Alabama Sales Tax

Alabama's sales tax is an important aspect of the state's revenue generation and has a significant impact on both consumers and businesses. With a unique structure and some interesting exemptions, understanding Alabama's sales tax system is crucial for individuals and companies operating within the state. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of Alabama's sales tax, its rates, applicability, and how it affects different sectors and consumers.
Understanding Alabama Sales Tax
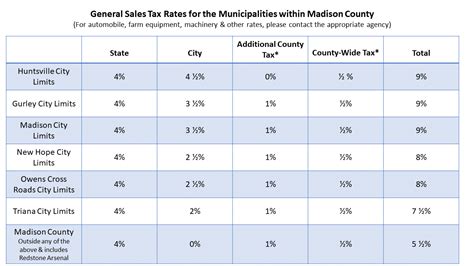
Alabama’s sales tax system is a complex combination of state, county, and city taxes, resulting in varying rates across the state. The state sales tax is a uniform 4% applied to most transactions, but local taxes can increase this rate. For instance, in Birmingham, the total sales tax rate is 10%, comprising the state’s 4% and additional city and county taxes.
The sales tax in Alabama is primarily a transaction-based tax levied on the retail sale of tangible personal property and certain services. This includes items like electronics, clothing, furniture, and groceries. However, Alabama also imposes sales tax on some services, such as repairs, installation, and certain entertainment services.
Taxable Items and Exemptions
Alabama’s sales tax is applicable to a wide range of goods and services, but there are notable exemptions. For example, groceries, prescription drugs, and certain medical devices are exempt from sales tax. This exemption is a significant relief for consumers, especially those with lower incomes, as it reduces the tax burden on essential items.
Additionally, Alabama has specific exemptions for certain industries. For instance, the sale of aircraft parts is exempt from sales tax if the parts are used for the repair or maintenance of aircraft. This exemption encourages aviation-related businesses to operate within the state.
| Taxable Items | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Electronics | 4% (state) + Local Rates |
| Clothing | 4% (state) + Local Rates |
| Groceries | Exempt |
| Prescription Drugs | Exempt |
| Aircraft Parts (for repair/maintenance) | Exempt |
Sales Tax Registration and Collection

Businesses operating in Alabama are responsible for registering for sales tax, collecting the appropriate taxes from customers, and remitting these taxes to the Alabama Department of Revenue. The registration process involves obtaining a Business Tax Registration Certificate, which authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax.
The frequency of sales tax filing and remittance depends on the business's estimated sales tax liability. Businesses with higher liabilities are required to file more frequently, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis. Those with lower liabilities may file annually.
To ensure compliance, the Alabama Department of Revenue provides resources and guidelines for businesses, including tax rate lookup tools, filing instructions, and payment options.
Online Sales and Alabama Sales Tax
With the growth of e-commerce, Alabama has implemented measures to ensure sales tax is collected on online transactions. This includes the requirement for out-of-state sellers to collect and remit Alabama sales tax if they meet certain thresholds of sales into the state. This policy aims to level the playing field for in-state businesses and ensure all retailers contribute to the state’s revenue.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The sales tax in Alabama has a significant impact on both consumers and businesses. For consumers, the tax directly affects their purchasing power and can influence buying decisions. A higher sales tax rate can deter consumers from making certain purchases, especially discretionary items.
On the other hand, for businesses, the sales tax affects pricing strategies and operational costs. Businesses must factor in the sales tax when setting their prices, and they also bear the administrative burden of collecting and remitting the tax. However, the sales tax also provides a stable source of revenue for the state, which can be used for various public services and infrastructure development.
The varying sales tax rates across Alabama also create a competitive advantage for certain areas. For instance, a lower sales tax rate in one city might attract more shoppers from neighboring cities, leading to increased economic activity in that area.
Comparative Analysis with Other States
Alabama’s sales tax system is unique compared to other states. While the state sales tax rate of 4% is relatively standard, the addition of local taxes can make Alabama’s overall sales tax rate higher than many other states. For example, a state like Delaware has no sales tax, making it an attractive destination for shoppers from neighboring states.
However, Alabama's sales tax system is also more straightforward than some other states. Unlike states with varying sales tax rates for different items, Alabama has a consistent rate for most goods and services. This simplicity can be beneficial for both businesses and consumers, as it simplifies the tax calculation process.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
The future of Alabama’s sales tax system is likely to be influenced by various factors, including economic trends, technological advancements, and policy changes. One potential area of change is the continued shift towards online sales and the associated challenges of tax collection.
As e-commerce continues to grow, Alabama may need to adapt its sales tax policies to ensure fair taxation of online transactions. This could involve further refining the policies for out-of-state sellers or exploring new methods of tax collection, such as marketplace facilitator laws.
Additionally, changes in the economic landscape, such as shifts in consumer spending patterns or the emergence of new industries, could prompt adjustments to Alabama's sales tax system. For instance, the rise of the gig economy and the sharing economy could lead to new considerations for sales tax applicability.
What is the current sales tax rate in Alabama?
+
The current state sales tax rate in Alabama is 4%. However, the total sales tax rate can vary depending on the location, as local taxes are added on top of the state rate.
Are there any items exempt from sales tax in Alabama?
+
Yes, several items are exempt from sales tax in Alabama. This includes groceries, prescription drugs, and certain medical devices. There are also specific exemptions for industries like aviation.
How often do businesses need to file and remit sales tax in Alabama?
+
The frequency of filing and remittance depends on the business’s estimated sales tax liability. Businesses with higher liabilities are required to file more frequently, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, while those with lower liabilities may file annually.
How does Alabama collect sales tax from out-of-state online sellers?
+
Alabama requires out-of-state sellers to collect and remit sales tax if they meet certain thresholds of sales into the state. This policy aims to ensure fair taxation of online transactions.
What potential changes might Alabama’s sales tax system see in the future?
+
Future changes could include adaptations to address the growth of e-commerce and the gig economy. Alabama may also need to respond to economic shifts and emerging industries to ensure its sales tax system remains effective and fair.



