What Is Nys Sales Tax
The New York State Sales Tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and certain services within the state. It is an essential component of New York's revenue system, contributing significantly to the state's budget and funding various public services and infrastructure projects. Understanding the intricacies of the NYS sales tax is crucial for both businesses and consumers alike, as it impacts pricing, budgeting, and compliance.
The Basics of NYS Sales Tax

The NYS sales tax is imposed on the retail sale, lease, or rental of tangible personal property, as well as on certain services. The tax is collected by the seller and remitted to the state, with the ultimate economic burden typically borne by the consumer. The rate varies depending on the location of the sale, as New York allows for local and municipal governments to impose additional sales taxes.
For instance, consider a purchase made in New York City. The current state sales tax rate is 4%, but the city imposes an additional 4.5% tax, resulting in a combined rate of 8.5%. This means that for every $100 spent on taxable goods or services, $8.50 goes towards sales tax.
| Sales Tax Rate by Jurisdiction | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| New York State | 4% |
| New York City | 8.5% |
| Long Island (Nassau & Suffolk Counties) | 6% |
| Albany County | 4.5% |
| Other Counties | Varies |
The sales tax is calculated based on the purchase price, including any applicable discounts or promotions. It's important to note that not all goods and services are subject to sales tax. Certain categories, such as groceries, prescription drugs, and clothing items under a specific price threshold, are exempt from the tax.
Exemptions and Special Cases
Understanding the exemptions and special cases under the NYS sales tax is crucial for both businesses and consumers. For instance, while clothing is generally subject to sales tax, items costing 110 or less per article are exempt. This means that a shirt costing 100 would not be taxed, but a suit priced at $200 would incur sales tax.
Similarly, certain services are exempt from sales tax. For example, legal and professional services, such as those provided by attorneys, accountants, and architects, are not subject to the tax. Additionally, many types of repairs and maintenance services, such as automotive repairs and home improvements, are also exempt.
It's important to note that while these categories are generally exempt, there may be specific circumstances or localities where additional taxes or surcharges apply. For instance, some localities impose an additional tax on prepared foods or on certain entertainment services.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
Sales tax collection and remittance is a critical aspect of compliance for businesses operating in New York. As a seller, it’s your responsibility to collect the appropriate tax from customers and remit it to the state on a regular basis. The frequency of remittance depends on your business’s tax liability, with options ranging from monthly to annually.
The process typically involves registering your business with the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance, obtaining a sales tax certificate of authority, and then collecting the tax at the point of sale. The tax is usually calculated and displayed separately on the customer's receipt, ensuring transparency in the transaction.
Remitting the collected tax involves filing a sales tax return with the Department of Taxation and Finance. This return details the total sales tax collected during the reporting period and includes any applicable adjustments or credits. Failure to remit sales tax accurately and on time can result in penalties and interest, so it's crucial to stay organized and up-to-date with your obligations.
Sales Tax Filing and Due Dates
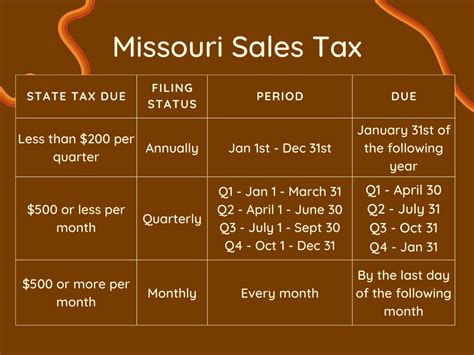
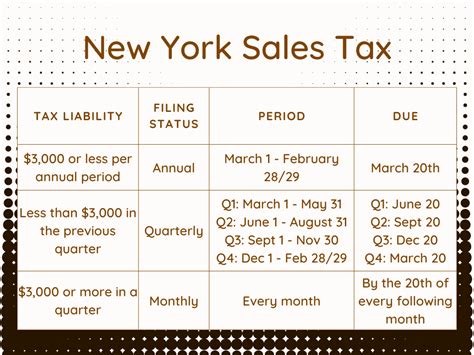
Sales tax filing in New York is a straightforward process, but it’s important to understand the deadlines to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. The due date for filing and remitting sales tax depends on the frequency of your reporting period, which is determined by your business’s tax liability.
For most businesses, the reporting period is monthly, with the sales tax return and payment due on the 20th day of the following month. So, for sales made in January, the return and payment would be due on February 20th. However, if the 20th falls on a weekend or holiday, the due date is typically extended to the next business day.
For businesses with lower tax liabilities, the reporting period may be quarterly or even annually. Quarterly filers have due dates in April, July, October, and January, while annual filers typically have a due date of January 31st.
It's important to note that while these are the standard due dates, certain circumstances, such as natural disasters or technological issues, may lead to extensions or changes in due dates. Always refer to the official guidelines and notifications from the Department of Taxation and Finance for the most up-to-date information.
Compliance and Penalties
Compliance with NYS sales tax regulations is essential for businesses to avoid penalties and maintain a positive relationship with the state. Failure to collect and remit sales tax accurately can result in significant financial consequences, including penalties, interest, and even legal action.
Penalties for non-compliance can be steep, with the Department of Taxation and Finance imposing fines based on the amount of tax owed and the severity of the violation. Interest is also charged on any outstanding tax liabilities, accruing from the due date of the tax until it's paid in full.
In addition to financial penalties, non-compliance can lead to audits and investigations, which can be time-consuming and disruptive for businesses. During an audit, the Department of Taxation and Finance may examine a business's records, including sales receipts, invoices, and accounting ledgers, to ensure accurate tax reporting and collection.
Tips for Staying Compliant
Staying compliant with NYS sales tax regulations is essential for businesses, and it starts with understanding the rules and staying informed about any changes. Here are some practical tips to help you maintain compliance:
- Register your business with the Department of Taxation and Finance and obtain a sales tax certificate of authority.
- Clearly display the applicable sales tax rate at your place of business and on your website (if applicable).
- Ensure your point-of-sale system is programmed to calculate and display the correct tax.
- Keep accurate records of all sales, including exempt and taxable transactions.
- Regularly review your sales tax liabilities and adjust your remittance schedule as needed.
- Stay updated with any changes in tax rates or regulations, especially if you operate in multiple jurisdictions.
- Consider using accounting software or hiring a tax professional to assist with sales tax compliance.
By staying informed and organized, businesses can navigate the complexities of the NYS sales tax system with ease, ensuring compliance and avoiding unnecessary penalties.
NYS Sales Tax and E-Commerce
The rise of e-commerce has significantly impacted the collection and enforcement of sales tax, especially in New York. With the growth of online shopping, the state has had to adapt its regulations to ensure that sales tax is collected fairly and efficiently from remote sellers.
One of the key changes is the implementation of economic nexus, which means that out-of-state sellers with substantial connections to New York, such as a certain level of sales or a physical presence, are required to collect and remit sales tax on transactions with New York customers. This ensures that online retailers, even those without a physical store in the state, contribute to the state's revenue stream.
For instance, an online retailer based in California that sells products to New York residents may be required to register with the Department of Taxation and Finance and collect sales tax on those transactions if their sales to New York customers exceed a certain threshold.
Challenges and Solutions for E-Commerce Sellers
Navigating the complexities of sales tax in the e-commerce world can be challenging for online sellers, especially those who operate in multiple states. Here are some key considerations and strategies to help e-commerce businesses stay compliant with NYS sales tax regulations:
- Understand the concept of economic nexus and determine whether your business has a nexus in New York based on sales or physical presence.
- If you have nexus, register with the Department of Taxation and Finance and obtain a sales tax certificate of authority.
- Use sales tax automation software to calculate and collect the correct tax rates for each transaction, taking into account the buyer's location.
- Stay updated with any changes in tax rates or regulations, as they can vary significantly between jurisdictions.
- Consider the use of a marketplace facilitator, especially if you sell through third-party platforms. Marketplace facilitators are often responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax on behalf of sellers.
- Regularly review your sales tax liabilities and remittances to ensure accuracy and compliance.
By staying informed and utilizing the right tools and strategies, e-commerce sellers can navigate the complexities of NYS sales tax and ensure they're contributing fairly to the state's revenue system.
Future of NYS Sales Tax

As New York continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic and technological landscapes, the future of its sales tax system is likely to see further innovations and reforms. Here are some potential developments and their implications:
Expanding Online Sales Tax Collection
With the continued growth of e-commerce, New York is likely to further expand its efforts to collect sales tax from online sellers. This may involve stricter enforcement of economic nexus rules and the potential introduction of new regulations or legislation to ensure fair taxation of remote sellers.
For businesses, this could mean increased compliance obligations and the need to adapt their sales tax strategies to stay compliant. It's essential to stay updated with any changes in regulations and consider investing in sales tax automation tools to streamline the process.
Exploring Alternative Tax Structures
New York, like many states, is exploring alternative tax structures to address concerns about the regressiveness of sales tax and its impact on low-income households. One potential alternative is a value-added tax (VAT), which is common in many countries but less so in the United States.
A VAT is a consumption tax placed on the value added at each stage of the supply chain, from production to final sale. It's typically easier to administer and can provide a more stable revenue stream. However, it may also be more complex for businesses to navigate.
Should New York move towards a VAT or other alternative tax structures, businesses would need to adapt their accounting and tax strategies accordingly. It's important to stay informed about any proposed changes and their potential impact on your operations.
Focus on Compliance and Education
As the sales tax system becomes more complex, especially with the integration of e-commerce and potential structural changes, New York may place a greater emphasis on compliance and education. This could involve increased outreach and resources to help businesses understand their obligations and stay compliant.
Businesses can expect more guidance and support from the Department of Taxation and Finance, as well as potentially more stringent enforcement measures to ensure compliance. Staying engaged with these resources and being proactive about compliance can help businesses navigate the complexities of the NYS sales tax system effectively.
Conclusion
The NYS sales tax is a critical component of New York’s revenue system, funding essential public services and infrastructure. While it can be complex, especially for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions or online, understanding the rules and staying compliant is essential. By staying informed, utilizing the right tools, and adapting to changes, businesses can navigate the NYS sales tax system successfully and contribute fairly to the state’s economy.
What goods and services are exempt from NYS sales tax?
+Many goods and services are exempt from NYS sales tax, including groceries, prescription drugs, and clothing items under a certain price threshold. Additionally, legal and professional services, as well as many types of repairs and maintenance services, are also exempt.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in New York?
+The frequency of sales tax remittance depends on a business’s tax liability. Most businesses remit sales tax monthly, but quarterly or annual remittance is also possible for those with lower tax liabilities. The due date is typically the 20th day of the following month, or the next business day if it falls on a weekend or holiday.
What happens if a business fails to remit sales tax on time in New York?
+Failure to remit sales tax accurately and on time can result in penalties and interest. The Department of Taxation and Finance imposes fines based on the amount of tax owed and the severity of the violation. Interest is also charged on outstanding tax liabilities, accruing from the due date until paid in full. In severe cases, non-compliance can lead to audits and legal action.
How does economic nexus impact e-commerce sellers in New York?
+Economic nexus requires out-of-state sellers with substantial connections to New York, such as a certain level of sales or a physical presence, to collect and remit sales tax on transactions with New York customers. This means that e-commerce sellers may need to register with the Department of Taxation and Finance, collect sales tax, and remit it to the state based on their nexus status.
What are the potential future developments for NYS sales tax?
+The future of NYS sales tax is likely to involve further expansion of online sales tax collection, exploration of alternative tax structures like a value-added tax (VAT), and a continued focus on compliance and education to help businesses navigate the complexities of the tax system.