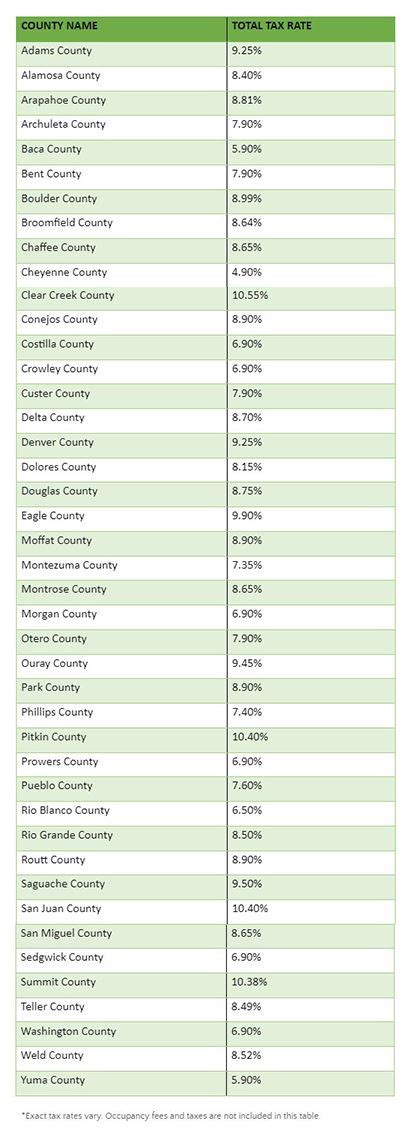
Sales Tax Payable

Sales tax is a crucial aspect of the retail industry, impacting businesses and consumers alike. It is an essential revenue source for governments, providing funds for various public services and infrastructure development. This article aims to delve into the concept of sales tax payable, exploring its intricacies, implications, and best practices for compliance.
Understanding Sales Tax Payable
Sales tax payable, often simply referred to as sales tax, is a tax levied on the sale of goods and services by businesses to their customers. It is a percentage of the sale price that is collected by the seller and remitted to the government. Sales tax is a critical component of a country’s tax system, as it generates substantial revenue for the government while also regulating consumption patterns and influencing economic decisions.
The concept of sales tax varies across jurisdictions, with different countries, states, and provinces implementing their own rules and regulations. These variations can be complex, making it essential for businesses to understand the specific requirements of the regions they operate in.
Key Considerations for Sales Tax Payable
When it comes to sales tax payable, several factors come into play:
- Tax Rates: Sales tax rates can differ based on the type of goods or services being sold, the location of the transaction, and even the end-use of the product. For instance, essential items like groceries may have lower tax rates, while luxury goods might be subject to higher taxes.
- Taxable Items: Not all goods and services are taxable. Certain items, such as prescription medications or educational materials, are often exempt from sales tax. Understanding which items are taxable is crucial for accurate tax calculation.
- Tax Collection and Remittance: Businesses act as tax collectors on behalf of the government. They are responsible for collecting the sales tax from customers at the point of sale and then remitting these funds to the appropriate tax authority within a specified timeframe.
- Registration and Compliance: To comply with sales tax regulations, businesses must register with the relevant tax authority. This registration process ensures that businesses are officially recognized and held accountable for their sales tax obligations.
- Reporting and Record-Keeping: Accurate record-keeping is essential for sales tax compliance. Businesses must maintain detailed records of all sales transactions, including the tax collected, to facilitate accurate reporting and potential audits.
Failing to comply with sales tax regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines, interest charges, and even revocation of business licenses. Therefore, businesses must prioritize understanding and adhering to sales tax requirements to avoid legal and financial repercussions.
Sales Tax Payable in Practice
Let’s explore some real-world examples to illustrate the concept of sales tax payable:
Example 1: Online Retailer
Consider an online retailer, ShopItOnline, based in California. California has a sales tax rate of 7.25% for most goods. ShopItOnline sells a variety of products, including clothing, electronics, and home goods. When a customer purchases a laptop for $1,200, the sales tax payable would be calculated as follows:
| Laptop Price | $1,200 |
|---|---|
| Sales Tax Rate | 7.25% |
| Sales Tax Payable | $87 |
So, ShopItOnline would collect $87 in sales tax from the customer and remit this amount to the California tax authority. This process ensures compliance with sales tax regulations and contributes to the state's revenue.
Example 2: Restaurant Business
Now, let’s look at a restaurant business, Tasty Treats, located in New York City. New York City has a sales tax rate of 8.875% for restaurant services. Tasty Treats offers a diverse menu, serving meals and beverages to its customers.
When a customer orders a meal totaling $50, the sales tax payable would be:
| Meal Price | $50 |
|---|---|
| Sales Tax Rate | 8.875% |
| Sales Tax Payable | $4.44 |
Tasty Treats would add $4.44 to the bill as sales tax, making the total amount payable by the customer $54.44. This sales tax is then collected by the restaurant and remitted to the New York City tax authority.
Example 3: Exemptions and Special Cases
Not all sales are subject to the standard sales tax rate. Some items are exempt from sales tax, and there are also special cases where reduced rates or additional surcharges may apply.
For instance, in certain states, groceries are exempt from sales tax. Let's say a customer in this state purchases $100 worth of groceries from a local supermarket. In this case, there would be no sales tax payable on the groceries, saving the customer money and promoting essential spending.
On the other hand, there may be special circumstances where sales tax is applied differently. For example, some jurisdictions have tourism-related surcharges on hotel accommodations or rental cars. These additional taxes are often implemented to support local tourism infrastructure and development.
Best Practices for Sales Tax Compliance
To ensure compliance with sales tax regulations and avoid potential issues, businesses should consider the following best practices:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest sales tax regulations and changes in your operating regions. Tax laws can evolve rapidly, so regular monitoring is essential.
- Implement Robust Systems: Utilize reliable accounting and point-of-sale systems that automatically calculate and track sales tax. These systems can simplify the tax calculation process and reduce the risk of errors.
- Train Staff: Ensure that your staff, especially those involved in sales and accounting, are well-versed in sales tax procedures. Training can help them understand the importance of accurate tax calculation and reporting.
- Regular Audits: Conduct internal audits to verify the accuracy of your sales tax calculations and reporting. This practice can identify potential issues and ensure compliance before official audits take place.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider engaging tax professionals or consultants who specialize in sales tax. They can provide expert guidance and ensure your business remains compliant with complex tax regulations.
The Future of Sales Tax Payable
The landscape of sales tax payable is evolving, influenced by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. Here are some trends and implications to consider:
Online Sales and E-Commerce
The rise of e-commerce has significantly impacted sales tax payable. Online retailers must navigate a complex web of sales tax regulations across different states and countries. This has led to the development of specialized software and services that help businesses calculate and collect sales tax accurately for online transactions.
Marketplace Facilitator Laws
Many states have introduced marketplace facilitator laws, holding online marketplace platforms responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax on behalf of their third-party sellers. This shift places the onus on the marketplace platforms to ensure compliance, simplifying the process for smaller sellers.
Sales Tax Simplification Efforts
There is a growing movement towards sales tax simplification, with initiatives aiming to standardize sales tax rates and regulations across states. These efforts aim to reduce the administrative burden on businesses and promote fairness in tax collection.
Technology-Driven Compliance
Advancements in technology, such as automated tax calculation software and AI-powered auditing tools, are transforming the sales tax landscape. These technologies enhance accuracy, efficiency, and compliance, helping businesses stay ahead of changing tax regulations.
FAQ
How often should businesses remit sales tax to the tax authority?
+
The frequency of sales tax remittance can vary by jurisdiction. Some require monthly, quarterly, or even annual remittances. It’s essential for businesses to understand the specific requirements of their operating regions to ensure timely compliance.
Are there any exceptions or special cases where sales tax is not applicable?
+
Yes, there are several exceptions and special cases. These can include exemptions for certain types of goods (like groceries), sales to tax-exempt entities (like government agencies), and special tax rates for specific industries or regions. Understanding these exceptions is crucial for accurate tax calculation.
What happens if a business fails to remit sales tax on time or makes errors in calculation?
+
Late or incorrect remittances can result in penalties, interest charges, and potential legal consequences. Tax authorities take these matters seriously, and businesses should prioritize accurate and timely sales tax compliance to avoid such issues.
How can businesses stay updated with sales tax rate changes and regulations?
+
Businesses should subscribe to official tax authority notifications, follow industry publications, and utilize tax compliance software that provides real-time updates on sales tax rates and regulations. Staying informed is key to maintaining compliance.
Are there any international considerations for sales tax payable when selling goods across borders?
+
Yes, international sales can introduce complexities. Businesses must understand the sales tax requirements of the countries they sell to, including potential value-added taxes (VAT) or goods and services taxes (GST). Consulting with tax professionals is advisable when dealing with international sales tax obligations.