Define Ad Valorem Taxes

Ad Valorem Taxes, often simply referred to as "ad valorem," are a fundamental component of the global tax system, playing a pivotal role in generating revenue for governments while also influencing economic behavior. These taxes are deeply rooted in history, dating back to ancient civilizations, and have evolved into a crucial tool for modern governments to finance public services and infrastructure.
At its core, the term "Ad Valorem" originates from Latin, translating to "according to value." This definition encapsulates the essence of these taxes, which are levied based on the value or worth of a property, asset, or transaction. Ad Valorem Taxes are a flexible and widely applicable form of taxation, making them a cornerstone of many jurisdictions' revenue strategies.
Understanding Ad Valorem Taxes

Ad Valorem Taxes encompass a broad range of tax types, each designed to capture value in different economic scenarios. Here's a closer look at some key categories:
Property Taxes
One of the most common forms of Ad Valorem Taxes is property tax. This tax is assessed on the value of real estate, including land, buildings, and improvements. Property taxes are a significant revenue source for local governments, funding vital services like education, emergency response, and infrastructure maintenance.
| Property Type | Average Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Residential | 1-2% |
| Commercial | 1.5-3% |
| Industrial | 2-4% |

Sales and Use Taxes
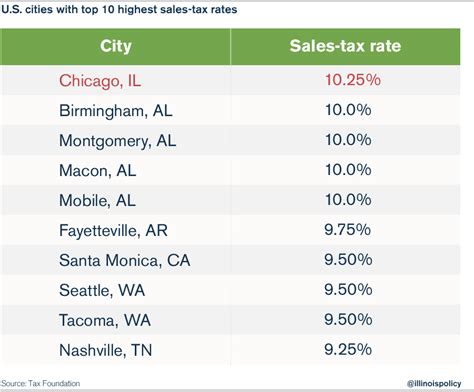
Sales and Use Taxes are levied on the sale or use of goods and services. These taxes are a significant source of revenue for state and local governments, especially in regions with thriving retail sectors. Sales taxes are typically added to the purchase price, making them a transparent and easily collectible tax.
On the other hand, Use Taxes are imposed when a taxable item is used, stored, or consumed within a jurisdiction without the corresponding sales tax being paid. This tax ensures fairness and prevents tax evasion.
| State | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| California | 7.25% |
| Texas | 6.25% |
| New York | 4% |
Capital Gains Taxes
Capital Gains Taxes are a form of Ad Valorem Tax applied to the profits made from the sale of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or businesses. These taxes are crucial in regulating wealth accumulation and providing revenue for governments.
The tax rate for capital gains can vary depending on factors like the type of asset, the holding period, and the taxpayer's income bracket. Long-term capital gains, where assets are held for over a year, often enjoy preferential tax rates compared to short-term gains.
| Asset Type | Capital Gains Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Stocks | 0-20% |
| Real Estate | 15-25% |
| Business Assets | 21% |
Estate and Inheritance Taxes
Estate and Inheritance Taxes are levied on the transfer of wealth, typically upon an individual’s death. These taxes ensure that significant wealth transfers are taxed, contributing to government revenue and addressing wealth inequality.
Estate Taxes are assessed on the total value of an individual's estate, while Inheritance Taxes are levied on the value of specific gifts or inheritances received by beneficiaries.
| Jurisdiction | Estate/Inheritance Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| United States | Up to 40% |
| United Kingdom | Up to 40% |
| Canada | 1.92-13.85% |
The Impact and Considerations of Ad Valorem Taxes

Ad Valorem Taxes have far-reaching implications, influencing not just government revenue but also economic decisions and market behavior. Here's a deeper look at their impact and considerations:
Revenue Generation
Ad Valorem Taxes are a primary source of revenue for governments at all levels. This revenue is crucial for funding public services, infrastructure development, and social welfare programs. For instance, property taxes fund local schools, while sales taxes contribute to state road networks.
Economic Efficiency
These taxes can incentivize or deter certain economic behaviors. For example, high property taxes can discourage property speculation, while sales taxes can influence consumer spending patterns. Governments often use these taxes strategically to promote economic efficiency and fairness.
Equity and Fairness
Ad Valorem Taxes are designed to be fair and equitable, taxing individuals or entities based on their ability to pay. For instance, progressive capital gains tax rates ensure that those with higher incomes pay a larger share. However, the complexity of these taxes can sometimes lead to debates about tax fairness.
Compliance and Administration
Ensuring compliance and effectively administering Ad Valorem Taxes is a significant challenge. Governments must invest in robust tax collection systems and enforcement mechanisms to ensure fair taxation. This includes regular property assessments, sales tax audits, and capital gains reporting requirements.
International Considerations
In an increasingly globalized economy, Ad Valorem Taxes can have cross-border implications. This is particularly true for capital gains and estate taxes, where the movement of assets and wealth across borders can trigger tax liabilities. International tax treaties often address these complexities to avoid double taxation.
Conclusion: Navigating the Ad Valorem Tax Landscape
Ad Valorem Taxes are a multifaceted aspect of the global tax system, offering governments a flexible tool to generate revenue and influence economic behavior. From property taxes to capital gains, these taxes shape the financial landscape, impacting individuals, businesses, and the overall economy.
Understanding Ad Valorem Taxes is crucial for anyone navigating the financial world, whether as a taxpayer, investor, or policy maker. By comprehending these taxes and their implications, individuals can make informed decisions, plan their finances strategically, and contribute effectively to the broader economic ecosystem.
What is the difference between Ad Valorem Taxes and other types of taxes?
+Ad Valorem Taxes differ from other taxes like specific or excise taxes, which are levied based on quantity or type, rather than value. Ad Valorem Taxes are more flexible and adaptable, making them a preferred choice for governments to tax a wide range of assets and transactions.
How are Ad Valorem Taxes calculated for real estate properties?
+Property taxes are calculated by multiplying the assessed value of the property by the applicable tax rate. The assessed value is typically determined by a professional appraiser or a set formula, considering factors like location, size, and improvements.
Are there any strategies to minimize Ad Valorem Tax liabilities?
+Yes, there are legal strategies to minimize tax liabilities, such as taking advantage of deductions, credits, and exemptions. For instance, homeowners can deduct property taxes from their federal income taxes in the United States, reducing their overall tax burden.