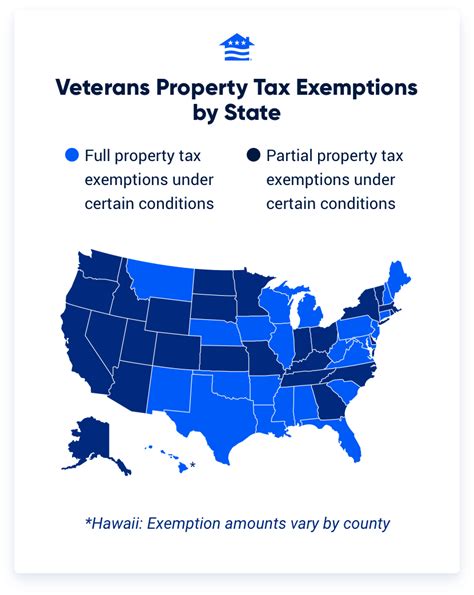
Washington State B And O Tax

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Washington State Business and Occupation (B&O) Tax, a critical component of doing business in the Evergreen State. This article aims to provide you with an in-depth understanding of this tax, its intricacies, and its impact on businesses of all sizes and industries. By the end of this read, you should have a clear grasp of what the B&O tax entails, how it's calculated, and the steps you can take to ensure compliance.
Unraveling the Washington State B&O Tax
The Business and Occupation (B&O) tax is a critical element of Washington’s tax structure, serving as a primary revenue source for the state. It’s a privilege tax imposed on the act or right of engaging in business activities within the state’s borders. This tax is unique in its structure and application, making it an essential topic for businesses to understand.
Unlike many other state taxes, the B&O tax is not a traditional income or sales tax. Instead, it's a gross receipts tax, meaning it's calculated based on the total revenue generated by a business from all sources within the state. This includes income from sales, services, and other business activities. The tax rate and classification depend on the nature of the business, making it a complex but fair system tailored to each industry.
B&O Tax Rates and Categories
Washington State categorizes businesses into different classes for B&O tax purposes, each with its own specific tax rate. These categories are designed to ensure fairness and reflect the unique characteristics of each industry. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the primary B&O tax classifications and their corresponding rates:
| B&O Tax Category | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Retail Sales | 0.471% (with potential for higher rates in some cities) |
| Wholesale Sales | 0.448% |
| Manufacturing/Processing | 0.484% |
| Service and Other Activities | 1.8% |
| Public Utility | 3.955% |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change, and certain industries or activities may have specific modifications or exemptions. Additionally, Washington offers a variety of tax incentives and credits that can significantly impact a business's tax liability. Understanding these classifications and potential deductions is crucial for effective tax planning.
Calculating B&O Tax: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating your B&O tax liability involves several steps, each dependent on your business’s specific activities and revenue streams. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Determine your business's primary activity or activities. This will help you identify the correct B&O tax category or categories that apply to your business.
- Identify all sources of revenue within the state of Washington. This includes sales, services, rentals, and any other business-related income.
- Classify each revenue stream according to the appropriate B&O tax category. For example, revenue from sales of tangible goods would fall under the Retail Sales category, while revenue from providing a service would fall under the Service and Other Activities category.
- Calculate the B&O tax liability for each category using the applicable tax rate. This involves multiplying the total revenue for each category by its respective tax rate.
- Add up the B&O tax liabilities from each category to arrive at your total B&O tax liability for the reporting period.
- Deduct any applicable tax credits or incentives from your total B&O tax liability to determine your final tax liability. These credits can significantly reduce your tax burden and are often based on specific business activities or investments.
It's crucial to keep accurate records of all revenue sources and expenses to ensure an accurate calculation and to support any deductions or credits claimed. Additionally, businesses should be aware of potential audit risks and maintain proper documentation to substantiate their tax filings.
Compliance and Reporting Requirements
Compliance with the B&O tax is a critical aspect of doing business in Washington. The state has strict reporting requirements, and businesses must adhere to specific deadlines to avoid penalties and interest charges. Here’s a general overview of the compliance process:
- Registration: All businesses engaging in taxable activities within Washington must register with the Washington Department of Revenue. This process involves providing detailed information about your business activities, tax classification, and estimated tax liability.
- Tax Return Filing: The frequency of filing B&O tax returns depends on your business's tax liability and the type of activities you engage in. Monthly, quarterly, or annual filing may be required. Tax returns must be filed by the 25th day of the month following the reporting period.
- Payment: Taxes must be paid along with the filing of the tax return. The payment method and timing may vary based on your business's tax liability and the preferences of the Department of Revenue.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate and detailed records is crucial for B&O tax compliance. These records should include all revenue sources, expenses, and any supporting documentation for deductions or credits claimed. The Department of Revenue may request these records during an audit.
- Audits and Examinations: The Department of Revenue has the authority to conduct audits to ensure compliance with the B&O tax laws. These audits can be comprehensive, so being prepared and maintaining proper records is essential. During an audit, the Department may request additional documentation to support your tax filings.
Staying informed about your B&O tax obligations and maintaining open communication with the Department of Revenue can help mitigate potential compliance issues. Additionally, staying updated on any changes to tax laws and regulations is crucial to ensure ongoing compliance.
Future Outlook and Implications
The B&O tax system in Washington has been a subject of debate and reform efforts over the years. While the current structure provides a stable revenue stream for the state, there are ongoing discussions about potential reforms to make the tax system more equitable and business-friendly. Here are some key considerations for the future:
- Tax Reform Initiatives: There have been proposals to modify the B&O tax structure, including introducing a flat tax rate for all businesses or shifting to a value-added tax (VAT) system. These reforms aim to simplify the tax system and reduce the tax burden on certain industries.
- Economic Impact: The B&O tax significantly impacts businesses' bottom lines, especially those with high gross revenues. Reforms could potentially reduce this burden, making Washington a more attractive place to do business.
- Political Landscape: The political climate in Washington plays a crucial role in shaping the future of the B&O tax. Any changes to the tax system would require legislative action, which is influenced by various interest groups and public opinion.
- Technology and Digital Economy: With the rise of the digital economy, there's a growing need to adapt tax systems to accommodate new business models. Washington's B&O tax system will need to evolve to address the unique challenges posed by e-commerce and digital services.
Staying informed about these developments and engaging in discussions around tax reform can help businesses anticipate changes and adapt their strategies accordingly. It's an exciting time for Washington's tax landscape, with potential for significant shifts that could impact businesses across the state.
Conclusion
The Washington State Business and Occupation (B&O) tax is a vital component of the state’s tax system, playing a significant role in funding essential services and infrastructure. While it may be complex, understanding this tax and staying compliant is essential for any business operating within the state’s borders. By grasping the nuances of the B&O tax, businesses can navigate its complexities, leverage available incentives, and contribute effectively to the state’s economy.
How often do I need to file B&O tax returns in Washington State?
+
The filing frequency for B&O tax returns in Washington depends on your business’s tax liability and activities. If your annual B&O tax liability exceeds 20,000, you must file monthly returns. For liabilities between 10,000 and 20,000, quarterly filing is required. If your liability is below 10,000, you can file annually. However, it’s important to note that these thresholds may change, so it’s best to check with the Washington Department of Revenue for the most up-to-date information.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available for B&O tax in Washington State?
+
Yes, Washington offers a variety of tax incentives and credits to support businesses and encourage specific activities. These include credits for research and development, manufacturing, job creation, and more. It’s worth exploring these incentives, as they can significantly reduce your B&O tax liability. However, eligibility criteria and requirements vary, so it’s best to consult with a tax professional or the Department of Revenue for detailed information.
What happens if I miss the deadline for filing my B&O tax return in Washington State?
+
Missing the deadline for filing your B&O tax return can result in penalties and interest charges. The Department of Revenue may impose a late filing penalty of up to 10% of the tax due, along with interest on the outstanding tax liability. It’s important to stay on top of filing deadlines and consider engaging a tax professional or utilizing tax software to ensure timely submissions.
How can I prepare for a B&O tax audit in Washington State?
+
Preparing for a B&O tax audit involves maintaining accurate and detailed records. Ensure you have documentation to support your revenue sources, expenses, and any deductions or credits claimed. Stay organized and keep a record of all communications with the Department of Revenue. It’s also beneficial to understand the audit process and your rights during an examination. Consider seeking guidance from a tax professional if you have concerns or questions.