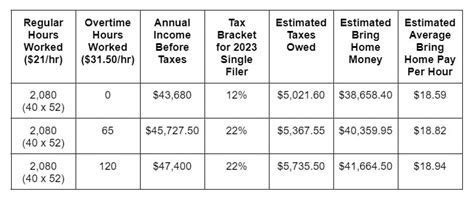
Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form
In the state of Wisconsin, the tax system is designed to ensure that residents and businesses alike understand their obligations and the potential for tax exemptions. The Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form is a crucial document that enables eligible entities to claim exemption from certain taxes, thereby reducing their overall tax liability. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding and utilizing the Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form, its purpose, requirements, and the process of obtaining and maintaining tax-exempt status.
Understanding the Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form

The Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form, officially known as the Form EX-32, is a legal document that allows eligible organizations and individuals to claim exemption from specific taxes. This form is integral to the state’s tax system, as it provides a mechanism for certain entities to avoid paying taxes on goods, services, or property that are deemed exempt under Wisconsin law.
The tax exemption process in Wisconsin is governed by the Wisconsin Statutes and Annotations, particularly Chapter 77, which outlines the criteria and procedures for obtaining tax-exempt status. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of the Form EX-32, its applicability, and the steps involved in obtaining and maintaining tax exemption.
Eligibility Criteria
Not all organizations or individuals are eligible for tax exemption in Wisconsin. The state has established specific criteria that determine whether an entity qualifies for tax-exempt status. These criteria primarily revolve around the nature and purpose of the organization or individual’s activities.
Organizations that are typically eligible for tax exemption include non-profit entities, charitable organizations, religious institutions, educational institutions, and certain government entities. The eligibility is based on the organization's mission, purpose, and the benefit it provides to the public or a specific segment of the community.
For individuals, tax exemption is generally granted to those who meet specific criteria, such as veterans, persons with disabilities, or individuals with low incomes. The state offers various exemptions, including the Homestead Credit, which provides a tax credit for eligible homeowners, and the Earned Income Tax Credit, which benefits low-income earners.
Types of Tax Exemptions
Wisconsin offers a range of tax exemptions, each tailored to specific situations and entities. Understanding the different types of exemptions is crucial for determining which form and process to follow.
- Sales and Use Tax Exemption: This exemption applies to organizations that purchase goods or services for use in their exempt activities. Eligible entities can claim this exemption by obtaining a Sales and Use Tax Certificate of Exemption (Form SC-135) and providing it to vendors or service providers.
- Property Tax Exemption: Certain properties, such as those owned by non-profit organizations or used for religious, educational, or governmental purposes, may qualify for property tax exemption. The process involves submitting the appropriate form, such as the Application for Property Tax Exemption (Form PT-120), to the local assessor's office.
- Income Tax Exemption: Wisconsin offers various income tax exemptions, including those for certain types of income, such as income from qualified retirement plans or income earned by students. The applicable forms and procedures depend on the specific exemption being claimed.
The Process of Obtaining Tax-Exempt Status
Obtaining tax-exempt status in Wisconsin requires a systematic approach, starting with determining eligibility and gathering the necessary documentation. The process can vary depending on the type of exemption sought, but there are common steps that apply to most scenarios.
Step 1: Determine Eligibility
The first step is to thoroughly review the eligibility criteria outlined in the Wisconsin Statutes and Annotations to determine if your organization or individual circumstances meet the requirements for tax exemption. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire process.
Step 2: Gather Documentation
Once eligibility is established, it’s essential to gather the necessary documentation to support your claim. This may include articles of incorporation, bylaws, financial statements, and other documents that demonstrate compliance with the eligibility criteria. For individuals, documentation may include proof of income, residency, or disability status.
Step 3: Complete the Appropriate Forms
Based on the type of exemption you are seeking, you will need to complete the corresponding Wisconsin tax forms. These forms typically require detailed information about your organization or individual circumstances, including the purpose of the exemption, the activities conducted, and the expected impact of the exemption.
Step 4: Submit the Forms and Documentation
After completing the forms and gathering all the required documentation, the next step is to submit them to the appropriate state or local authority. This may involve sending the forms and documentation to the Wisconsin Department of Revenue or the local assessor’s office, depending on the type of exemption.
Step 5: Await Approval or Denial
Once the forms and documentation are submitted, the reviewing authority will assess your application. The processing time can vary, but it’s essential to remain patient during this period. If your application is approved, you will receive notification and instructions on how to maintain your tax-exempt status.
Step 6: Maintain Tax-Exempt Status
Obtaining tax-exempt status is just the beginning. To maintain this status, you must comply with the ongoing requirements and regulations set forth by the state. This may involve periodic reporting, maintaining certain financial records, and ensuring that your activities continue to align with the eligibility criteria.
| Exemption Type | Form Name | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Sales and Use Tax | Form SC-135 | Eligible organizations must submit a certificate to vendors for purchases related to exempt activities. |
| Property Tax | Form PT-120 | Organizations must apply for exemption with the local assessor's office, providing proof of eligibility. |
| Income Tax | Varies by exemption | Income tax exemptions have specific forms and criteria, such as retirement plan income or student earnings. |
Benefits and Implications of Tax-Exempt Status
Obtaining tax-exempt status in Wisconsin can provide significant benefits to eligible entities. These benefits extend beyond the immediate reduction in tax liability and can have a profound impact on the organization’s operations and financial health.
Financial Benefits
The most apparent benefit of tax exemption is the reduction in tax liability. By obtaining tax-exempt status, organizations can save a substantial amount of money that would otherwise be paid in taxes. This financial relief can be redirected towards the organization’s mission, operations, or other essential areas, such as funding programs, improving infrastructure, or increasing salaries.
Operational Advantages
Tax-exempt status can also provide operational advantages. For non-profit organizations, tax exemption enhances their credibility and standing within the community. It demonstrates a commitment to the public good and can attract donors, volunteers, and other supporters who are drawn to organizations that align with their values.
Additionally, tax-exempt status can simplify certain administrative tasks. For instance, eligible organizations may be able to procure goods and services tax-free, which can streamline their procurement processes and reduce administrative burdens.
Implications and Responsibilities
While tax-exempt status offers numerous benefits, it also comes with certain responsibilities and implications. Organizations must ensure they maintain compliance with the criteria for tax exemption and continue to operate in a manner that aligns with their stated purpose. Failure to do so can result in the revocation of tax-exempt status, leading to significant financial and legal consequences.
Furthermore, tax-exempt organizations are subject to public scrutiny and must maintain transparency in their financial and operational activities. This includes filing annual reports, maintaining accurate financial records, and ensuring that funds are used for their intended purposes.
Common Misconceptions and Challenges
The process of obtaining and maintaining tax-exempt status in Wisconsin can be complex, and there are several misconceptions and challenges that entities may encounter.
Misconception: Automatic Exemption for Non-Profits
One common misconception is that all non-profit organizations are automatically exempt from taxes. While non-profit status is a prerequisite for tax exemption, it does not guarantee exemption. Organizations must meet specific criteria and demonstrate their eligibility through the proper application process.
Challenge: Navigating Complex Tax Laws
Wisconsin’s tax laws can be intricate and subject to frequent changes. Keeping up with the latest regulations and understanding the nuances of tax exemption can be challenging, especially for smaller organizations or individuals without legal or accounting expertise. It’s crucial to seek professional advice and stay informed about any updates to the tax code.
Misconception: Tax-Exempt Status is Permanent
Another misconception is that tax-exempt status is permanent once obtained. In reality, tax-exempt status is not a one-time grant but an ongoing responsibility. Organizations must continually meet the eligibility criteria and comply with the regulations to maintain their tax-exempt status. Failure to do so can result in the loss of exemption, leading to significant tax liabilities and legal complications.
The Future of Tax Exemption in Wisconsin

The landscape of tax exemption in Wisconsin is subject to change, influenced by economic, political, and social factors. While the state currently offers a range of tax exemptions to eligible entities, future policy decisions and economic conditions may impact the availability and scope of these exemptions.
Policy Changes and Economic Factors
Tax laws are often subject to political influence and economic considerations. As Wisconsin’s economic climate evolves, so too may the state’s approach to tax exemption. Changes in leadership, budgetary constraints, or shifts in public opinion can lead to revisions in tax policies, including the criteria for exemption and the types of entities eligible for tax relief.
Potential for Expansion or Contraction
The future of tax exemption in Wisconsin could see either expansion or contraction, depending on the state’s economic priorities and the needs of its residents. In times of economic prosperity, the state may choose to expand tax exemptions to encourage certain activities or support specific sectors. Conversely, during economic downturns, tax exemptions may be reviewed and potentially reduced to generate additional revenue.
Continuing Education and Compliance
For entities that currently hold tax-exempt status, staying informed about any changes to tax laws and maintaining compliance with the latest regulations is essential. This includes regularly reviewing the state’s tax publications, attending relevant workshops or seminars, and consulting with tax professionals to ensure continued eligibility and compliance.
The Role of Advocacy and Community Engagement
Advocacy and community engagement play a crucial role in shaping the future of tax exemption policies in Wisconsin. Entities that benefit from tax exemption can actively participate in the policy-making process by engaging with local representatives, attending public hearings, and sharing their perspectives on the impact of tax exemption on their operations and the community at large.
Conclusion: Navigating Wisconsin’s Tax Exempt Form
The Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form, or Form EX-32, is a vital tool for organizations and individuals seeking tax relief in the state. Understanding the eligibility criteria, the application process, and the ongoing responsibilities associated with tax-exempt status is crucial for successful navigation of Wisconsin’s tax system.
By thoroughly researching the applicable tax laws, gathering the necessary documentation, and completing the appropriate forms, eligible entities can obtain tax-exempt status and unlock a range of benefits. These benefits extend beyond financial savings, offering operational advantages and enhanced credibility within the community.
While the process can be complex, seeking professional guidance and staying informed about tax laws can help entities successfully navigate the intricacies of Wisconsin's tax exemption system. As the landscape of tax exemption continues to evolve, remaining engaged and proactive in the policy discussion is essential for ensuring that tax exemption policies remain beneficial to both the state and the entities they serve.
What is the purpose of the Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form (Form EX-32)?
+The Wisconsin Tax Exempt Form, or Form EX-32, is used by eligible organizations and individuals to claim exemption from specific taxes in the state of Wisconsin. It allows entities to reduce their overall tax liability by demonstrating their eligibility for tax-exempt status.
Who is eligible to apply for tax exemption in Wisconsin?
+Eligibility for tax exemption in Wisconsin varies depending on the type of exemption. Generally, non-profit organizations, charitable institutions, religious entities, educational institutions, and certain government bodies may be eligible. For individuals, exemptions are often based on criteria such as income level, disability status, or veteran status.
What are the key benefits of obtaining tax-exempt status in Wisconsin?
+The benefits of tax-exempt status in Wisconsin include financial savings on taxes, enhanced credibility within the community, and operational advantages such as streamlined procurement processes. Tax exemption allows organizations to redirect funds towards their mission and operations, improving overall efficiency and impact.
How often do I need to renew my tax-exempt status in Wisconsin?
+The renewal requirements for tax-exempt status in Wisconsin vary depending on the type of exemption. Some exemptions, such as property tax exemption, may require periodic renewal, often on an annual basis. Other exemptions, like income tax exemptions, may have different renewal periods or be valid indefinitely if the eligibility criteria continue to be met.
What happens if I fail to maintain compliance with tax-exempt status requirements?
+Failure to maintain compliance with tax-exempt status requirements in Wisconsin can result in the revocation of tax-exempt status. This may lead to significant tax liabilities, penalties, and legal consequences. It is crucial for entities to stay informed about the ongoing requirements and consult with tax professionals to ensure continued compliance.