Earned Income Tax Eligibility

The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a crucial financial incentive program offered by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. It aims to provide a helping hand to low- to moderate-income workers, offering a much-needed boost to their tax refunds or reducing their tax liabilities. This program has had a significant impact on the financial well-being of millions of Americans, especially those struggling to make ends meet. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of the Earned Income Tax Credit, exploring its eligibility criteria, impact, and the steps one needs to take to claim this valuable benefit.
Understanding the Earned Income Tax Credit

The Earned Income Tax Credit, often referred to as the EITC or EIC, is a refundable tax credit designed to provide a financial boost to eligible workers. It was introduced as a way to encourage employment and reduce poverty levels, especially among working families. The credit is based on a taxpayer’s earned income, and it can either offset tax liabilities or result in a refund, even if no tax is owed. This makes it a powerful tool for improving the financial stability of those who need it most.
The EITC has been a cornerstone of the US tax system since its inception in 1975, and its impact has only grown over the years. In 2020 alone, the IRS estimates that the EITC program delivered over $65 billion in tax refunds to eligible taxpayers. This credit not only provides immediate financial relief but also serves as a long-term incentive for individuals to enter and remain in the workforce.
Eligibility Criteria: Who Qualifies for the EITC

Understanding the eligibility criteria for the Earned Income Tax Credit is essential for taxpayers to know if they qualify for this beneficial program. The IRS sets specific guidelines to determine who is eligible for the EITC, and these criteria are based on a combination of factors, including income, marital status, and the number of qualifying children.
Income Limits
One of the primary eligibility factors is income. The EITC is designed to assist low- to moderate-income earners, so there are maximum income limits that vary based on marital status and the number of qualifying children. For example, in 2023, the income limit for a single filer with no children is 16,370, while for a married couple filing jointly with three or more qualifying children, the income limit is 57,414. These income limits are adjusted annually to account for inflation.
| Filing Status | Number of Qualifying Children | Maximum Income for EITC Eligibility (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Single | 0 | $16,370 |
| Head of Household | 1 | $22,830 |
| Married Filing Jointly | 2 | $49,078 |
| Married Filing Jointly | 3 or More | $57,414 |
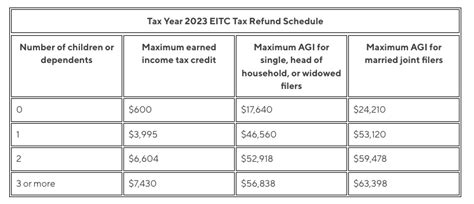
It's important to note that these income limits are subject to change each year, so taxpayers should refer to the most recent IRS guidelines for the most accurate information.
Qualifying Children
The presence of qualifying children can significantly impact EITC eligibility and the amount of credit received. A qualifying child is a dependent who meets specific criteria, including age, relationship to the taxpayer, and residency. Generally, a qualifying child must be under the age of 19 (or under 24 if a full-time student) at the end of the tax year, live with the taxpayer for more than half of the year, and not provide more than half of their own support.
The number of qualifying children can increase the amount of EITC received, as there are different credit amounts for taxpayers with one child, two children, or three or more children. For instance, in 2023, the maximum EITC for a taxpayer with three or more qualifying children is $6,935, while a taxpayer with no qualifying children can receive up to $1,125.
Other Eligibility Factors
In addition to income and the presence of qualifying children, there are other factors that determine EITC eligibility. Taxpayers must have earned income from employment or self-employment, and this income must be above a certain threshold to qualify. The threshold varies based on the number of qualifying children and the taxpayer’s filing status.
Furthermore, taxpayers must have a valid Social Security number and cannot be claimed as a dependent on another person's tax return. They must also meet certain residency requirements, such as being a U.S. citizen, national, or resident alien for the entire tax year.
Claiming the Earned Income Tax Credit
Claiming the Earned Income Tax Credit involves a series of steps to ensure that eligible taxpayers receive the full benefit of the credit. It is important to understand the process to avoid any potential mistakes or missed opportunities.
Step 1: Determine Eligibility
The first step in claiming the EITC is to determine if you meet the eligibility criteria. This involves reviewing your income, marital status, and the number of qualifying children you have. The IRS provides online tools and resources to help taxpayers assess their eligibility, such as the EITC Assistant on their website.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Documents
Once you’ve confirmed your eligibility, the next step is to gather the required documents. This typically includes W-2 forms from employers, income statements from self-employment, and documentation related to any other sources of income. If you have qualifying children, you’ll need to provide their Social Security numbers and birthdates.
Step 3: Complete the Necessary Forms
To claim the EITC, you must complete the appropriate tax forms. The main form used is Schedule EIC, which is attached to your federal income tax return. This form requires detailed information about your income, the number of qualifying children, and other relevant details. It’s crucial to fill out this form accurately to avoid any delays or issues with your tax refund.
Step 4: File Your Tax Return
After completing the necessary forms, you can file your tax return. You can file electronically or by mail, depending on your preference and the complexity of your tax situation. It’s important to ensure that your tax return is complete and accurate to avoid any potential audits or penalties.
Step 5: Receive Your EITC
Once your tax return is processed, the IRS will calculate your EITC amount based on the information you’ve provided. If you’re due a refund, including the EITC, you’ll receive it according to the method you chose (direct deposit or check). It’s essential to keep track of your refund status, especially if you’re expecting a substantial EITC amount.
Maximizing Your EITC Benefits
Maximizing your Earned Income Tax Credit benefits involves understanding the various factors that can impact the amount you receive. By taking certain steps and being aware of the rules, you can ensure that you’re getting the most out of this valuable tax credit.
Consider Filing as Head of Household
The filing status you choose can have a significant impact on your EITC amount. If you’re an unmarried taxpayer with a qualifying child who lives with you for more than half of the year, you may be able to file as Head of Household. This status often results in a higher EITC amount compared to filing as Single or Married Filing Separately.
Keep Accurate Records
Maintaining accurate records of your income and expenses is crucial for claiming the EITC. This includes keeping track of all W-2s, 1099s, and other income statements. Additionally, if you have qualifying children, it’s important to keep records of their birthdates, Social Security numbers, and residency status.
Take Advantage of Free Tax Preparation Services
The IRS offers free tax preparation services for eligible taxpayers through its Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) and Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE) programs. These services can help you navigate the complexities of claiming the EITC and ensure that you receive the full benefit you’re entitled to. You can find a VITA or TCE site near you using the IRS’s online locator tool.
Stay Informed About Changes
The EITC guidelines can change from year to year, so it’s important to stay informed about any updates. The IRS provides regular updates and resources on its website, including publications and fact sheets that outline the latest eligibility criteria and credit amounts. Keeping up with these changes can help you maximize your EITC benefits each tax season.
Impact of the Earned Income Tax Credit
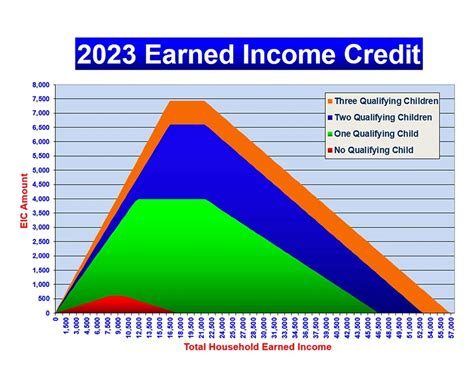
The Earned Income Tax Credit has had a profound impact on the lives of millions of Americans. Beyond providing a financial boost to eligible taxpayers, the EITC has broader societal implications. It serves as a powerful tool for reducing poverty, encouraging employment, and improving the overall financial stability of working families.
Reducing Poverty
The EITC has been instrumental in lifting millions of Americans out of poverty. A study by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities found that the EITC lifted 5.5 million people, including 3 million children, out of poverty in 2020 alone. This credit provides a critical source of income for low-income families, helping them meet their basic needs and improve their living conditions.
Encouraging Employment
The EITC acts as an incentive for individuals to enter and remain in the workforce. By providing a financial reward for work, the EITC encourages individuals to seek employment rather than relying solely on government assistance. This not only benefits the individual but also contributes to a stronger economy and a more productive workforce.
Improving Financial Stability
For many eligible taxpayers, the EITC provides a much-needed cushion against financial hardships. It can help families pay for essential expenses, such as housing, healthcare, and education. The credit also allows families to save for the future, whether it’s for emergency funds, retirement, or educational expenses for their children. This improved financial stability can lead to better long-term outcomes and increased economic mobility.
Strengthening Communities
The positive impact of the EITC extends beyond individual households. As more families become financially stable, communities as a whole benefit. With improved financial stability, families are more likely to invest in their local communities, supporting local businesses and contributing to the overall economic growth of the area. Additionally, children from families receiving the EITC are more likely to succeed academically and have better long-term outcomes, leading to a more skilled and productive future workforce.
Future Implications and Policy Considerations
The Earned Income Tax Credit has proven to be a successful policy tool for reducing poverty and encouraging employment. As such, it continues to be a focus of discussion and potential reform in tax policy. Here are some key future implications and considerations surrounding the EITC.
Expanding Eligibility
One potential direction for the EITC is to expand eligibility criteria to include more taxpayers. Currently, there are discussions about raising the income limits and including more workers without qualifying children. This would ensure that a larger portion of the workforce benefits from the credit, further reducing poverty and encouraging employment.
Increasing Credit Amounts
Increasing the amount of the EITC for eligible taxpayers is another potential avenue for reform. This could provide an even greater financial boost to low-income families, helping them meet their needs and save for the future. However, increasing the credit amount also comes with considerations, such as the potential impact on the federal budget and the complexity of the tax code.
Streamlining the Claim Process
Simplifying the process for claiming the EITC could make it more accessible to eligible taxpayers. This could involve simplifying the forms and instructions, as well as improving the online tools and resources provided by the IRS. Making the claim process more user-friendly would ensure that more eligible taxpayers receive the benefits they deserve.
Addressing Fraud and Misuse
While the EITC is a crucial program, it is not without its challenges. Fraud and misuse of the credit remain concerns, as some taxpayers may intentionally or unintentionally claim ineligible dependents or provide inaccurate information. The IRS has implemented measures to address these issues, but ongoing efforts are needed to ensure the integrity of the program.
What is the maximum EITC amount I can receive in 2023?
+The maximum EITC amount varies based on the number of qualifying children and your filing status. For example, in 2023, the maximum EITC for a taxpayer with three or more qualifying children is 6,935, while a taxpayer with no qualifying children can receive up to 1,125.
Can I still claim the EITC if I didn’t work the entire year?
+Yes, you can still be eligible for the EITC even if you didn’t work the entire year. The credit is based on your earned income for the tax year, so as long as your income exceeds the minimum threshold, you may qualify. However, the amount of EITC you receive may be lower if your income is below the maximum limit.
How can I check the status of my EITC refund?
+You can check the status of your EITC refund by using the IRS’s Where’s My Refund tool on their website. You’ll need your Social Security number, filing status, and the exact amount of your expected refund to track its progress.
Are there any penalties for claiming the EITC incorrectly?
+Yes, there can be penalties for claiming the EITC incorrectly. If you provide false or inaccurate information, you may face fines, interest, or even criminal charges. It’s important to carefully review your tax return and seek professional assistance if needed to avoid any potential issues.
Can I receive the EITC if I’m a non-citizen?
+Yes, certain non-citizens may be eligible for the EITC. To qualify, you must have a valid Social Security number, be a U.S. resident or national, and meet all other eligibility criteria. However, certain non-resident aliens and undocumented immigrants are not eligible for the credit.