Tax Id Number Vs Ssn
The world of business and personal finance often involves navigating a complex web of identification numbers and their unique purposes. Among these, the Tax ID Number and the Social Security Number (SSN) stand out as crucial elements in the United States, each serving distinct and vital functions.
Understanding the differences and specific uses of these identification systems is essential for individuals and businesses alike. Let's delve into the intricacies of the Tax ID Number and the SSN, exploring their roles, applications, and the scenarios where one might be more appropriate than the other.
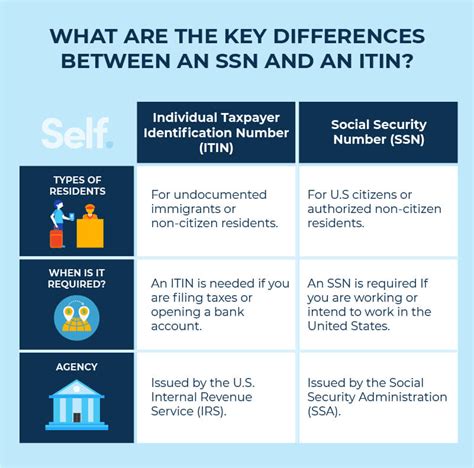
The Social Security Number (SSN): A Personal Identifier

The Social Security Number is a nine-digit numerical identifier issued by the Social Security Administration (SSA) in the United States. Its primary purpose is to track individuals’ earnings and benefits for Social Security purposes. Every U.S. citizen, permanent resident, and eligible non-resident worker receives a unique SSN, which is used for a multitude of purposes beyond social security benefits.
Key Applications of the SSN
The SSN is a cornerstone of personal identification in the U.S. Here are some of its critical applications:
- Tax Reporting: The SSN is used to report earnings to the IRS. Employers use it to identify employees and report wages and taxes.
- Credit Reports: SSNs are key to building and maintaining credit history. Lenders use them to pull credit reports and assess creditworthiness.
- Government Services: Many government agencies, including the SSA, IRS, and state agencies, use SSNs for identification and to provide services.
- Personal Identification: The SSN serves as a unique identifier for individuals, used for various official purposes, including driver’s licenses and state-issued IDs.
Who Should Use an SSN?
SSNs are primarily intended for individuals, especially U.S. citizens and permanent residents. They are integral to personal financial matters, such as tax filing, credit management, and accessing government benefits.
The Tax ID Number: A Business Companion

A Tax ID Number, often referred to as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), is a unique nine-digit identifier assigned by the IRS to businesses operating in the U.S. It serves as a vital tool for tax administration and business identification.
Key Uses of a Tax ID Number
The Tax ID Number plays a pivotal role in various business operations and tax-related processes:
- Tax Administration: The EIN is used to identify a business entity on tax returns, payroll taxes, and other tax-related documents.
- Business Operations: It is crucial for opening business bank accounts, applying for business loans, and establishing credit for the business.
- Employment: Employers use the EIN to report employee wages and taxes. It is also required for hiring employees and issuing W-2 forms.
- Legal and Financial Matters: The Tax ID Number is often necessary for registering a business, obtaining licenses, and engaging in various legal and financial transactions.
When to Choose a Tax ID Number
A Tax ID Number is essential for businesses, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and certain trusts. It is required for businesses with employees, multiple owners, or specific types of entities, such as LLCs.
Comparing the Two: Tax ID Number vs. SSN
While both identification systems are vital, they serve distinct purposes and cater to different needs. Here’s a side-by-side comparison to highlight their differences:
| Attribute | Tax ID Number (EIN) | Social Security Number (SSN) |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Internal Revenue Service (IRS) | Social Security Administration (SSA) |
| Purpose | Tax administration for businesses | Tracking earnings and benefits for individuals |
| Target Audience | Businesses, including sole proprietors, partnerships, corporations, and certain trusts | U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and eligible non-resident workers |
| Use Cases | Tax filing, business banking, hiring employees, legal transactions | Tax filing, credit management, government benefits, personal identification |
| Format | Nine-digit number, e.g., 12-3456789 | Nine-digit number, e.g., 000-00-0000 |

Choosing the Right Identifier
The decision between a Tax ID Number and an SSN depends on the context and purpose. If you’re operating a business, an EIN is crucial for tax compliance and business operations. On the other hand, an SSN is essential for individuals managing personal finances, credit, and accessing government services.
Protecting Your Identifiers
Given the critical role these identifiers play, safeguarding them is paramount. Both the Tax ID Number and SSN are sensitive pieces of information that, if compromised, can lead to identity theft and financial fraud.
Best Practices for Security
- Secure Storage: Keep physical records of your Tax ID Number and SSN in a secure location, such as a locked cabinet or safe.
- Digital Security: If storing electronically, ensure your devices are password-protected and employ robust cybersecurity measures.
- Limited Sharing: Be cautious about sharing your identifiers. Only provide them when necessary, and verify the legitimacy of the requesting party.
- Regular Monitoring: Stay vigilant by regularly checking your tax records and credit reports for any signs of unauthorized activity.
FAQs
Can I use my SSN as my Tax ID Number for business purposes?
+
No, it’s important to understand that the SSN and Tax ID Number serve different purposes. While your SSN is for personal identification and tax reporting, a Tax ID Number is specifically for business entities. Using your SSN for business purposes can lead to complications with tax administration and may even result in penalties. It’s best to obtain a separate Tax ID Number for your business.
Do I need a Tax ID Number if I’m a sole proprietor with no employees?
+
As a sole proprietor, you may choose to operate under your SSN for tax purposes. However, obtaining a Tax ID Number can provide several benefits. It simplifies tax filing, especially if you have employees or need to report payroll taxes. Additionally, a Tax ID Number can enhance your business’s credibility and make it easier to open business bank accounts and engage in certain transactions.
What happens if I lose my Tax ID Number or SSN?
+
If you lose or misplace your Tax ID Number or SSN, you can apply for a new one. For a Tax ID Number, you’ll need to complete Form SS-4 and submit it to the IRS. For an SSN, you’ll need to contact the Social Security Administration and provide proof of identity and citizenship or immigration status. It’s important to act promptly to avoid delays in your business operations or personal financial matters.
Are Tax ID Numbers and SSNs at risk of fraud or identity theft?
+
Unfortunately, both Tax ID Numbers and SSNs are vulnerable to fraud and identity theft. Criminals may use these identifiers to commit tax fraud, open fraudulent accounts, or access sensitive information. It’s crucial to safeguard your identifiers, regularly monitor your accounts and tax records, and take immediate action if you suspect any unauthorized activity.
Can I have multiple Tax ID Numbers for different business entities?
+
Yes, it’s possible to have multiple Tax ID Numbers if you operate multiple business entities. Each distinct business structure, such as a corporation, partnership, or LLC, may require its own Tax ID Number. This allows for separate tax reporting and administration for each entity. However, it’s essential to maintain accurate records and ensure compliance with tax regulations for each business.



