Do Puerto Ricans Pay Taxes To Us

The tax system in Puerto Rico is a unique and often misunderstood aspect of its relationship with the United States. Puerto Rico's status as a U.S. territory has led to a complex tax structure that is distinct from that of the 50 states. Understanding how Puerto Ricans pay taxes is crucial to grasping the economic dynamics of the island and its relationship with the U.S. mainland.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Puerto Rico's tax system, exploring the various taxes Puerto Ricans pay, the reasons behind these taxes, and how they differ from taxes in the U.S. states. We will also examine the economic implications of this system and its potential impact on Puerto Rico's development and future.
The Unique Tax Structure of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico’s tax system is governed by a combination of local laws and regulations, as well as certain federal laws that apply specifically to the island. This hybrid system has evolved over time, shaped by Puerto Rico’s political status and its relationship with the U.S. government.
Federal Taxes
One of the most notable aspects of Puerto Rico’s tax system is that Puerto Ricans are generally exempt from federal income taxes. This exemption is a result of the Puerto Rican federal relations act, which provides that individuals who are residents of Puerto Rico are not subject to federal income taxes on income sourced from Puerto Rico.
However, there are some exceptions to this rule. Puerto Ricans who work for the U.S. government or certain U.S. corporations in Puerto Rico may still be subject to federal income taxes on their earnings. Additionally, Puerto Ricans who derive income from sources outside of Puerto Rico, such as investments or business interests in the U.S. mainland, may also be liable for federal taxes on that income.
Local Taxes
While Puerto Ricans are largely exempt from federal income taxes, they are subject to a range of local taxes imposed by the government of Puerto Rico. These taxes play a crucial role in funding public services and infrastructure on the island.
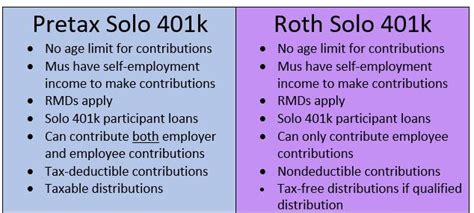
One of the primary sources of revenue for the Puerto Rican government is the sales and use tax (known as Impuesto sobre Ventas y Uso or IVU in Spanish). This tax is applied to most goods and services purchased within Puerto Rico, similar to the sales tax in U.S. states. The rate of the IVU varies depending on the type of product or service, with essential items often having a lower tax rate.
| Tax Category | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| General Sales Tax | 11.5% |
| Prepared Food and Beverage | 7% |
| Non-Prepared Food | 7% |
| Essential Services | 0% |

In addition to the sales tax, Puerto Rico also imposes various other taxes, including a property tax, excise taxes on specific goods like alcohol and tobacco, and corporate taxes on businesses operating in Puerto Rico.
The Internal Revenue Service of Puerto Rico (Hacienda)
The collection and administration of local taxes in Puerto Rico is the responsibility of the Internal Revenue Service of Puerto Rico, commonly known as Hacienda. This agency, akin to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS), ensures that individuals and businesses comply with Puerto Rico’s tax laws and regulations.
Hacienda plays a crucial role in the island's economy, as the revenue it collects is vital for funding public services, infrastructure projects, and social programs. The agency's effectiveness in tax collection and administration is a key factor in Puerto Rico's fiscal health and its ability to provide essential services to its residents.
The Economic Impact of Puerto Rico’s Tax System
Puerto Rico’s unique tax structure has significant economic implications for the island and its residents. On the one hand, the exemption from federal income taxes can make Puerto Rico an attractive location for businesses and individuals seeking tax advantages. This has led to the establishment of various industries, such as manufacturing and finance, which contribute to the island’s economy.
However, the reliance on local taxes, particularly the sales tax, can place a heavy burden on Puerto Rican residents, especially those with lower incomes. The high sales tax rate can make essential goods and services more expensive, potentially impacting the standard of living for many Puerto Ricans. Additionally, the limited revenue base, largely dependent on consumption taxes, can make it challenging for the government to provide adequate funding for public services and infrastructure development.
Challenges and Opportunities
The economic challenges posed by Puerto Rico’s tax system are further exacerbated by the island’s ongoing financial crisis and its complex relationship with the U.S. government. The limited revenue streams and the exemption from federal income taxes have contributed to Puerto Rico’s debt crisis, as the government has struggled to balance its budget and meet its financial obligations.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for economic growth and development. The island's strategic location, its skilled workforce, and its unique tax advantages can attract investment and foster the growth of new industries. Furthermore, efforts to diversify the economy, such as promoting tourism, renewable energy, and technology sectors, can help reduce Puerto Rico's reliance on a few key industries and create a more resilient economic landscape.
The Future of Puerto Rico’s Tax System
As Puerto Rico navigates its economic challenges and works towards a more stable and prosperous future, its tax system will likely undergo changes and reforms. The island’s leaders and policymakers are engaged in ongoing discussions and negotiations with the U.S. government to address the fiscal crisis and find sustainable solutions.
One potential avenue for reform is the exploration of new revenue streams, such as the introduction of a value-added tax (VAT) or the expansion of the tax base to include more sources of income. Additionally, efforts to enhance tax collection and compliance, as well as combat tax evasion, can help ensure that the revenue generated from taxes is maximized and allocated effectively.
Furthermore, there is a growing recognition of the need to address the impact of taxes on Puerto Rico's residents, particularly those from lower-income brackets. Proposals to introduce tax credits, incentives, or other forms of relief could help alleviate the burden of taxes on everyday Puerto Ricans, promoting economic equality and social welfare.
Conclusion: A Complex, Yet Crucial, System
In conclusion, the tax system in Puerto Rico is a complex and multifaceted structure that plays a critical role in the island’s economy and its relationship with the United States. While it presents both challenges and opportunities, a deep understanding of this system is essential for comprehending Puerto Rico’s economic dynamics and its potential for growth and development.
As Puerto Rico continues to navigate its fiscal challenges and work towards a brighter future, the evolution of its tax system will be a key factor in shaping the island's economic landscape. By striking a balance between attracting investment, promoting economic growth, and ensuring social welfare, Puerto Rico can forge a path towards a more prosperous and equitable future for its residents.
Why are Puerto Ricans exempt from federal income taxes?
+
Puerto Ricans are exempt from federal income taxes due to the Puerto Rican federal relations act, which provides that residents of Puerto Rico are not subject to federal income taxes on income sourced from Puerto Rico. This exemption is a result of Puerto Rico’s unique political status as a U.S. territory.
What are the main sources of revenue for the Puerto Rican government?
+
The main sources of revenue for the Puerto Rican government include the sales and use tax (IVU), property taxes, excise taxes on goods like alcohol and tobacco, and corporate taxes on businesses operating in Puerto Rico. These taxes fund public services, infrastructure, and social programs.
How does the tax system in Puerto Rico impact its economic development?
+
The tax system in Puerto Rico has both positive and negative impacts on its economic development. While the exemption from federal income taxes can attract investment and promote certain industries, the reliance on local taxes, particularly the sales tax, can place a burden on residents and limit the government’s revenue streams, impacting its ability to fund public services and infrastructure projects.