Are Legal Fees Tax Deductible

When navigating the complex world of personal finance and tax obligations, one frequently asked question revolves around the tax deductibility of legal fees. This is particularly relevant for individuals and businesses alike, as legal expenses can often be a significant financial burden. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of legal fee deductibility, exploring the criteria, exceptions, and best practices to ensure you optimize your tax strategy while remaining compliant with tax regulations.
Understanding Legal Fee Deductibility
The deductibility of legal fees is governed by a set of specific criteria outlined by tax authorities. Generally, legal expenses are considered tax-deductible when they are directly related to a taxpayer's income-generating activities or business operations. This principle is known as the ordinary and necessary expense doctrine, which forms the foundation for many tax deductions.
Legal fees that fall under this category include those incurred for activities such as negotiating contracts, resolving disputes, or defending against lawsuits related to your business or professional endeavors. These expenses are viewed as necessary to maintain and enhance your income-generating capacity, thus qualifying for tax deduction.
Key Considerations for Deductibility
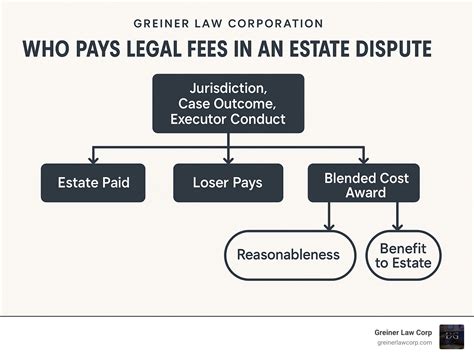
When assessing the deductibility of legal fees, it's crucial to consider the nature of the legal services and their direct correlation to income generation. For instance, fees associated with buying or selling a personal residence are typically not deductible, as they are considered personal expenses rather than business-related costs. Similarly, expenses related to family law matters, such as divorce or child custody, are generally not tax-deductible due to their personal nature.
However, there are exceptions to this rule. If a legal dispute arises from a business activity or if the taxpayer's professional reputation is at stake, legal fees incurred to resolve such matters may be deductible. This highlights the importance of understanding the specific circumstances and the potential impact on one's business or professional standing.
| Deductible Legal Fees | Non-Deductible Legal Fees |
|---|---|
| Contract negotiations for business operations | Personal residence-related expenses |
| Defense against business-related lawsuits | Family law matters (divorce, custody) |
| Intellectual property protection | Personal injury claims |
| Employment law matters | Tax-related fees (unless specifically deductible) |

In addition to the nature of the legal services, the timing of the expenses also plays a role in their deductibility. Legal fees incurred during the tax year for which you are filing are typically deductible on that year's tax return. However, if the fees are paid in advance for services to be rendered in a future tax year, they may need to be amortized or expensed over multiple years.
Deducting Legal Fees: A Step-by-Step Guide

To ensure that your legal fees are properly deducted, it's essential to follow a systematic approach. Here's a detailed guide to help you navigate the process:
Step 1: Determine Deductibility
Start by evaluating the nature of the legal services and their connection to your income-generating activities. Ask yourself:
- Are these fees directly related to my business or profession?
- Do they help maintain or improve my income-generating capacity?
- Is this a one-time expense or an ongoing legal matter?
If the answer to these questions is affirmative, you may have a strong case for deductibility.
Step 2: Gather Supporting Documentation
Thorough documentation is key to substantiating your legal fee deductions. Collect and organize the following:
- Invoices or bills from your legal service providers detailing the services rendered and the fees charged.
- Contracts, agreements, or correspondence related to the legal matter.
- Any court documents, settlement agreements, or other legal records.
- Records of payments made, including checks, bank statements, or credit card receipts.
Ensure that all documentation is accurate, complete, and easily accessible for tax purposes.
Step 3: Choose the Right Tax Form
The choice of tax form depends on your filing status and the nature of your income. For most individuals, legal fee deductions are reported on Schedule A of Form 1040 as Itemized Deductions. However, for businesses, the appropriate form may vary. Consult with a tax professional to determine the most suitable form for your specific circumstances.
Step 4: Calculate the Deduction
The calculation of legal fee deductions can be straightforward or complex, depending on the nature of the expenses. For simple cases, the deduction is typically the full amount of the legal fees. However, for more complex situations, such as when fees are paid in advance or relate to multiple tax years, you may need to prorate or amortize the expenses.
Seek guidance from a tax professional or use reputable tax software to ensure accurate calculations.
Step 5: File and Claim Your Deductions
Once you have gathered your documentation, calculated your deductions, and chosen the appropriate tax form, it's time to file your tax return. Be sure to include all relevant information and supporting documents to support your claim for legal fee deductions.
Remember, accurate and complete documentation is crucial to avoid potential audits or penalties.
Maximizing Legal Fee Deductions: Strategies and Tips
To optimize your tax strategy and make the most of legal fee deductions, consider the following strategies and best practices:
Maintain Detailed Records
Accurate and organized record-keeping is essential for supporting your legal fee deductions. Maintain a dedicated file or digital folder for all legal-related documents, including invoices, correspondence, and payment records. This ensures that you have easy access to the information when preparing your tax return and can provide clear evidence if your deductions are ever questioned.
Consult a Tax Professional
Tax laws and regulations can be complex, and legal fee deductibility is no exception. Consulting with a qualified tax professional, such as a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or a tax attorney, can provide valuable insights and guidance tailored to your specific circumstances. They can help you navigate the intricacies of tax law, ensure compliance, and maximize your deductions.
Explore Alternative Fee Arrangements
When engaging legal services, explore alternative fee arrangements with your attorney or law firm. Options such as flat fees, contingency fees, or deferred payment plans can provide greater predictability and control over your legal expenses. By negotiating favorable fee structures, you may be able to better manage your cash flow and optimize your tax strategy.
Consider Business Structure
The structure of your business can impact the deductibility of legal fees. For example, incorporating your business may provide certain tax advantages, including the ability to deduct a wider range of business expenses, including legal fees. Consult with a tax advisor to explore the most suitable business structure for your needs and maximize your tax benefits.
The Future of Legal Fee Deductibility
The landscape of legal fee deductibility is continually evolving, influenced by changes in tax laws and regulations. Staying informed about these developments is essential to ensure compliance and optimize your tax strategy. Here are a few key considerations for the future:
Potential Changes in Tax Laws
Tax laws are subject to change, and legal fee deductibility may be impacted by future legislative actions. Stay abreast of any proposed or enacted changes to tax laws, especially those related to business deductions. This will enable you to adapt your tax strategy and ensure compliance with any new regulations.
Advancements in Legal Technology
The legal industry is embracing technology to streamline processes and reduce costs. As legal technology advances, it may impact the way legal services are delivered and billed. Keep an eye on emerging legal tech solutions, such as online dispute resolution platforms or legal document automation tools, which could potentially reduce legal fees and, in turn, affect their deductibility.
Global Tax Considerations
For businesses operating internationally, understanding the tax laws and regulations of different jurisdictions is crucial. Legal fee deductibility may vary across countries, and businesses must navigate these differences to ensure compliance and optimize their tax strategy. Engage with tax advisors who specialize in international tax matters to stay informed and compliant.
Conclusion

Legal fees can be a significant financial burden, but understanding their deductibility can help alleviate some of the financial strain. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can navigate the complexities of legal fee deductibility with confidence. Remember, accurate record-keeping, professional guidance, and staying informed about tax laws are essential to optimize your tax strategy and ensure compliance.
Can I deduct legal fees for personal matters?
+Generally, legal fees for personal matters are not deductible. However, there may be exceptions, such as when a legal dispute impacts your business or professional reputation. Consult a tax professional for specific guidance.
Are there limits to how much I can deduct for legal fees?
+The deductibility of legal fees is subject to certain limits and thresholds. For individuals, there may be caps on itemized deductions, which could impact the amount you can deduct. For businesses, there may be specific rules and regulations regarding the deduction of legal expenses. Consult a tax professional to understand the limits applicable to your situation.
What if I’m unsure whether my legal fees are deductible?
+If you’re unsure about the deductibility of your legal fees, it’s best to consult a tax professional. They can provide guidance based on your specific circumstances and help you navigate the complexities of tax law to ensure you’re claiming all eligible deductions while remaining compliant.