World War Two German Guns: A Deep Dive Into World War Two German Guns

World War Two German Guns played a pivotal role in shaping battlefield tactics and industrial output across Europe. This article provides an informative overview of the era’s most influential firearms, from rifle and pistol designs to machine gun innovations, and explains how engineering choices balanced firepower, reliability, and manufacturability in a total-war context. If you’re seeking a clear, SEO-friendly guide to the weapons that defined a conflict, you’ve found it in this exploration of World War Two German Guns.
Key Points
- German small arms blended rugged reliability with wartime mass production to sustain long campaigns.
- The MG34 and MG42 redefined sustained-fire capability and influenced later European and postwar designs.
- The StG 44 introduced early assault- rifle concepts that foreshadowed postwar infantry rifles.
- Standard service rifles and pistols, such as the Kar98k and Luger P08/Walther P38, emphasized maintainability under harsh conditions.
- Logistics, interchangeability, and modular components shaped production lines and theater-level supply.
Historical Context and Design Ethos
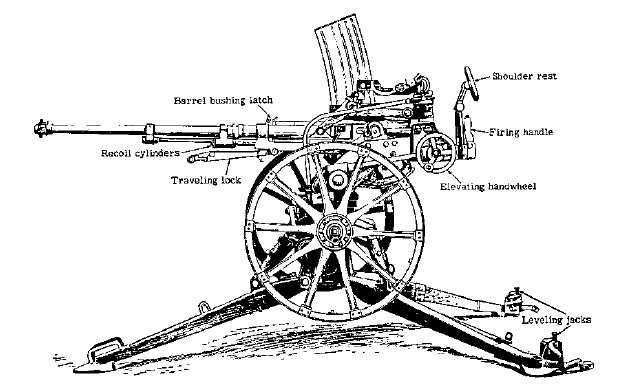
In World War Two, German arms engineering prioritized a blend of firepower, reliability, and ease of production. The burden of a total war required weapons that could be manufactured at scale, repaired under field conditions, and adapted to rapidly changing battlefronts. World War Two German Guns reflect this balance, with weapons that could be produced in vast quantities while still delivering decisive performance in the hands of trained soldiers.
World War Two German Guns: Rifles and Carbines

The Karabiner 98k, commonly known as the Kar98k, served as the standard bolt-action rifle for German infantry. Its rugged construction and compatibility with a broad range of ammunition made it durable in varied theaters. As the war progressed, semi-automatic options like the G41 and Gewehr 43 (G43) offered improved firepower without sacrificing reliability. Together, these rifles illustrate how World War Two German Guns evolved to meet battlefield demands while maintaining manufacturability on a sprawling home front.
World War Two German Guns: Machine Guns and Submachine Guns

Two iconic machine guns define this era: the MG34 and MG42. The MG34 introduced a versatile, fully adaptable platform with a detachable barrel changing system and high-velocity performance. The MG42, known for its exceptionally high rate of fire and robust construction, became a symbol of German industrial efficiency on the front lines. Submachine guns like the MP40 complemented squad tactics with controlled automatic fire in close quarters, reinforcing the emphasis on coordinated crew roles and volume of fire.
World War Two German Guns: Handguns and Autoloading Pistols

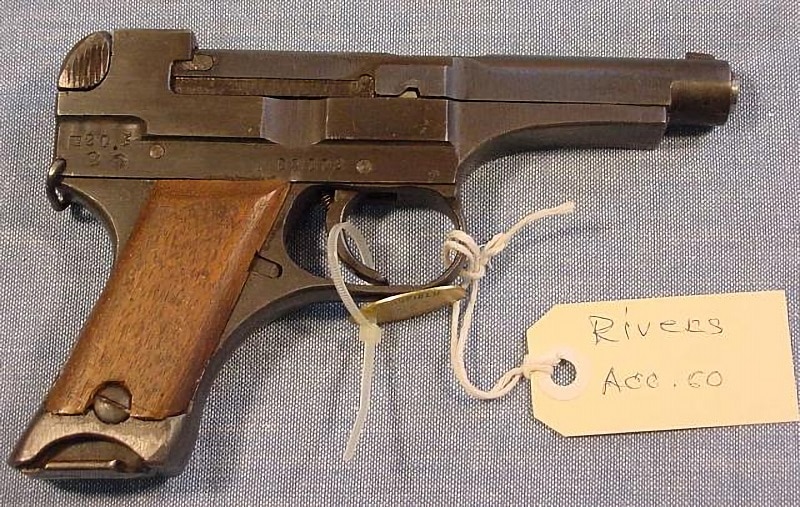
Sidearms such as the Luger P08 and the Walther P38 exemplified a shift toward reliable, semi-automatic handguns suited for field use. The Walther P38, in particular, offered improved ergonomics and a simpler, more durable action compared to earlier designs, aligning with a broader push toward standardized service pistols that could be produced at scale and sustained in the field.
World War Two German Guns: Influence on Tactics and Production

Beyond individual weapons, the design philosophy of World War Two German Guns influenced tactical doctrine and logistics. High-fire-rate machine guns supported mobile infantry and defensive belts of fire, while rifle and pistol platforms emphasized durability and ease of repair. The wartime push for standardized components helped streamline supply chains, maintenance, and repair across diverse theaters, contributing to the overall effectiveness of German armed forces during the conflict.
As a result, the study of World War Two German Guns reveals how engineering choices, production constraints, and battlefield experience intersected to shape both weapon design and military strategy in a transformative period of history.
What was the most influential World War Two German Gun on battlefield tactics?

+
The MG42 stands out for its impact on tactics due to its high rate of fire, reliability, and infantry support role. Its effectiveness in sustained-fire roles influenced squad formations and defensive layouts across multiple fronts.
How did production constraints shape the design of World War Two German Guns?

+
Wartime constraints pushed designers toward modular components and interchangeable parts, enabling faster manufacturing, easier field repairs, and more scalable supply chains across theaters.
Did World War Two German Guns influence postwar firearm development?

+
Yes. Features from rifles like the Gewehr 43 and the StG 44 variants informed postwar small-arms design globally, inspiring later assault rifle concepts and modular weapon systems.
Which World War Two German Guns were most widely produced?
+Mass-produced items like the Kar98k rifle, MG34, and MG42 machine guns were manufactured in very large numbers, reflecting the emphasis on standardization and throughput in German arms production.