Colorado State Income Tax Rate
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Colorado State Income Tax, where we delve into the specifics of this essential aspect of the state's tax system. Understanding income tax rates is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within Colorado, as it directly impacts their financial planning and compliance with state regulations. Let's explore the intricacies of the Colorado State Income Tax Rate and its implications.
Colorado State Income Tax: An Overview

The Colorado Department of Revenue is responsible for administering the state’s income tax laws, ensuring compliance, and providing guidance to taxpayers. The state’s income tax system is designed to generate revenue for various public services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and more.
Colorado's income tax is a progressive tax, meaning that as your income increases, so does the tax rate applied to your earnings. This structure aims to ensure that higher-income earners contribute a larger share of their income to the state's revenue. The progressive nature of the tax system also helps promote economic equality and provides essential funding for vital state services.
Income Tax Rates in Colorado

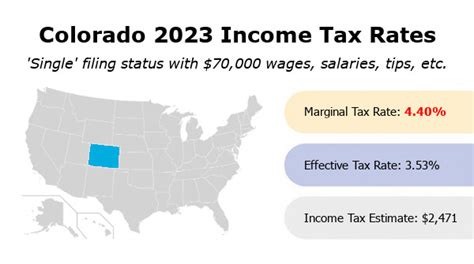
Colorado has a relatively straightforward income tax rate structure, with a flat tax rate applied to most types of income. As of my last update in January 2023, the state income tax rate in Colorado is 4.55%, which applies to most taxable income sources.
Here's a breakdown of the key income tax rates in Colorado:
| Income Tax Category | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| State Income Tax | 4.55% |
| Personal Income Tax (PIT) | 4.55% |
| Corporate Income Tax | 4.55% (for C-corporations) |

It's important to note that while the state income tax rate is consistent across most income types, there are certain exceptions and additional considerations. For instance, pass-through entities like partnerships and S-corporations are subject to the Colorado Limited Liability Entity Tax, which has a different rate structure.
Colorado Limited Liability Entity Tax
The Colorado Limited Liability Entity Tax, often referred to as the LLC tax, applies to pass-through entities such as partnerships, limited liability companies (LLCs), S-corporations, and trusts. These entities are taxed at a rate of 4.4% on their taxable income.
Here's a quick comparison between the state income tax rate and the LLC tax rate in Colorado:
| Entity Type | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| C-Corporations | 4.55% |
| Pass-through Entities (LLCs, Partnerships, S-Corps) | 4.4% |
The LLC tax is a crucial consideration for business owners choosing the structure of their enterprises in Colorado. While the state income tax rate is the same for most income types, understanding the LLC tax rate can help business owners make informed decisions about their tax obligations and strategies.
Income Tax Brackets in Colorado
While Colorado has a flat income tax rate for most income types, it’s important to understand the concept of tax brackets. Tax brackets refer to the income ranges at which different tax rates are applied. Colorado’s tax brackets are based on federal adjusted gross income (AGI) and are updated annually to account for inflation.
For the 2023 tax year, Colorado's income tax brackets are as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Single Filers | Married Filing Jointly |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $0 - $5,950 | $0 - $11,900 |
| 2 | $5,951 - $11,900 | $11,901 - $23,800 |
| 3 | $11,901 - $17,850 | $23,801 - $35,750 |
| 4 | $17,851 - $35,750 | $35,751 - $71,500 |
| 5 | $35,751 - $71,500 | $71,501 - $143,000 |
| 6 | $71,501 - $143,000 | $143,001 - $286,000 |
| 7 | $143,001 and above | $286,001 and above |
It's worth noting that the tax brackets are designed to ensure that individuals and families with lower incomes pay a smaller percentage of their income in taxes, while higher-income earners contribute a larger share. This progressive tax structure is a key component of Colorado's income tax system.
Colorado Tax Credits and Deductions
Colorado offers a range of tax credits and deductions to help reduce the tax burden for individuals and businesses. These incentives can provide significant savings and are an essential part of the state’s tax system. Some of the key tax credits and deductions in Colorado include:
- Federal Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): Colorado allows residents to claim the federal EITC, which provides a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income working individuals and families.
- Senior Citizen Property Tax Exemption: This credit exempts a portion of the assessed value of a primary residence from property taxes for qualified seniors.
- Sales Tax Holiday: Colorado occasionally holds sales tax holidays, during which certain purchases are exempt from sales tax, providing a temporary tax relief for consumers.
- Business Tax Incentives: Colorado offers various tax incentives for businesses, including tax credits for job creation, research and development, and more. These incentives aim to encourage economic growth and investment.
Exploring these tax credits and deductions can be a valuable strategy for individuals and businesses looking to optimize their tax obligations and take advantage of the benefits offered by the state.
Income Tax Filing and Payment in Colorado
Colorado taxpayers have various options for filing their state income tax returns and making payments. The Colorado Department of Revenue provides resources and guidance to ensure a smooth filing process.
Online Filing and Payment
The Colorado Department of Revenue offers an online filing system, Colorado eFile, which allows taxpayers to file their state income tax returns electronically. This system is secure, efficient, and provides a convenient way to manage tax obligations. Additionally, taxpayers can make online payments through the Colorado eFile system, ensuring a seamless and timely payment process.
Paper Filing and Payment
For those who prefer traditional methods, Colorado also accepts paper tax returns. Taxpayers can download and print the necessary forms from the Colorado Department of Revenue’s website or request a paper copy by mail. Payment options for paper filers include checks, money orders, and electronic funds transfer (EFT) payments.
It's important to note that while paper filing is an option, online filing offers several advantages, including faster processing times, reduced errors, and the ability to track the status of your return online.
Tax Payment Plans
Colorado understands that taxpayers may face financial challenges, and it offers tax payment plans to assist individuals and businesses in managing their tax obligations. These plans allow taxpayers to pay their taxes over time, reducing the financial burden of a lump-sum payment. To be eligible for a payment plan, taxpayers must meet certain criteria and agree to specific terms and conditions.
The Colorado Department of Revenue provides detailed information on its website about the tax payment plan options, including the application process, fees, and requirements. It's crucial to explore these options if you're facing financial difficulties and need a more flexible approach to meeting your tax obligations.
Future Implications and Considerations
As we look to the future, it’s essential to consider the potential changes and developments in Colorado’s income tax system. While the state’s tax rates and brackets are relatively stable, various factors can influence future tax policies.
Economic Conditions and Tax Revenue
Colorado’s tax revenue is closely tied to the state’s economic performance. During periods of economic growth, the state may experience increased tax revenue, allowing for potential tax rate adjustments or the expansion of tax credits and deductions. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to budget constraints and the need for tax policy adjustments to maintain fiscal stability.
Political and Legislative Changes
Political dynamics and legislative decisions can significantly impact the state’s tax system. Changes in leadership or shifts in political priorities can lead to tax reform, the introduction of new tax incentives, or adjustments to existing tax rates and brackets. Staying informed about political developments and proposed tax legislation is crucial for taxpayers and businesses operating in Colorado.
Population Growth and Demographic Shifts
Colorado’s population growth and demographic shifts can influence the state’s tax base and revenue needs. As the state’s population increases, particularly in urban areas, the demand for public services and infrastructure development may rise, potentially impacting tax policies and rates.
Additionally, demographic changes, such as an aging population or shifts in income distribution, can affect the state's tax structure and the distribution of tax burdens. Understanding these demographic trends is essential for predicting future tax policy directions.
Conclusion
Colorado’s state income tax system is a critical component of the state’s financial landscape, impacting individuals, businesses, and the overall economic health of the region. By understanding the state’s income tax rates, brackets, and the various tax credits and deductions available, taxpayers can make informed decisions and effectively manage their tax obligations.
Staying informed about tax policy changes, economic developments, and legislative proposals is essential for navigating the state's tax system successfully. As Colorado continues to evolve and adapt to changing circumstances, taxpayers and businesses can leverage this knowledge to optimize their financial strategies and contribute to the state's economic prosperity.
How often are Colorado’s income tax rates updated, and when is the next update expected?
+
Colorado’s income tax rates are typically updated annually to account for inflation and other economic factors. The next update is expected to be announced in the fall of 2023, with the new rates taking effect for the 2024 tax year.
Are there any plans to change the state income tax rate in the near future?
+
As of my knowledge cutoff in January 2023, there were no announced plans to change the state income tax rate. However, it’s important to stay updated on legislative developments, as tax policy proposals can emerge at any time.
How does Colorado’s state income tax rate compare to other states in the region?
+
Colorado’s state income tax rate of 4.55% is relatively competitive compared to neighboring states. For example, Wyoming has no state income tax, while Utah has a flat rate of 4.95%. Understanding regional tax rates can be crucial for businesses considering expansion or relocation.
What are the key differences between the state income tax and the LLC tax in Colorado?
+
The key difference is the tax rate applied to different types of entities. The state income tax rate of 4.55% applies to most income types, including C-corporations. However, pass-through entities like LLCs are taxed at a slightly lower rate of 4.4%. This distinction is important for business owners choosing their entity structure.