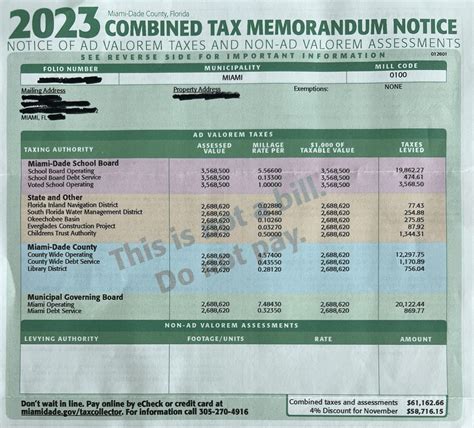
Ct State Sales Tax Rate
The state of Connecticut, often referred to as the "Constitution State," boasts a rich history and a vibrant economy. When it comes to sales tax, Connecticut has a robust system in place to generate revenue for various state initiatives and services. Let's delve into the intricacies of the Connecticut state sales tax rate, its application, and its impact on businesses and consumers alike.
Understanding the Connecticut Sales Tax Rate

Connecticut imposes a state sales and use tax on the retail sale, rental, and lease of most goods, as well as some services. The primary purpose of this tax is to generate funds for essential state services, such as education, infrastructure development, and public safety initiatives.
As of [date of update], the Connecticut state sales tax rate stands at 6.35%, which is applied uniformly across the state. This rate is mandated by the Connecticut Department of Revenue Services (CT DRS) and is subject to periodic reviews and adjustments to align with the state's fiscal needs.
Exemptions and Special Considerations
While the Connecticut sales tax applies to a wide range of goods and services, there are certain exemptions and special provisions in place to accommodate specific industries and scenarios. Here’s an overview of some key exemptions:
- Groceries and Food: Certain food items, including unprepared groceries, are exempt from the sales tax, providing some relief to households' grocery budgets.
- Prescription Drugs: Sales of prescription medications are tax-exempt, ensuring that essential healthcare items are more affordable for residents.
- Manufacturing: The state offers a Manufacturing Sales and Use Tax Exemption for manufacturers to promote economic growth and encourage investment in the state's manufacturing sector.
- Resale and Inventory: Businesses engaged in wholesale or resale operations can claim exemptions for inventory purchases, allowing them to avoid double taxation.
These exemptions, along with others, help streamline the tax system and provide targeted support to specific industries and consumer groups.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance

The responsibility of collecting and remitting sales tax falls on the shoulders of businesses, whether they are brick-and-mortar stores, online retailers, or service providers. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Registration and Compliance
Any business engaging in taxable sales or providing taxable services within Connecticut must obtain a Connecticut Seller’s Permit from the CT DRS. This permit authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state.
To ensure compliance, businesses are required to:
- Display the sales tax rate clearly at the point of sale.
- Include the sales tax in the total price of goods or services.
- Provide detailed sales tax records and reports to the CT DRS on a regular basis.
- Remit the collected sales tax to the state within specified deadlines.
Remote Sellers and Marketplace Facilitators
In today’s digital age, online sales have become increasingly prevalent. Connecticut’s sales tax laws apply to remote sellers and marketplace facilitators who sell goods or services to Connecticut residents. These entities are required to register with the CT DRS, collect sales tax, and remit it accordingly.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The Connecticut sales tax rate has a direct impact on both businesses and consumers. Let’s explore how it influences their decisions and operations.
Businesses
For businesses, the sales tax rate is a crucial factor in their pricing strategies and overall profitability. Here’s how it affects them:
- Pricing: Businesses must carefully consider the impact of the sales tax on their pricing models. They need to ensure that their prices are competitive while still allowing for a reasonable profit margin after accounting for the tax.
- Compliance Costs: The administrative burden of collecting and remitting sales tax can be significant. Businesses must invest in accounting systems and personnel to ensure accurate tax collection and reporting.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses may explore ways to offer tax-free transactions or provide discounts to customers to stay competitive in the market.
Consumers
Consumers, on the other hand, are directly impacted by the sales tax rate at the time of purchase. Here’s how it influences their spending habits:
- Budgeting: The sales tax adds to the final cost of goods and services, impacting consumers' purchasing power and budgeting decisions.
- Comparison Shopping: Consumers may engage in comparison shopping across different retailers or online platforms to find the best prices, taking the sales tax into account.
- Tax-Free Periods: Connecticut sometimes offers tax-free periods for specific items, such as back-to-school supplies, which can encourage consumers to make larger purchases during those times.
| Sales Tax Rate | 6.35% |
|---|---|
| Effective Date | [date of update] |
| Primary Purpose | Generate revenue for state services |
| Exemptions | Groceries, prescription drugs, manufacturing, and resale |

Are there any local sales tax rates in Connecticut?
+Yes, in addition to the state sales tax, there are local sales tax rates in certain municipalities. These rates vary and are applied on top of the state sales tax. For instance, the city of Hartford has a local sales tax rate of 1.5%, bringing the total sales tax to 7.85% within that jurisdiction.
How often is the Connecticut sales tax rate reviewed and adjusted?
+The Connecticut sales tax rate is typically reviewed annually by the Connecticut Department of Revenue Services. Adjustments are made based on the state’s fiscal needs and economic conditions. However, in some cases, special legislation may be passed to temporarily adjust the rate for specific purposes.
What happens if a business fails to collect and remit sales tax correctly?
+Businesses that fail to comply with sales tax regulations can face severe penalties. These may include fines, interest on overdue taxes, and even revocation of their Connecticut Seller’s Permit. It is crucial for businesses to understand their obligations and seek professional guidance if needed.