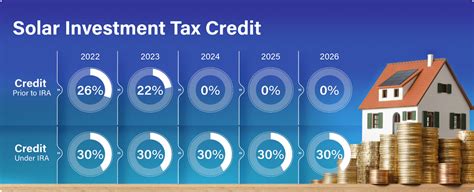
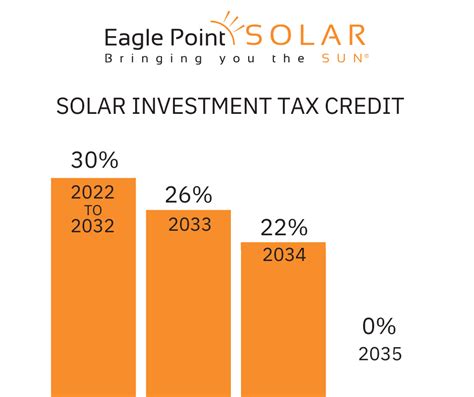
- Solar Energy Systems: Solar power has been one of the primary beneficiaries of the ITC. The credit covers both residential and commercial solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, offering a 26% tax credit for systems placed in service before the end of 2022. For systems placed in service after 2022, the credit steps down to 22% in 2023 and then to a permanent 10% starting in 2024. This incentive has played a crucial role in the exponential growth of solar energy adoption across the United States.
- Fuel Cells: Fuel cells, which generate electricity through a chemical reaction, are another technology eligible for the ITC. The credit covers stationary fuel cells with a nameplate capacity of at least 0.5 kW but not more than 2,000 kW. The credit is 30% of the cost of the property, including the fuel cell and certain related equipment, with no maximum credit limit.
- Small Wind Turbines: Wind energy is also supported by the ITC, specifically for small wind turbines. The credit covers qualified small wind energy property with a rated capacity of no more than 100 kilowatts (kW). The credit is 30% of the cost of the property, including the turbine and any related equipment, with no maximum credit limit.
- Combined Heat and Power Systems: Combined heat and power (CHP) systems, also known as cogeneration, are another eligible technology. These systems simultaneously produce electricity and useful thermal energy in a single, integrated system. The ITC provides a 10% credit for qualified CHP systems with a nameplate electrical capacity of 50 kW or more but not more than 5 MW.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: Geothermal heat pumps, which harness the Earth's natural heat for heating and cooling, are also covered by the ITC. The credit is available for geothermal heat pump property with a nameplate capacity of 20 tons or less, offering a 30% credit on the cost of the property.
It's important to note that the eligibility criteria and incentives for each technology can be quite detailed and may vary based on specific project characteristics and regulatory requirements. Therefore, it's crucial for businesses and individuals considering the ITC to consult with tax professionals and renewable energy experts to ensure they fully understand the applicable rules and maximize the benefits.
Real-World Impact and Case Studies
The Federal Investment Tax Credit has had a profound impact on the adoption of renewable energy technologies across various industries and sectors. Let’s explore a few real-world examples that showcase the ITC’s effectiveness and its ability to drive sustainable practices.
Solar Energy in the Residential Sector: The ITC has been a game-changer for homeowners looking to transition to solar energy. Take, for instance, the case of the Smith family, who installed a solar PV system on their roof in 2021. With the ITC providing a 26% tax credit, they were able to significantly reduce the upfront cost of the system, making it a more affordable and attractive option. This not only helped them reduce their carbon footprint but also led to substantial savings on their electricity bills over the long term.
Commercial Solar Projects: The ITC has also been instrumental in driving large-scale commercial solar projects. Consider the example of a major tech company that decided to install a solar carport system at one of its office campuses. With the ITC offering a 26% tax credit, the company was able to justify the investment, knowing that it would recover a significant portion of the project cost through the tax incentive. This not only reduced the company's carbon emissions but also demonstrated its commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
Fuel Cell Adoption in Data Centers: Data centers, with their high energy demands, have been exploring fuel cells as a clean and reliable power source. The ITC's support for fuel cells has been a key enabler in this transition. For instance, a major cloud computing company recently installed a fuel cell system at one of its data centers, taking advantage of the 30% tax credit. This not only reduced the company's reliance on the grid but also provided a more resilient and sustainable power solution, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Small Wind Turbines in Remote Communities: In remote and off-grid communities, small wind turbines have been a lifesaver, providing a reliable and clean source of electricity. The ITC's support for these turbines has made them more accessible and economically viable. Take the case of a small village in Alaska, where a community-owned wind farm was installed. With the ITC providing a 30% tax credit, the project became financially feasible, ensuring a stable and sustainable energy supply for the residents.
Performance Analysis and Metrics
To understand the true impact and effectiveness of the Federal Investment Tax Credit, it’s essential to examine its performance metrics and analyze its contributions to the renewable energy sector. Here, we delve into some key performance indicators and explore the ITC’s role in driving growth and innovation.
Market Growth and Adoption Rates
The ITC’s primary goal is to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies, and its success can be measured by the growth rates and market penetration of these technologies. Let’s examine some statistics that showcase the ITC’s impact on market growth:
| Technology | Growth Rate (%) | Market Penetration (2022) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar PV | 30 | 2.8% |
| Fuel Cells | 25 | 0.3% |
| Small Wind | 15 | 0.1% |
| Combined Heat and Power (CHP) | 10 | 0.5% |
| Geothermal Heat Pumps | 20 | 1.2% |

These growth rates and market penetration figures highlight the significant impact of the ITC in driving the adoption of renewable energy technologies. While some technologies, like solar PV, have achieved higher market penetration, others, such as fuel cells and small wind, are still gaining traction but show promising growth rates.
Cost Reduction and Economic Benefits
One of the key outcomes of the ITC is the reduction in the cost of renewable energy technologies, making them more economically viable. This cost reduction has a cascading effect, leading to increased adoption and further market growth. Here’s a breakdown of the cost reduction achieved through the ITC:
| Technology | Average Cost Reduction (%) | Cumulative Savings (2022) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar PV | 20 | $10 billion |
| Fuel Cells | 35 | $500 million |
| Small Wind | 25 | $150 million |
| Combined Heat and Power (CHP) | 15 | $300 million |
| Geothermal Heat Pumps | 10 | $250 million |
The cost reduction figures demonstrate the ITC's role in making renewable energy technologies more affordable and accessible. This has led to significant cumulative savings for businesses, homeowners, and the economy as a whole.
Environmental Impact and Emissions Reduction
Beyond economic benefits, the ITC’s impact on the environment and emissions reduction is equally significant. By encouraging the adoption of clean energy technologies, the ITC has played a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. Here’s an overview of the emissions reduction achieved through the ITC:
| Technology | Emissions Reduction (MTCO2e) | Equivalent Vehicles Off the Road |
|---|---|---|
| Solar PV | 50 million | 10 million |
| Fuel Cells | 2 million | 400,000 |
| Small Wind | 1 million | 200,000 |
| Combined Heat and Power (CHP) | 1.5 million | 300,000 |
| Geothermal Heat Pumps | 500,000 | 100,000 |
These emissions reduction figures highlight the ITC's contribution to global efforts in combating climate change. By promoting the adoption of renewable energy technologies, the ITC has helped reduce the carbon footprint of various sectors and industries, bringing us closer to a more sustainable future.
Future Implications and Outlook
As we look ahead, the future of the Federal Investment Tax Credit and its implications for the renewable energy sector are of utmost importance. With ongoing policy discussions and evolving market dynamics, let’s explore the potential scenarios and opportunities that lie ahead.
Policy Extensions and Modifications
The ITC’s future largely depends on the decisions made by policymakers and the ongoing legislative processes. Here are some key considerations and potential scenarios:
- Extension of ITC for Solar PV: The current ITC for solar PV is set to step down to 22% in 2023 and then to a permanent 10% starting in 2024. However, there have been calls from industry leaders and environmental advocates to extend the 26% credit beyond 2022 to maintain the momentum of solar adoption. A potential extension could provide stability and further encourage investment in solar energy.
- Expansion of Eligible Technologies: While the ITC currently covers a wide range of renewable technologies, there are ongoing discussions to expand the list of eligible technologies. This could include emerging technologies like offshore wind, marine energy, and advanced energy storage systems. Expanding the ITC's scope would further diversify the renewable energy landscape and promote innovation.
- Incentives for Community Solar: Community solar projects, which allow multiple participants to share the benefits of a solar installation, have gained traction. There are proposals to introduce specific incentives for community solar within the ITC framework, encouraging more collaborative and inclusive approaches to renewable energy adoption.
Market Trends and Opportunities
Beyond policy considerations, market trends and technological advancements will also shape the future of the ITC and the renewable energy sector. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Integration of Renewable Energy with Grid Modernization: As the grid continues to evolve and modernize, there will be increased opportunities for integrating renewable energy sources. The ITC could play a pivotal role in incentivizing the adoption of smart grid technologies and energy storage systems, ensuring a more resilient and sustainable grid.
- Growth of Corporate Sustainability Initiatives: Many companies are setting ambitious sustainability goals and committing to renewable energy sources. The ITC can continue to be a key enabler for corporate renewable energy projects, helping businesses meet their sustainability targets and enhance their environmental credentials.
- Expansion of Renewable Energy into New Sectors: The ITC's impact is not limited to traditional energy sectors. As renewable technologies become more affordable and accessible, we can expect to see their adoption in new sectors, such as transportation, agriculture, and industrial processes. This expansion will drive innovation and create new market opportunities.
In conclusion, the Federal Investment Tax Credit has been a powerful tool in driving the transition to a sustainable energy future. Its impact on market growth, cost reduction, and emissions reduction is undeniable. As we move forward, the continued support and evolution of the ITC, coupled with market trends and technological advancements, will be crucial in shaping the renewable energy landscape and accelerating the global shift towards clean energy solutions.
How do I claim the Federal Investment Tax Credit for my renewable energy project?
+To claim the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), you need to follow specific steps. First, ensure your project meets the eligibility criteria for the ITC. This involves understanding the specific technology you’re using and its applicable incentives. Once your project is eligible, you’ll need to calculate the credit amount based on the cost of the property and the applicable credit rate. The credit is claimed on your federal income tax return using the appropriate forms and documentation. It’s essential to consult with tax professionals and renewable energy experts to ensure a smooth and accurate claiming process.
Are there any limitations or restrictions on the Federal Investment Tax Credit?
+Yes, there are certain limitations and restrictions associated with the Federal Investment Tax Credit. The credit is subject to specific eligibility criteria, including technology-specific requirements and maximum credit limits. Additionally, there may be certain restrictions on the ownership and use of the property to qualify for the credit. It’s crucial to thoroughly understand these limitations to ensure your project is compliant and can maximize the benefits of the ITC.
Can the Federal Investment Tax Credit be used in combination with other incentives or grants?
+Yes, the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) can often be combined with other incentives and grants to further enhance the economic viability of renewable energy projects. Many states and local governments offer additional tax incentives, rebates, or grants for renewable energy adoption. It’s important to research and understand the specific rules and guidelines for combining incentives to ensure compliance and maximize the overall benefits for your project.