City Of Hartford Taxes
The city of Hartford, located in Connecticut, is renowned for its rich history, vibrant culture, and thriving urban landscape. However, when it comes to financial matters, particularly taxes, residents and businesses often have numerous questions and concerns. Hartford's tax structure, like that of many cities, is intricate and multifaceted, encompassing various types of taxes that contribute to the city's revenue and overall economic health.
This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the tax landscape of Hartford, offering a detailed exploration of the different types of taxes, their rates, and the implications for both residents and businesses. By delving into the intricacies of Hartford's tax system, we can gain a clearer understanding of the financial obligations and opportunities that exist within this dynamic city.
Understanding Hartford’s Tax Structure
Hartford’s tax structure is a complex interplay of various taxes, each serving a specific purpose and contributing to the city’s fiscal stability. These taxes can be broadly categorized into several key types, each with its own unique characteristics and impact on the local economy.
Property Taxes
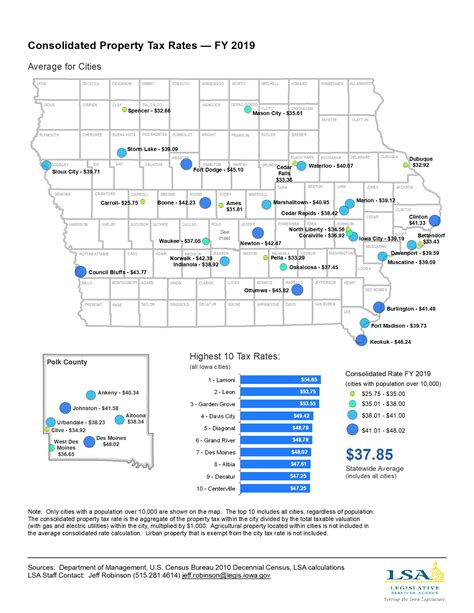
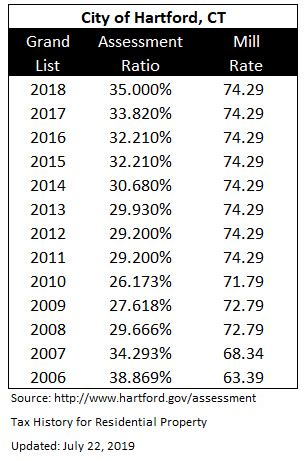
Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for the city of Hartford. These taxes are levied on both residential and commercial properties, with rates varying based on the assessed value of the property. The assessment process involves evaluating the market value of properties and applying a predetermined tax rate to determine the annual tax liability.
For instance, consider a residential property in Hartford with an assessed value of $300,000. The city's current tax rate is 70 mills, which equates to $0.07 per $100 of assessed value. By applying this rate, the annual property tax for this property would amount to $2,100. This tax contributes to the city's general fund, which is utilized for various public services and infrastructure development.
| Property Type | Assessed Value | Tax Rate (Mills) | Annual Tax |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | $300,000 | 70 | $2,100 |
| Commercial | $500,000 | 80 | $4,000 |

It's important to note that property tax rates can vary from year to year, influenced by factors such as budget requirements, economic conditions, and changes in state legislation. Property owners in Hartford can stay informed about tax rate adjustments by referring to official notices and updates from the city's tax assessor's office.
Income Taxes
Hartford, like many cities, imposes income taxes on its residents and businesses. These taxes are calculated based on the income earned within the city limits. For individuals, the tax rate may vary depending on their residency status and income bracket. Similarly, businesses are subject to different tax rates based on their legal structure and revenue generation.
Let's take the example of a single individual residing in Hartford who earns an annual income of $60,000. The city's income tax rate for this income bracket is 3%. By applying this rate, the individual's income tax liability would amount to $1,800. This tax is crucial for funding essential city services, such as public safety, education, and social welfare programs.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate | Annual Income | Tax Liability |
|---|---|---|---|
| $0 - $50,000 | 2% | $45,000 | $900 |
| $50,001 - $100,000 | 3% | $60,000 | $1,800 |
| Over $100,000 | 4% | $120,000 | $4,800 |
Businesses, on the other hand, face a slightly different tax landscape. The city of Hartford imposes a flat tax rate of 2.5% on corporate income. This means that regardless of revenue size, all corporations operating within the city limits are subject to the same tax rate. For instance, a corporation with annual revenue of $500,000 would owe an income tax of $12,500 to the city.
Sales and Use Taxes
Sales and use taxes are an essential component of Hartford’s tax structure, contributing to the city’s revenue and supporting local businesses. These taxes are applied to the sale of goods and services within the city limits, as well as to certain purchases made outside the city but used within Hartford.
The sales tax rate in Hartford is currently set at 6.35%, which is applied to most retail transactions. This tax is collected by businesses and remitted to the city on a regular basis. For instance, if a customer purchases a new laptop for $1,000 at a local electronics store, the sales tax due would be $63.50. This tax not only generates revenue for the city but also helps regulate and stabilize the local economy.
In addition to sales tax, Hartford also imposes a use tax on certain goods and services that are purchased out-of-state but used or consumed within the city limits. This tax ensures that businesses and individuals are not able to avoid taxes by making purchases outside of Hartford. The use tax rate is typically the same as the sales tax rate, ensuring a level playing field for local businesses.
Other Taxes and Fees
Beyond the aforementioned taxes, Hartford also collects various other taxes and fees to support specific initiatives and services. These include but are not limited to:
- Hotel and Motel Taxes: Lodging establishments within Hartford are subject to a hotel occupancy tax, which is typically added to the room rate and collected by the hotel. These taxes contribute to the city's tourism and hospitality development funds.
- Meals and Beverage Taxes: Certain food and beverage establishments are required to collect and remit a tax on prepared meals and beverages. This tax is often used to support local restaurants and promote culinary tourism.
- Vehicle Registration Fees: Hartford residents registering their vehicles within the city are required to pay a registration fee, which contributes to the city's transportation and infrastructure development.
- Entertainment and Admission Taxes: Events, concerts, and amusement venues often charge an admission tax, which is collected and used to support cultural and recreational programs within the city.
Tax Incentives and Relief Programs

Recognizing the impact of taxes on the local economy and the financial well-being of its residents and businesses, Hartford offers various tax incentives and relief programs. These initiatives aim to encourage economic growth, promote business development, and provide financial support to those in need.
Property Tax Exemptions and Abatements
To alleviate the financial burden of property taxes, Hartford provides several exemptions and abatements to eligible residents and businesses. These programs aim to promote homeownership, support low-income individuals, and foster economic development.
One notable exemption is the homestead exemption, which reduces the taxable value of a primary residence for homeowners over the age of 65 or with disabilities. This exemption helps seniors and those with special needs retain more of their property value and reduce their annual tax liability. For instance, a senior homeowner with a property assessed at $250,000 could receive a $50,000 exemption, lowering their taxable value to $200,000 and reducing their annual property tax.
Additionally, Hartford offers tax abatements for new construction and rehabilitation projects. These abatements provide a temporary reduction in property taxes for a specified period, typically ranging from 5 to 10 years. This incentive encourages developers to invest in the city's real estate market and revitalizes older neighborhoods. By offering these abatements, Hartford aims to stimulate economic growth and create a more vibrant urban environment.
Income Tax Credits and Deductions
To ease the tax burden on individuals and families, Hartford provides various income tax credits and deductions. These incentives aim to support low- and middle-income households, promote employment, and encourage financial stability.
One notable income tax credit is the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). This credit is available to working individuals and families with low to moderate incomes. The EITC reduces the amount of income tax owed and, in some cases, provides a refundable credit, offering a financial boost to those who need it most. For instance, a single parent with two children earning $30,000 annually could qualify for a substantial EITC, potentially reducing their tax liability or even receiving a refund.
Hartford also offers deductions for certain expenses, such as education costs and charitable contributions. By allowing taxpayers to deduct these expenses from their taxable income, the city encourages investment in education and supports local charities and non-profit organizations. These deductions not only provide a financial benefit to taxpayers but also contribute to the overall well-being and development of the community.
Business Tax Incentives
To attract and retain businesses, Hartford provides a range of tax incentives aimed at fostering economic growth and job creation. These incentives are designed to support businesses of all sizes and industries, from startups to established corporations.
One prominent incentive is the Enterprise Zone Program, which offers reduced tax rates and other benefits to businesses operating within designated enterprise zones. These zones are typically located in economically disadvantaged areas, and by offering tax incentives, the city aims to stimulate investment, create jobs, and promote economic revitalization. Businesses located within these zones may be eligible for reduced income tax rates, property tax abatements, and other financial incentives.
Additionally, Hartford provides tax credits for businesses that invest in research and development (R&D). By encouraging innovation and technological advancement, the city aims to position itself as a hub for cutting-edge industries. Businesses engaged in R&D activities can claim tax credits, which help offset the costs associated with research and development efforts. These credits not only support the growth of local businesses but also contribute to the city's reputation as an innovation-driven economy.
Tax Administration and Compliance
Ensuring efficient tax administration and fostering tax compliance is a crucial aspect of Hartford’s tax system. The city’s tax department plays a pivotal role in implementing and enforcing tax laws, collecting revenues, and providing support and guidance to taxpayers.
Tax Collection and Payment Options
Hartford offers a range of convenient payment options for taxpayers to fulfill their tax obligations. Residents and businesses can choose from various methods, including online payments, direct bank transfers, credit/debit card payments, and traditional check or money order payments. These options provide flexibility and ease of use, allowing taxpayers to select the method that best suits their preferences and financial circumstances.
Online payment platforms, in particular, offer a secure and efficient way to pay taxes. Taxpayers can access their account information, view tax balances, and make payments from the comfort of their homes or offices. This digital approach not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors and delays associated with traditional paper-based methods.
For taxpayers who prefer in-person interactions, Hartford's tax office provides walk-in services, allowing individuals to speak directly with tax professionals and receive personalized assistance. This face-to-face approach is particularly beneficial for those who may have complex tax situations or require additional support and guidance.
Tax Forms and Filing Requirements
Hartford’s tax department provides comprehensive resources and guidance to help taxpayers understand their filing requirements and complete the necessary tax forms accurately. The department offers user-friendly online resources, including instructional videos, step-by-step guides, and downloadable forms, making the tax filing process more accessible and less daunting.
Taxpayers can access a wide range of forms, from individual income tax returns to business tax filings, directly from the city's website. These forms are regularly updated to reflect any changes in tax laws and regulations, ensuring that taxpayers have access to the most current and accurate information. Additionally, the tax department provides detailed instructions and examples to assist taxpayers in completing their forms correctly and efficiently.
For taxpayers who prefer personalized assistance, the tax department offers dedicated helplines and walk-in support services. Tax professionals are available to answer questions, provide clarification on specific tax issues, and offer guidance on completing complex tax forms. This level of support ensures that taxpayers receive the assistance they need to navigate the tax system confidently and accurately.
Tax Compliance and Enforcement
Hartford’s tax department places a strong emphasis on tax compliance, ensuring that all taxpayers fulfill their legal obligations. The department employs a range of measures to enforce tax laws and promote voluntary compliance.
One key strategy is the implementation of a robust audit program. Audits are conducted to verify the accuracy of tax returns and ensure that taxpayers are reporting their income and expenses correctly. These audits are conducted randomly, as well as based on specific criteria such as high-risk industries or patterns of non-compliance. By conducting audits, the tax department sends a clear message that tax evasion and non-compliance will not be tolerated.
In addition to audits, Hartford's tax department actively pursues delinquent taxpayers through various enforcement actions. This may include issuing penalties and interest on late payments, levying bank accounts or seizing assets, and, in extreme cases, pursuing criminal charges for tax fraud. These enforcement measures serve as a deterrent and encourage taxpayers to remain compliant with their tax obligations.
Impact of Taxes on the Hartford Economy
The taxes collected by the city of Hartford play a pivotal role in shaping the local economy, influencing investment decisions, business growth, and overall economic development. Understanding the impact of taxes is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and residents alike, as it sheds light on the intricate relationship between taxation and economic prosperity.
Revenue Generation and Fiscal Stability
Taxes are a primary source of revenue for the city of Hartford, providing the financial resources necessary to fund essential public services and infrastructure projects. The diverse tax structure, encompassing property taxes, income taxes, sales taxes, and various fees, ensures a steady stream of revenue that supports the city’s operations and long-term financial stability.
The revenue generated through taxes is allocated across various sectors, including public safety, education, healthcare, social services, and infrastructure development. These funds are crucial for maintaining a high quality of life for residents and creating an attractive business environment. By investing in these areas, Hartford can foster economic growth, attract new businesses, and retain existing ones, ultimately contributing to the city's overall prosperity.
Economic Development and Business Growth
The tax policies and incentives implemented by Hartford play a significant role in shaping the city’s economic landscape and encouraging business growth. By offering tax abatements, credits, and exemptions, the city creates a favorable environment for businesses to thrive and expand.
For instance, tax abatements on new construction projects stimulate investment in real estate development, leading to the creation of new residential and commercial spaces. This, in turn, attracts businesses and residents, boosting the local economy. Similarly, tax credits for research and development activities incentivize businesses to innovate and stay at the forefront of their industries, positioning Hartford as a hub for cutting-edge technology and entrepreneurship.
Additionally, Hartford's tax structure, including competitive income tax rates and a streamlined tax filing process, simplifies the business environment and reduces administrative burdens. This encourages startups and small businesses to establish themselves in the city, contributing to job creation and economic diversification.
Impact on Residents and Community Development
The tax system in Hartford not only affects businesses but also has a profound impact on residents and community development. Taxes provide the funding necessary for essential services, such as education, healthcare, and social welfare programs, ensuring that all residents have access to basic needs and opportunities.
Through tax-funded initiatives, Hartford can invest in improving the quality of life for its residents. This includes enhancing public transportation systems, developing recreational facilities, and supporting cultural and artistic endeavors. By allocating tax revenues to these areas, the city fosters a vibrant and inclusive community, attracting residents from diverse backgrounds and creating a sense of pride and belonging.
Furthermore, tax incentives and exemptions aimed at supporting low- and moderate-income households help alleviate financial burdens and promote social mobility. Programs such as the homestead exemption and the Earned Income Tax Credit provide much-needed relief to seniors, individuals with disabilities, and working families, allowing them to retain more of their income and invest in their future.
Future Outlook and Potential Reforms

As Hartford continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic conditions, the city’s tax system will likely undergo periodic reviews and potential reforms to ensure its effectiveness and fairness. Staying ahead of emerging trends and addressing the needs of residents and businesses is crucial for maintaining a sustainable and thriving economy.
Potential Tax Reform Initiatives
One potential area of focus for tax reform in Hartford could be simplifying the tax structure and reducing administrative complexities. While the current tax system serves its purpose, streamlining processes and eliminating unnecessary burdens could enhance efficiency and improve the overall taxpayer experience.
For instance, consolidating various taxes and fees into a more integrated system could reduce the administrative burden on businesses and taxpayers alike. This could involve combining property taxes and income taxes into a single tax assessment process, making it more convenient for taxpayers to manage their