When Is No Tax On Overtime Start

Understanding when no tax is applied to overtime earnings is a crucial aspect of financial planning, especially for individuals who frequently work beyond their regular hours. This article delves into the intricacies of overtime tax laws, offering a comprehensive guide to help workers maximize their earnings while adhering to legal regulations.
Overtime Tax Exemption: Navigating the Legal Landscape

The concept of overtime tax exemption varies significantly across jurisdictions, with different rules governing when and how overtime pay is taxed. While some regions impose tax on all forms of income, including overtime, others provide specific exemptions or deductions to incentivize productivity and reward hard work.
In the United States, for instance, the Fair Labor Standards Act mandates that non-exempt employees must be paid time-and-a-half for hours worked beyond the standard workweek. This premium pay, however, may or may not be subject to federal, state, and local taxes, depending on the applicable laws.
Key Factors Influencing Overtime Tax Exemption
The determination of whether overtime pay is taxable or exempt hinges on a variety of factors, including:
- The employee’s tax filing status and withholding allowances, which influence the amount of tax withheld from regular pay and, consequently, overtime pay.
- State and local tax laws, which can vary significantly and may impose additional taxes on overtime earnings.
- The nature of the work and the employee’s job classification, as certain professions or industries may be subject to different tax rules.
- Employment contracts and collective bargaining agreements, which may include provisions regarding overtime pay and tax liability.
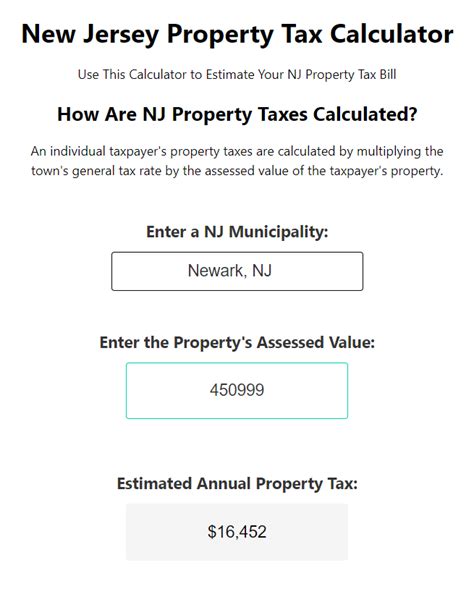
For example, in certain states like Texas and Florida, there is no state income tax, which means that overtime pay is only subject to federal and local taxes. In contrast, states like California and New York have their own income tax systems, which can result in higher tax burdens for overtime work.
| State | Income Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Texas | 0% |
| Florida | 0% |
| California | 1-13.3% |
| New York | 4-8.82% |

Maximizing Your Overtime Earnings: Strategies and Tips
Understanding the tax implications of overtime work is just the first step. To make the most of your overtime earnings, consider the following strategies:
- Review your pay stubs regularly to ensure that your overtime pay is calculated correctly and that the appropriate taxes are being withheld.
- If you’re eligible for tax deductions or credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit, ensure you claim them when filing your taxes to reduce your overall tax liability.
- Consider adjusting your withholding allowances to optimize your tax situation. This can help ensure you’re not overpaying on taxes throughout the year, leaving you with a larger refund or minimizing your tax bill at the end of the year.
Conclusion: Empowering Workers with Knowledge

The world of overtime tax laws can be complex, but with the right information, workers can navigate these regulations with confidence. By understanding when overtime pay is exempt from taxes and employing strategic financial planning, individuals can maximize their earnings and make the most of their hard work.
Stay informed, stay proactive, and always seek professional advice when needed. Your financial well-being is a priority, and knowledge is a powerful tool in achieving it.
Are there any situations where overtime pay is always exempt from taxes?
+In general, overtime pay is subject to taxes, but there are specific cases where it might be exempt. For instance, some government employees, such as military personnel, may have certain overtime pay exempt from federal taxes. However, these situations are rare and vary greatly depending on the jurisdiction and employment context.
How can I calculate my potential tax liability on overtime pay?
+Calculating tax liability on overtime pay involves understanding your tax bracket, applicable tax rates, and the tax laws in your jurisdiction. It’s best to consult a tax professional or use reliable tax calculation tools to ensure accuracy.
What happens if I don’t pay the correct amount of tax on my overtime earnings?
+Failing to pay the correct amount of tax on overtime earnings can lead to penalties and interest charges. It’s important to accurately report and pay taxes to avoid legal issues and financial burdens.