What Is Ad Valorem Tax
Ad valorem tax, a fundamental component of fiscal policy, is a term often encountered in discussions about property and consumption taxation. Its significance extends beyond mere taxation, impacting economic policies, consumer behavior, and the overall financial landscape. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of ad valorem tax, exploring its definition, historical context, types, and its far-reaching implications on individuals, businesses, and governments.
Understanding Ad Valorem Tax: A Comprehensive Overview
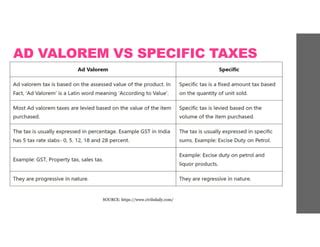
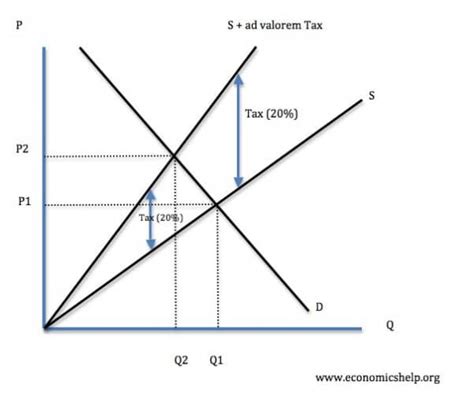
At its core, ad valorem tax is a percentage-based levy applied to the assessed value of a property, good, or service. Unlike other taxes, such as specific or per unit taxes, ad valorem taxes are directly proportional to the value of the item being taxed. This makes it a flexible and scalable form of taxation, allowing governments to collect revenue based on the market value of goods and services.
The concept of ad valorem tax has a rich historical background, dating back to ancient civilizations. Early forms of this tax were implemented by various societies, with the Romans being one of the earliest adopters. They levied a 10% tax on the value of goods sold at auctions, a practice that laid the foundation for modern ad valorem taxation systems.
Today, ad valorem taxes are widely used by governments worldwide to generate revenue and regulate economic activities. They are a key tool in fiscal policies, influencing consumer behavior, business strategies, and the overall economic climate.
Types of Ad Valorem Tax: A Detailed Exploration

Ad valorem taxes can be categorized into several types, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these types is crucial to grasp the versatility and impact of ad valorem taxation.
Property Taxes
Property taxes are a common form of ad valorem tax, where the levy is imposed on the value of real estate properties. This includes land, buildings, and improvements, with the tax amount determined by the assessed value of the property. Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments, funding essential services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
The assessment process for property taxes involves a thorough evaluation of the property's features, location, and market trends. Professional assessors use various methods, including the sales comparison approach, cost approach, and income approach, to determine the fair market value of the property.
| Property Type | Assessment Method |
|---|---|
| Residential Properties | Sales Comparison Approach |
| Commercial Properties | Income Approach |
| Special Use Properties | Cost Approach |

Sales and Use Taxes
Sales and use taxes are ad valorem taxes applied to the purchase of goods and services. These taxes are typically imposed at the point of sale, with the amount calculated as a percentage of the sale price. Sales taxes are a major source of revenue for state and local governments, funding a wide range of public services and infrastructure projects.
The use tax, a counterpart to the sales tax, is applied to goods and services purchased from out-of-state vendors or through online platforms. This ensures that consumers pay taxes on all purchases, regardless of where the transaction takes place. Use taxes help level the playing field for local businesses and prevent tax evasion.
Value Added Tax (VAT)
Value Added Tax, or VAT, is an ad valorem tax imposed on the value added to a product at each stage of its production and distribution. It is a consumption tax, meaning it is ultimately borne by the end consumer. VAT is a popular tax system in many countries, known for its efficiency and ability to capture a broad tax base.
The mechanism of VAT involves taxing each stage of production and distribution separately, with the tax amount being calculated on the difference between the selling price and the purchase price of goods or services. This multi-stage approach ensures that taxes are collected at each step, reducing the likelihood of tax evasion.
Excise Taxes
Excise taxes are ad valorem taxes levied on specific goods or services, often to discourage consumption or generate revenue from specific industries. These taxes are typically applied to luxury items, harmful substances, or environmentally sensitive products. Excise taxes can be based on the value of the product or a fixed amount per unit.
For example, many countries impose excise taxes on tobacco products, alcohol, and fuel. These taxes not only generate revenue but also serve as a tool for public health and environmental policies, discouraging consumption of harmful substances and promoting sustainable practices.
The Impact and Implications of Ad Valorem Taxation
Ad valorem taxes have far-reaching implications on various aspects of society and the economy. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike.
Revenue Generation and Fiscal Policy
Ad valorem taxes are a significant source of revenue for governments at all levels. They provide a stable and predictable stream of income, enabling governments to fund public services, infrastructure projects, and social welfare programs. The flexibility of ad valorem taxes allows governments to adjust tax rates to meet fiscal needs and economic goals.
For instance, during economic downturns, governments may opt to increase ad valorem tax rates to generate additional revenue, while reducing rates during economic booms to stimulate consumption and investment.
Economic Incentives and Consumer Behavior
Ad valorem taxes have a direct impact on consumer behavior and market dynamics. By imposing taxes on certain goods or services, governments can influence consumer choices and market trends. This is particularly evident in the case of excise taxes, where higher taxes on harmful substances can discourage consumption and promote healthier lifestyles.
Additionally, ad valorem taxes can create incentives for businesses to innovate and develop new products. By taxing specific industries or products, governments can encourage the development of more efficient and sustainable alternatives, fostering economic growth and environmental sustainability.
International Trade and Global Economics
Ad valorem taxes also play a significant role in international trade and global economics. Countries often use import and export taxes to protect domestic industries, manage trade imbalances, and raise revenue. These taxes can impact the cost of imported goods, influencing trade patterns and the competitiveness of domestic industries.
For example, a country may impose high import taxes on foreign automobiles to protect its domestic automotive industry. This can lead to increased prices for imported cars, making them less attractive to consumers and potentially shifting the market towards domestic brands.
Social Equity and Income Distribution
Ad valorem taxes can also have implications for social equity and income distribution. By taxing higher-value properties or luxury goods at higher rates, governments can generate revenue from those with higher incomes, potentially reducing income inequality. Conversely, ad valorem taxes on essential goods and services can disproportionately impact low-income individuals, requiring careful consideration and potential exemptions or subsidies.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving Role of Ad Valorem Taxation
Ad valorem taxation is a dynamic and multifaceted tool in the realm of fiscal policy. Its impact extends beyond revenue generation, influencing economic growth, consumer behavior, international trade, and social equity. As economies evolve and new challenges arise, ad valorem taxes will continue to play a critical role in shaping economic policies and societal outcomes.
The ongoing debate surrounding ad valorem taxation revolves around finding the right balance between revenue generation and social equity. Policymakers must carefully consider the implications of tax policies, ensuring they promote economic growth, protect vulnerable populations, and contribute to a fair and sustainable society.
How are ad valorem taxes calculated?
+Ad valorem taxes are calculated as a percentage of the assessed value of a property, good, or service. The tax amount is determined by multiplying the assessed value by the applicable tax rate. For example, if a property is valued at 500,000 and the tax rate is 2%, the ad valorem tax would be 10,000.
Are ad valorem taxes the same as sales taxes?
+While both ad valorem taxes and sales taxes are levied on the value of goods or services, they have some key differences. Sales taxes are typically applied at the point of sale, whereas ad valorem taxes can be applied at various stages, such as production, distribution, or consumption. Additionally, sales taxes are often imposed by state or local governments, while ad valorem taxes can be levied by federal, state, or local authorities.
How do ad valorem taxes impact businesses?
+Ad valorem taxes can have a significant impact on businesses, especially those involved in production, distribution, or sale of goods and services. These taxes can increase the cost of doing business, impacting profit margins and pricing strategies. Businesses may also face challenges in managing cash flow due to the timing of tax payments. However, ad valorem taxes can also provide incentives for innovation and efficiency, leading to long-term business growth.