California Pay After Taxes

Understanding California's tax system is crucial, especially when considering the impact on one's disposable income. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of California's pay after taxes, shedding light on the various factors that influence take-home pay in the Golden State. From federal and state income taxes to deductions and withholdings, we will explore the financial landscape to provide a clear picture of what individuals can expect from their earnings.
Navigating California’s Tax Landscape

California, known for its diverse economy and vibrant workforce, boasts a robust tax system that contributes significantly to the state’s revenue. While the state offers a plethora of opportunities, it’s essential to understand the financial implications, particularly when it comes to take-home pay.
California's tax system operates on a progressive scale, meaning that higher incomes are taxed at higher rates. This system aims to distribute the tax burden fairly across different income levels. As of 2023, California has 10 income tax brackets ranging from 1% to 13.3%, with the highest rate applying to income above $1,000,000. This progressive structure ensures that individuals with higher earnings contribute a larger portion of their income to the state's coffers.
Federal Income Tax Considerations
In addition to state taxes, residents of California are subject to federal income tax. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) imposes federal income taxes, which fund various federal programs and services. The federal tax system also operates on a progressive scale, with seven tax brackets ranging from 10% to 37%. The specific bracket an individual falls into depends on their taxable income, filing status, and other factors.
It's important to note that federal income tax is separate from state income tax, and both must be considered when calculating one's overall tax liability. While federal tax rates are set by the federal government, California residents must also navigate their state's tax system, which can further impact their take-home pay.
California State Income Tax: A Closer Look
California’s state income tax is levied on both earned income (such as wages, salaries, and commissions) and unearned income (including interest, dividends, and capital gains). The state’s tax system is designed to capture a significant portion of high-income earners’ earnings, making it a vital source of revenue for state operations and services.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $9,867 | 1% |
| $9,868 - $19,734 | 2% |
| $19,735 - $29,601 | 4% |
| $29,602 - $39,468 | 6% |
| $39,469 - $49,335 | 8% |
| $49,336 - $592,000 | 9.3% |
| $592,001 - $742,666 | 10.3% |
| $742,667 - $1,000,000 | 11.3% |
| $1,000,001 and above | 13.3% |
These tax brackets are adjusted annually to account for inflation and changing economic conditions. It's essential for individuals to stay updated with the latest tax rates to accurately calculate their potential tax liability.
Withholdings and Deductions: Impact on Take-Home Pay
When considering take-home pay, it’s crucial to understand the role of withholdings and deductions. Withholdings are the amounts deducted from an individual’s paycheck to cover their anticipated tax liability. These withholdings are calculated based on various factors, including the individual’s tax bracket, filing status, and allowances claimed on their W-4 form.
Deductions, on the other hand, are expenses that can reduce an individual's taxable income. Common deductions include contributions to retirement accounts, student loan interest, medical expenses, and certain business expenses. By claiming eligible deductions, individuals can lower their taxable income and, consequently, their tax liability.
Factors Influencing California Pay After Taxes

Several key factors come into play when determining an individual’s pay after taxes in California. These factors can significantly impact one’s disposable income and should be carefully considered when planning finances.
Salary and Income Level
The most obvious factor influencing take-home pay is an individual’s salary or income level. Higher incomes generally result in higher tax liabilities, as they fall into higher tax brackets. As we’ve seen, California’s progressive tax system means that those with higher earnings contribute a larger portion of their income to state and federal taxes.
For example, consider two individuals earning significantly different incomes. Individual A earns $50,000 annually, while Individual B earns $200,000. While both will have federal and state taxes withheld from their paychecks, Individual B will face a higher effective tax rate due to their income falling into higher tax brackets.
Tax Filing Status
An individual’s tax filing status is another critical factor in determining their tax liability. The most common filing statuses are single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, and head of household. Each status has its own set of tax brackets and deductions, which can significantly impact an individual’s take-home pay.
For instance, a married couple filing jointly may benefit from lower tax rates and higher standard deductions compared to single filers. On the other hand, a head of household may be eligible for specific deductions or credits that aren't available to other filing statuses.
Deductions and Credits
Deductions and credits play a significant role in reducing an individual’s taxable income and, consequently, their tax liability. Deductions, as mentioned earlier, are expenses that can be subtracted from an individual’s gross income. Common deductions include mortgage interest, state and local taxes, and charitable contributions.
Credits, on the other hand, provide a direct reduction in an individual's tax liability dollar-for-dollar. Some credits, like the Child Tax Credit, can be claimed for each qualifying child, reducing an individual's tax bill. Other credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit, are designed to benefit low- and moderate-income earners.
Withholding Adjustments
Individuals can adjust their withholding allowances on their W-4 form to ensure they’re neither overpaying nor underpaying their taxes throughout the year. By completing a withholding calculator or consulting a tax professional, individuals can make informed decisions about their withholdings, aiming for a balance between minimizing their tax liability and avoiding penalties for underpayment.
Maximizing Your California Take-Home Pay
While taxes are an inevitable part of earning an income, there are strategies individuals can employ to maximize their take-home pay in California. By understanding the tax system and taking advantage of available deductions and credits, individuals can ensure they’re getting the most out of their earnings.
Strategic Tax Planning
Engaging in strategic tax planning can help individuals minimize their tax liability and increase their take-home pay. This involves understanding the various tax deductions and credits available and ensuring one meets the eligibility criteria. For instance, contributing to a retirement account like a 401(k) or IRA can reduce taxable income and provide tax benefits.
Additionally, keeping track of eligible expenses throughout the year can help maximize deductions. This includes business expenses, medical expenses, and charitable contributions. By documenting and organizing these expenses, individuals can ensure they're taking full advantage of the deductions they're entitled to.
Investment Strategies
Investing wisely can also play a role in maximizing take-home pay. While investments may not directly reduce tax liability, they can provide opportunities for growth and diversification. By carefully selecting investment vehicles and strategies, individuals can potentially increase their overall wealth, which can have a positive impact on their financial future.
For instance, investing in real estate or stocks can offer the potential for capital gains, which, if managed properly, can provide a source of additional income. It's important to consult with a financial advisor to understand the risks and benefits of different investment options and to ensure they align with one's financial goals and risk tolerance.
Tax-Efficient Retirement Planning
Planning for retirement is a critical aspect of financial well-being, and California residents have access to a range of tax-advantaged retirement savings options. By contributing to retirement accounts like 401(k)s, IRAs, or Roth IRAs, individuals can reduce their taxable income in the present and potentially benefit from tax-free or tax-deferred growth over time.
Additionally, California offers its own state-sponsored retirement savings plan, the CalSavers Retirement Savings Program. This program is designed to help private-sector employees without access to an employer-sponsored retirement plan save for retirement. By participating in such programs, individuals can take advantage of tax benefits and ensure a more secure financial future.
Conclusion: Understanding Your Financial Landscape
Navigating California’s tax system and understanding the factors that influence take-home pay is essential for financial well-being. By staying informed about tax rates, deductions, and credits, individuals can make informed decisions about their finances and maximize their disposable income.
Remember, while taxes are a necessary part of our economic system, there are strategies and resources available to help individuals minimize their tax liability and make the most of their earnings. By engaging in strategic tax planning, investing wisely, and taking advantage of tax-efficient retirement savings options, California residents can ensure they're on a path toward financial security and prosperity.
What is the average income in California after taxes?
+The average income in California varies greatly depending on factors such as occupation, location, and industry. However, according to recent data, the median household income in California is around $75,000. Keep in mind that this figure represents a broad average and individual experiences may vary significantly.
Are there any tax benefits for residents of California?
+Yes, California offers various tax benefits and incentives to its residents. For instance, the state provides tax credits for individuals with low to moderate incomes, such as the California Earned Income Tax Credit (CalEITC). Additionally, California allows certain deductions for state taxes, including deductions for mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and state sales tax.
How can I estimate my take-home pay in California?
+You can estimate your take-home pay by using online tax calculators or consulting with a tax professional. These tools take into account your income, deductions, and tax rates to provide an estimate of your net pay. Remember that this estimate is based on the information you provide, so ensure accuracy to get a realistic picture.
Are there any tax breaks for specific professions in California?
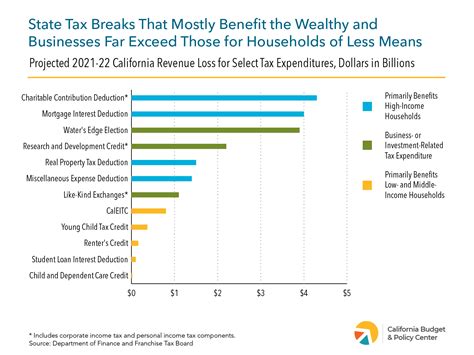
+California offers tax incentives and deductions for certain professions, especially those involved in research and development, manufacturing, and renewable energy. For example, the Research and Development Tax Credit provides a tax credit for qualified research expenses. Additionally, there are tax breaks for small businesses and startups.
How does California’s tax system compare to other states?
+California’s tax system is generally considered to be more progressive compared to other states. It has higher income tax rates, especially for high-income earners, and offers a wider range of deductions and credits. However, the overall tax burden can vary greatly depending on an individual’s specific circumstances and the state they reside in.