What Is A Schedule 1 Tax Form
In the complex realm of taxation, understanding the nuances of various forms is crucial for both individuals and businesses. One such form that often sparks curiosity and questions is the Schedule 1 tax form. This document plays a pivotal role in the US tax system, particularly for those with specific income sources and deductions. Let's delve into the details of Schedule 1, exploring its purpose, key components, and its significance in the tax landscape.
Unraveling Schedule 1: An Essential Tax Companion

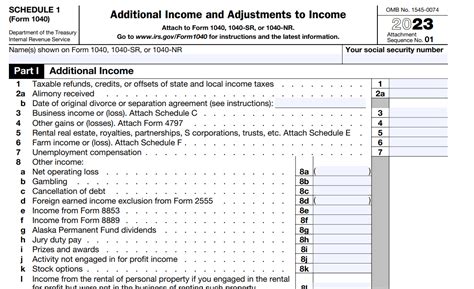
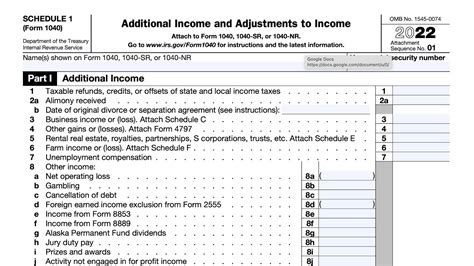
Schedule 1, officially known as the “Form 1040 Schedule 1 - Additional Income and Adjustments to Income,” is a supplementary document to the primary US individual income tax return form, Form 1040. While not all taxpayers need to file Schedule 1, it becomes a vital tool for those with certain income types and adjustments that require additional reporting.
The Purpose and Applicability of Schedule 1
Schedule 1 is designed to accommodate various income sources and deductions that do not fit neatly into the primary Form 1040. Its primary purpose is to provide a comprehensive breakdown of these additional income streams and adjustments, ensuring taxpayers accurately report their financial activities and determine their taxable income.
Here’s a glimpse at the key scenarios where Schedule 1 becomes a necessity:
- Alimony Received: Individuals receiving alimony payments must report this income on Schedule 1, as it is considered taxable.
- Capital Gains and Losses: Investors who sell assets, such as stocks or real estate, need to calculate and report capital gains or losses on Schedule 1.
- Business Income: Sole proprietors and single-member LLCs use Schedule 1 to report business income and expenses, often in conjunction with Schedule C.
- Additional Income Sources: Taxpayers with miscellaneous income, such as prizes, awards, or rental income, must include these on Schedule 1.
- Certain Deductions: Some deductions, like student loan interest or qualified tuition expenses, are reported on Schedule 1 and then transferred to Form 1040.
Completing Schedule 1: A Step-by-Step Guide
Completing Schedule 1 involves a systematic process of gathering the necessary information and entering it into the appropriate sections. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Gather Income Documents: Collect all relevant income statements, such as W-2 forms, 1099-MISC forms, or business income records.
- Identify Applicable Income: Review the income sources and determine which fall under the categories listed on Schedule 1.
- Calculate Adjustments: For items like capital gains/losses or student loan interest, calculate the adjustment amounts using the provided formulas or worksheets.
- Enter Income and Adjustments: Input the applicable income and adjustment amounts into the corresponding lines on Schedule 1.
- Transfer to Form 1040: Once completed, transfer the total additional income and adjustments from Schedule 1 to the appropriate lines on Form 1040.
It's essential to note that Schedule 1 is just one part of the broader tax return process. Depending on an individual's circumstances, other schedules and forms might also be necessary, such as Schedule C for business income or Schedule E for rental income.
The Impact of Schedule 1 on Tax Liability
Schedule 1 directly influences a taxpayer’s overall tax liability. By providing a detailed breakdown of additional income and adjustments, it ensures that taxpayers accurately report their financial activities. This transparency is crucial for the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to assess tax obligations accurately.
Moreover, Schedule 1 can impact tax refunds or the amount owed. For instance, reporting capital gains or business income on Schedule 1 might increase tax liability, while deductions like student loan interest could reduce it. Therefore, a thorough understanding of Schedule 1’s role is essential for optimizing tax strategies.
| Income Source | Schedule 1 Section |
|---|---|
| Alimony Received | Line 1 |
| Capital Gains | Lines 2-4 |
| Business Income | Line 12 |
| Miscellaneous Income | Line 14 |
FAQs
Do I Need to File Schedule 1 Every Year?
+No, Schedule 1 is only required if you have specific income sources or adjustments that fall under its categories. If your financial situation remains consistent, you might not need to file it annually.
Can I File Schedule 1 Electronically?
+Yes, Schedule 1 can be filed electronically as part of your tax return. Most tax preparation software and online filing platforms offer the option to complete and submit Schedule 1 digitally.
What Happens If I Forget to File Schedule 1?
+If you have income or adjustments that should be reported on Schedule 1 but forget to include it, you may face penalties or additional taxes. It’s crucial to review your tax return carefully before submission.
Can I File Schedule 1 if I’m Self-Employed?
+Yes, self-employed individuals often use Schedule 1 in conjunction with Schedule C to report business income and expenses. Schedule 1 helps capture additional income sources and adjustments related to self-employment.