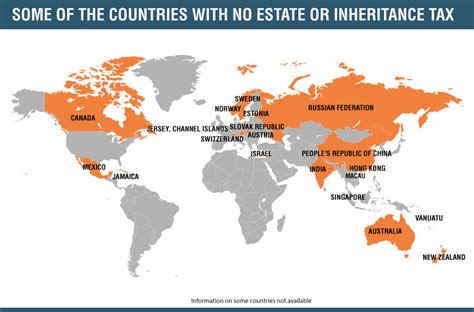
Countries Without Income Tax
Income tax is a fundamental component of many nations' fiscal policies, providing governments with a significant source of revenue to fund public services, infrastructure, and social programs. However, there are a few countries that have either abolished income tax altogether or have implemented unique systems that effectively minimize its impact on their citizens.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intriguing world of nations that operate without income tax, examining the reasons behind these policies, their potential advantages, and the broader implications for economic development and social welfare.
A Global Perspective on Income Tax

Income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses, typically calculated as a percentage of taxable income. It is a cornerstone of modern taxation systems, with many countries relying on it as a primary source of revenue. However, the rates and structures of income tax vary widely across the globe, with some countries opting for progressive tax rates that increase with income and others implementing flat tax rates.
The concept of income tax has a long history, dating back to ancient civilizations. However, its modern implementation and widespread adoption are relatively recent phenomena. In the 19th and 20th centuries, income tax became a critical tool for governments to finance industrial development, wars, and social welfare programs.
The Rise of Tax-Free Jurisdictions

Amidst the global landscape of income taxation, a handful of nations have carved out unique paths. These countries, often referred to as “tax havens” or “tax-free jurisdictions,” have implemented policies that either eliminate income tax entirely or dramatically reduce its impact on citizens and businesses.
Bermuda: A Pioneer in Tax-Free Living
Bermuda is renowned for its stunning beaches and picturesque scenery, but it also holds the distinction of being one of the oldest and most well-known tax-free jurisdictions in the world. The island nation has a long-standing policy of not imposing personal income tax on its residents.
Bermuda's tax system is centered around corporate taxes, which account for a significant portion of its revenue. The country's economy is largely driven by the financial services sector, which thrives in an environment free from income tax. This has attracted numerous international businesses, contributing to a robust economy.
| Economic Sector | Contribution to GDP |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | 33% |
| Tourism | 20% |
| International Business | 15% |

Bahamas: Sun, Sea, and Tax-Free Living
Like its neighboring island, the Bahamas also operates without personal income tax. This Caribbean nation has a diverse economy, with significant contributions from tourism, financial services, and international trade.
The absence of income tax in the Bahamas has fostered an environment conducive to business growth and investment. It has become a popular choice for individuals seeking a tax-efficient lifestyle and for companies looking to establish a presence in a stable, tax-free jurisdiction.
Monaco: A Haven for the Wealthy
Monaco, a small city-state nestled on the French Riviera, is renowned for its luxurious lifestyle and absence of income tax. This unique tax system has made Monaco an attractive destination for high-net-worth individuals and celebrities.
While Monaco does not levy income tax on its residents, it generates revenue through other means, including taxes on companies and value-added tax (VAT). The country's economy is heavily reliant on its financial services sector and tourism, with its glamorous reputation drawing visitors from around the world.
United Arab Emirates: A Diverse Tax-Free Economy
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a federation of seven emirates, each with its own unique characteristics. Interestingly, the UAE does not impose personal income tax on its citizens or expatriates. This policy has contributed to the country’s rapid economic growth and development.
The UAE's economy is diverse, with significant contributions from sectors such as oil and gas, tourism, finance, and trade. The absence of income tax has made it an appealing destination for businesses and investors, further fueling its economic success.
Saudi Arabia: Moving Towards Tax Reform
Historically, Saudi Arabia did not levy income tax on its citizens. However, in recent years, the country has undergone significant economic reforms as part of its Vision 2030 initiative. As part of these reforms, Saudi Arabia introduced a corporate income tax and a value-added tax (VAT) to diversify its revenue streams and reduce its reliance on oil revenues.
While personal income tax remains absent for Saudi nationals, these reforms signal a shift towards a more comprehensive tax system, aiming to sustain the country's economic growth and development.
The Impact and Implications of Income Tax-Free Policies
The decision to operate without income tax has profound implications for both the countries themselves and the global economic landscape.
Economic Growth and Development
Nations that eliminate or reduce income tax often experience significant economic growth. The absence of income tax can attract businesses and investors, leading to increased economic activity, job creation, and a thriving business environment. This, in turn, can enhance the overall standard of living and contribute to a country’s long-term economic sustainability.
Tax Competition and Global Economics
The existence of tax-free jurisdictions can spark a form of “tax competition” on the global stage. Countries may lower their tax rates or offer tax incentives to attract businesses and investors, leading to a complex web of international tax policies. This competition can have both positive and negative effects, influencing the flow of capital, talent, and economic activity across borders.
Social Welfare and Public Services
Income tax is often a crucial source of funding for public services, social programs, and infrastructure development. In countries without income tax, alternative revenue streams must be identified to support these essential services. This can include taxes on consumption, property, or specific industries, as well as foreign aid and investment.
Tax Avoidance and Transparency
Tax-free jurisdictions have sometimes been associated with tax avoidance and a lack of transparency. While many of these countries have made significant strides in enhancing their regulatory frameworks and cooperating with international tax authorities, concerns about tax evasion and money laundering persist.
Future Prospects and Considerations
The landscape of global taxation is continually evolving, and the future of tax-free jurisdictions remains a subject of debate and discussion.
Sustainable Revenue Models
As the world increasingly focuses on sustainable development and responsible economic practices, countries without income tax will need to adapt their revenue models. This may involve exploring new sources of revenue, such as green taxes or digital services taxes, to ensure long-term financial sustainability.
International Cooperation and Transparency
In an era of increasing globalization, international cooperation and transparency in tax matters are becoming increasingly important. Tax-free jurisdictions will need to engage constructively with global initiatives aimed at curbing tax evasion and promoting fair taxation practices.
Social Welfare and Equity
The absence of income tax can raise questions about social welfare and equity. Countries will need to carefully consider how to provide essential public services and support vulnerable populations without relying on income tax as a primary revenue source.
Digital Economy and Tax Challenges
The rise of the digital economy presents unique challenges for tax systems. As more economic activities move online, countries will need to adapt their tax policies to ensure they can effectively tax digital businesses and services, regardless of their physical location.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Taxation

The existence of countries without income tax underscores the complexity and diversity of global taxation systems. While these nations have carved out unique paths, they must navigate a delicate balance between economic growth, social welfare, and international cooperation.
As the world continues to evolve, the role and impact of income tax will remain a subject of scrutiny and debate. The choices made by these tax-free jurisdictions will undoubtedly shape the future of global taxation and economic development.
How do tax-free countries generate revenue without income tax?
+Tax-free countries generate revenue through a variety of means, including corporate taxes, value-added tax (VAT), property taxes, and taxes on specific industries or services. Additionally, some countries rely on foreign aid, investment, and tourism revenue to support their economies.
Are there any drawbacks to living in a tax-free country?
+While tax-free countries offer certain advantages, they may also have higher costs of living and limited access to public services. Additionally, the absence of income tax can impact social welfare programs and may require alternative funding sources.
What are the potential risks associated with tax-free jurisdictions?
+Tax-free jurisdictions can be associated with tax evasion and money laundering risks. However, many of these countries have implemented regulatory reforms and cooperate with international tax authorities to enhance transparency and combat illicit activities.