Does Missouri Tax Social Security

In the state of Missouri, the taxation of Social Security benefits is a topic of interest for many residents, especially retirees and those relying on Social Security income. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Missouri's stance on taxing Social Security benefits, delving into the specific regulations, exemptions, and the potential impact on individuals' financial well-being.
Understanding Missouri’s Social Security Taxation Policy
Missouri, like many other states, has its own set of rules regarding the taxation of Social Security benefits. While the federal government imposes taxes on certain Social Security benefits under specific circumstances, each state can choose whether to tax these benefits or not. Missouri, in particular, has adopted a unique approach to this matter, taking into account the financial needs of its residents and the potential impact on their retirement plans.
The Missouri State Constitution and Social Security Taxation
The taxation of Social Security benefits in Missouri is primarily governed by Article X, Section 6 of the Missouri State Constitution. This section outlines the state’s power to tax various forms of income, including retirement benefits. However, it also provides certain exemptions and limitations to ensure that the state’s taxation policies do not unduly burden its citizens, especially those who rely on Social Security for their livelihood.
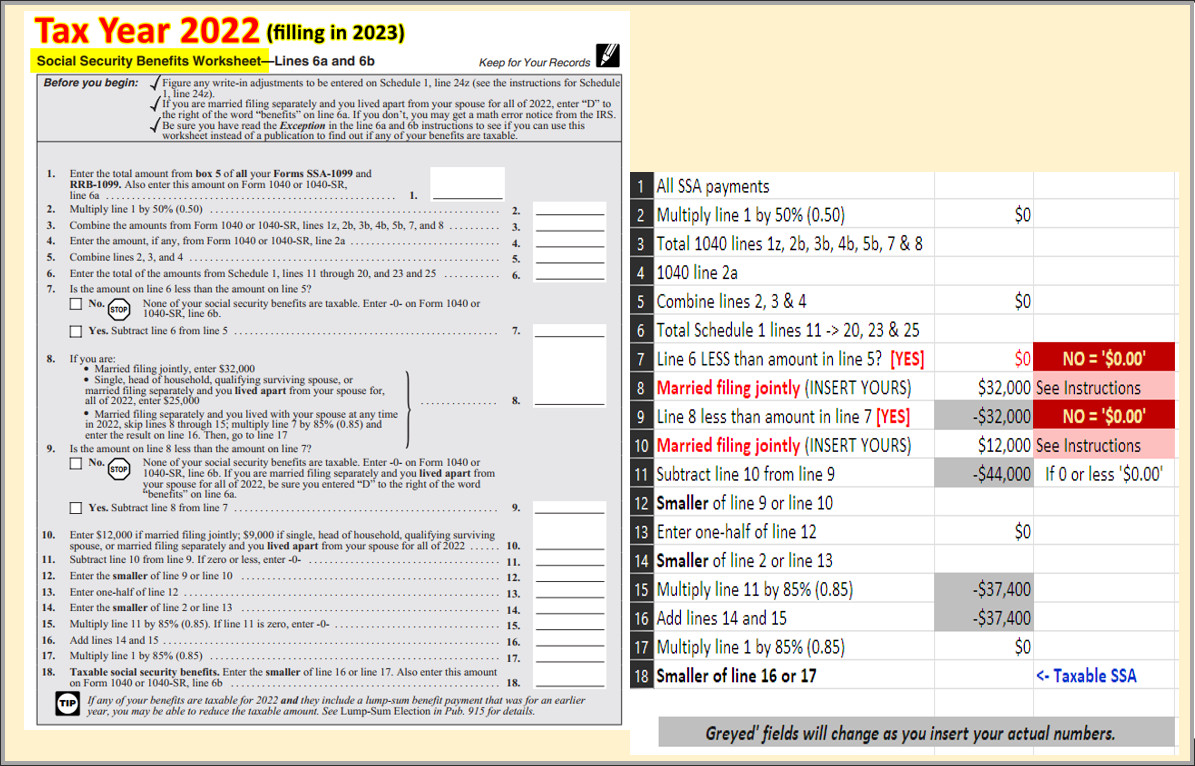
According to the Missouri Department of Revenue, the state follows a tiered approach when it comes to taxing Social Security benefits. This approach considers the taxpayer's income level and the amount of Social Security benefits received. The specific guidelines are as follows:
| Income Level | Taxation on Social Security Benefits |
|---|---|
| Single taxpayers with income under $28,000 | Social Security benefits are not taxable |
| Married taxpayers filing jointly with income under $36,000 | Social Security benefits are not taxable |
| Single taxpayers with income between $28,000 and $34,000 | Up to 50% of Social Security benefits may be taxable |
| Married taxpayers filing jointly with income between $36,000 and $42,000 | Up to 50% of Social Security benefits may be taxable |
| Single taxpayers with income over $34,000 | All Social Security benefits are taxable |
| Married taxpayers filing jointly with income over $42,000 | All Social Security benefits are taxable |

Exemptions and Special Considerations
Missouri recognizes the diverse financial situations of its residents and offers certain exemptions and special considerations when it comes to Social Security taxation. These include:
- Survivor Benefits: Social Security survivor benefits received by a spouse or child are generally not taxable in Missouri.
- Disability Benefits: Social Security disability benefits are also exempt from state taxation, providing financial relief to those with disabilities.
- Railroad Retirement Benefits: Benefits received under the Railroad Retirement Act are treated similarly to Social Security benefits, with the same income-based taxation rules applying.
- Tax Relief for Low-Income Residents: Missouri offers a Low Income Tax Credit to eligible taxpayers with limited income. This credit can offset the tax liability for Social Security benefits, providing additional financial support to those in need.
Impact on Missouri Residents and Retirement Planning

The taxation of Social Security benefits in Missouri can have a significant impact on the financial planning of its residents, particularly those in retirement. Understanding the state’s taxation policies is crucial for retirees to make informed decisions about their income sources and overall financial well-being.
Financial Planning Considerations
For those nearing retirement age or already retired, the state’s taxation of Social Security benefits can influence their overall retirement strategy. It may encourage individuals to explore alternative income sources or retirement accounts that offer tax advantages, such as Roth IRAs or municipal bonds. Additionally, retirees may need to carefully manage their income levels to stay within the exempt thresholds and minimize their tax liability.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
While Missouri’s taxation policies aim to be fair and accommodating, there may be instances where retirees face challenges. For example, a retiree with a modest income but significant Social Security benefits may find themselves in a higher tax bracket due to the inclusion of Social Security income. In such cases, seeking professional financial advice can help retirees navigate these complexities and explore potential solutions, such as adjusting income streams or utilizing tax-efficient investments.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
As with any taxation policy, Missouri’s approach to Social Security taxation may evolve over time. The state government continuously evaluates its tax structure to ensure fairness and economic growth. Retirees and those planning for retirement should stay informed about any potential changes to the state’s taxation policies, as these can significantly impact their financial strategies and overall retirement experience.
Are there any deductions or credits specifically for Social Security beneficiaries in Missouri?
+Yes, Missouri offers a Low Income Tax Credit that can provide tax relief for Social Security beneficiaries with limited income. This credit can help offset the tax liability for those whose Social Security benefits are taxable.
How often are the income thresholds for Social Security taxation adjusted in Missouri?
+The income thresholds are typically adjusted annually to account for inflation and cost-of-living changes. The Missouri Department of Revenue announces these adjustments each year, providing taxpayers with updated guidelines.
Are there any efforts to completely eliminate the taxation of Social Security benefits in Missouri?
+While there have been discussions and proposals to eliminate the taxation of Social Security benefits, there has not been a consensus among state policymakers. The current taxation policy is considered a balance between providing financial support to retirees and maintaining a sustainable tax structure for the state.