Does Utah Have State Income Tax
The state of Utah, nestled in the western United States, operates under a unique tax system that differs significantly from many other states in the country. Understanding Utah's approach to taxation is crucial for both residents and businesses operating within its borders, as it can have a direct impact on financial planning and decision-making.
The Utah Tax System: A Comprehensive Overview
Utah’s tax structure is a nuanced blend of various revenue streams, each designed to fund the state’s operations and public services. While some states rely heavily on income taxes, Utah takes a different path, opting for a more diversified approach to taxation.
Income Tax in Utah: A Notable Absence
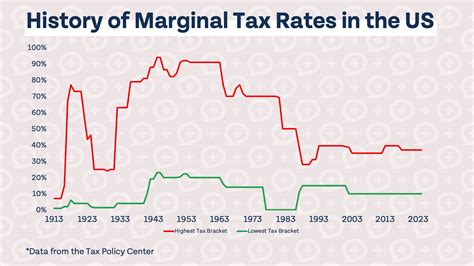
One of the most striking aspects of Utah’s tax system is the absence of a state-level income tax. Unlike many other states, Utah does not levy a tax on individual income, a move that has attracted attention and sparked debates among economists and policymakers alike.
The decision to forego a state income tax has its roots in Utah's history and culture. The state's leaders have long favored a system that promotes economic growth and individual financial freedom, believing that a lack of income tax can attract businesses and create a more competitive business environment.
However, it's important to note that while Utah doesn't impose an income tax, it does collect other forms of taxes to generate revenue. These alternative sources of income form the backbone of Utah's tax system and play a crucial role in funding the state's operations.
Utah’s Revenue Streams: A Diverse Approach
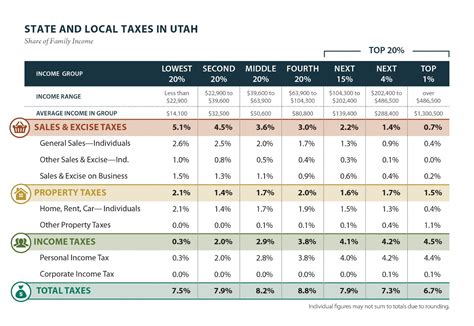
Utah’s tax system is characterized by its diversity, drawing revenue from a range of sources. Here’s a breakdown of the key revenue streams that contribute to the state’s financial stability:
- Sales and Use Tax: Utah imposes a sales tax on the purchase of goods and services, with rates varying depending on the jurisdiction. This tax is a significant contributor to the state's revenue, as it is collected from both residents and visitors alike.
- Property Tax: Property owners in Utah are subject to a property tax, which is based on the assessed value of their real estate. This tax is an essential source of funding for local governments and schools, ensuring the maintenance and improvement of public services.
- Corporate Income Tax: Despite the absence of an individual income tax, Utah does levy a corporate income tax on businesses operating within its borders. This tax contributes to the state's revenue and helps fund essential services and infrastructure.
- Fuel Taxes: Utah collects taxes on gasoline and diesel fuel, with rates varying based on the type of fuel and its usage. These taxes are crucial for funding transportation projects and maintaining the state's road network.
- Tobacco and Alcohol Taxes: Taxes on tobacco products and alcoholic beverages are another significant source of revenue for Utah. These taxes not only generate funds but also serve as a means of discouraging certain behaviors, promoting public health.
- Inheritance and Estate Taxes: Utah also collects taxes on inheritance and estates, ensuring that the transfer of wealth is subject to taxation. This revenue stream helps fund various state programs and services.
The Impact on Residents and Businesses
Utah’s decision to forego a state income tax has both advantages and challenges. For residents, the absence of an income tax can result in significant savings, especially for high-income earners. This, in turn, can attract professionals and businesses to the state, boosting the local economy.
However, the reliance on alternative revenue streams, particularly sales and property taxes, can place a heavier burden on lower-income individuals and families. Additionally, the lack of an income tax can limit the state's ability to generate revenue during economic downturns, potentially impacting public services and infrastructure projects.
Comparative Analysis: Utah vs. Other States
When compared to other states, Utah’s tax system stands out as a unique approach to revenue generation. While many states rely heavily on income taxes, Utah’s diversified strategy has allowed it to maintain a competitive business environment and attract investment.
For instance, neighboring states like Idaho and Nevada also lack a state income tax, creating a regional cluster of low-tax jurisdictions. This can lead to a concentration of economic activity and business growth in these areas, as companies seek to benefit from the reduced tax burden.
However, states like California and New York, which heavily rely on income taxes, offer a contrasting model. These states often have higher tax rates but also provide more extensive public services and infrastructure, creating a trade-off between tax burden and access to resources.
Performance Analysis: Utah’s Economic Outlook
Utah’s economic performance in recent years has been impressive, with steady growth and a thriving business environment. The state’s GDP has consistently outpaced the national average, and unemployment rates have remained relatively low.
| Economic Indicator | Utah | National Average |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | 4.2% (2022) | 2.9% (2022) |
| Unemployment Rate | 2.3% (2023) | 3.5% (2023) |

This economic success can be attributed, in part, to Utah's tax system. The absence of an income tax has made the state an attractive destination for businesses, leading to job creation and economic growth. Additionally, the diversified revenue streams have ensured a stable source of funding for public services and infrastructure development.
Future Implications and Considerations
As Utah continues to thrive economically, the question of its tax system’s sustainability arises. While the current approach has proven successful, future challenges may necessitate a reevaluation of the state’s tax policies.
One potential challenge is the impact of economic downturns. Without a significant source of income tax revenue, Utah may struggle to maintain its financial stability during recessions. This could lead to budget constraints and potential cuts to public services, impacting the state's residents and businesses.
Additionally, as the state's population grows and public service demands increase, the current tax system may need to be adjusted to meet these evolving needs. Finding the right balance between tax burden and public service provision will be crucial for Utah's long-term economic and social development.
In conclusion, Utah's decision to forego a state income tax has had a significant impact on its economic landscape. While it has attracted businesses and fostered growth, it has also created challenges, particularly in terms of funding public services and infrastructure. As the state moves forward, a careful assessment of its tax system's strengths and weaknesses will be essential to ensure continued prosperity and a high quality of life for its residents.
How does Utah’s lack of state income tax affect its revenue generation?
+Utah’s decision to forego a state income tax has led to a diversified revenue stream, with a focus on sales and property taxes. This approach has its advantages, attracting businesses and promoting economic growth, but it can also place a heavier burden on certain segments of the population.
What are the potential challenges of Utah’s tax system during economic downturns?
+During economic downturns, Utah’s reliance on sales and property taxes may limit its ability to generate revenue. This could result in budget constraints and potential cuts to public services, impacting the state’s residents and businesses.
How does Utah’s tax system compare to other states?
+Utah’s tax system is unique compared to many other states. While some states heavily rely on income taxes, Utah’s diversified approach, including the absence of a state income tax, has created a competitive business environment, attracting investment and fostering economic growth.