Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax
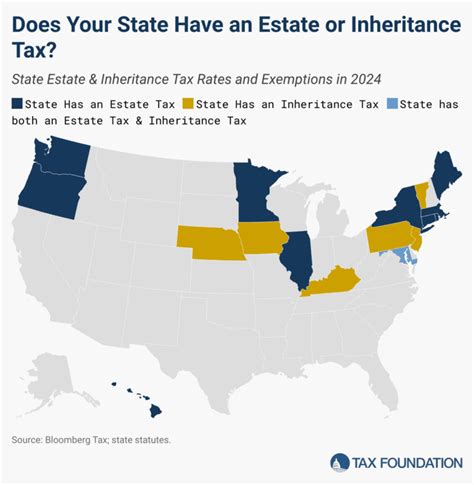
The Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax is an important aspect of estate planning and management in the state. It is a tax imposed on the transfer of assets from a deceased individual's estate to their beneficiaries. Understanding the intricacies of this tax is crucial for individuals and families to ensure a smooth and efficient estate settlement process. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax, providing valuable insights and information to help you navigate this complex topic.
Understanding the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax

The Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax, often referred to as the inheritance tax or estate tax, is a state-level tax that applies to certain individuals who inherit property or assets from a deceased Virginia resident. It is distinct from the federal estate tax, as each state has its own set of regulations and thresholds for inheritance taxation.
In Virginia, the inheritance tax is levied on the beneficiaries of the estate, rather than the estate itself. This means that the individuals who receive assets or property from the deceased person's estate are responsible for paying the tax. The tax rate and exemptions vary depending on the relationship between the beneficiary and the deceased, as well as the value of the inherited assets.
Tax Rates and Exemptions
The tax rates for the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax are progressive, meaning they increase as the value of the inherited assets rises. The tax is calculated based on the fair market value of the property or assets received by each beneficiary.
| Relationship to Deceased | Tax Rate | Exemption Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Spouse | 0% | $26,000,000 |
| Children | 6% (on amounts over $5,000) | $25,000 |
| Parents, Grandparents, Siblings | 6% (on amounts over $1,000) | $1,000 |
| All Other Individuals | 15% (on amounts over $500) | $500 |
It's important to note that the exemptions and tax rates are subject to change, so it is advisable to consult the latest Virginia tax regulations for the most accurate information.
Who is Liable for the Tax?
The liability for the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax falls on the beneficiaries of the estate. Each beneficiary is responsible for filing their own tax return and paying the applicable tax based on the value of the assets they receive. It is essential for beneficiaries to understand their tax obligations and comply with the reporting requirements to avoid penalties and interest.
Estate Planning and Tax Minimization Strategies
Estate planning is a crucial aspect of managing one’s assets and ensuring a smooth transition for their beneficiaries. In the context of the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax, there are several strategies that individuals can employ to minimize the tax burden and maximize the value of their estate.
Gifting Strategies
One effective way to reduce the value of an estate and potentially lower the inheritance tax liability is through strategic gifting. Virginia allows individuals to make gifts during their lifetime without triggering the inheritance tax. By gifting assets to beneficiaries in a structured manner, individuals can reduce the overall value of their estate and potentially minimize the tax burden for their heirs.
For example, an individual could gift a certain amount of assets each year to their children or grandchildren, utilizing the annual gift tax exclusion, which is currently set at $16,000 per beneficiary. This strategy can help transfer wealth tax-free and reduce the potential tax liability upon inheritance.
Trusts and Estate Planning Vehicles
Establishing trusts is another powerful tool for estate planning and tax minimization. Trusts can be designed to hold assets and distribute them to beneficiaries in a tax-efficient manner. By utilizing trusts, individuals can control the distribution of their assets, protect them from creditors, and potentially reduce the overall tax liability.
There are various types of trusts that can be utilized, such as revocable living trusts, irrevocable trusts, and charitable trusts. Each type has its own advantages and considerations, and it is important to work with an estate planning professional to determine the most suitable trust structure for your specific needs.
Charitable Giving
Donating to charitable organizations can also provide tax benefits and help reduce the overall value of an estate. Virginia, like many other states, offers tax incentives for charitable contributions. By making charitable gifts during one’s lifetime or as part of an estate plan, individuals can potentially lower their tax burden and support causes that are important to them.
Additionally, charitable lead trusts or charitable remainder trusts can be established to provide ongoing support to charities while also benefiting the trust's beneficiaries. These trusts can offer tax advantages and flexibility in estate planning.
The Role of Estate Executors and Fiduciaries
Estate executors and fiduciaries play a vital role in the administration and settlement of an estate. They are responsible for managing the estate’s assets, paying any outstanding debts and taxes, and distributing the remaining assets to the beneficiaries.
Executor’s Responsibilities
An executor is appointed by the deceased individual or named in their will. The executor’s primary duties include:
- Identifying and gathering the deceased's assets.
- Paying any outstanding debts, including funeral expenses and medical bills.
- Filing the necessary tax returns, including the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax return.
- Distributing the remaining assets to the beneficiaries in accordance with the will or state laws.
The executor must act in the best interests of the estate and its beneficiaries, ensuring that all legal and financial obligations are met.
Fiduciary Duties
Fiduciaries, such as trustees or power of attorney agents, have a legal duty to act in the best interests of the estate and its beneficiaries. They are responsible for managing and administering the estate’s assets according to the instructions provided in the estate planning documents.
Fiduciaries must exercise prudence and diligence in their decision-making, ensuring that the estate's assets are protected and managed effectively. They must also provide regular updates and accountings to the beneficiaries and ensure that all relevant tax obligations are met.
Challenges and Controversies in Estate Administration
Estate administration can be a complex process, and it is not without its challenges and potential controversies. Some common issues that may arise include:
Disputed Wills and Trusts
In some cases, the validity of a will or trust may be disputed by beneficiaries or other interested parties. This can lead to lengthy and costly legal battles, especially if there are questions about the testator’s mental capacity or potential undue influence.
Estate executors and fiduciaries should be prepared to navigate these disputes and work with legal professionals to resolve them in a timely and fair manner.
Beneficiary Disagreements
Disagreements among beneficiaries are not uncommon, especially when it comes to the distribution of assets. Beneficiaries may have differing opinions on how the estate should be divided, leading to potential conflicts and challenges for the executor or fiduciary.
Effective communication and a clear understanding of the estate plan can help mitigate these disagreements. In some cases, mediation or alternative dispute resolution methods may be necessary to resolve conflicts without resorting to litigation.
Tax Compliance and Audits
Ensuring tax compliance is a critical aspect of estate administration. Executors and fiduciaries must accurately report and pay any applicable taxes, including the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax. Failure to do so can result in penalties, interest, and legal consequences.
In certain cases, the Virginia Department of Taxation may conduct audits to ensure compliance with tax laws. Executors and fiduciaries should maintain proper records and documentation to support their tax filings and be prepared to address any inquiries or discrepancies.
Conclusion
The Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax is a complex aspect of estate planning and administration. Understanding the tax rates, exemptions, and strategies for minimization is essential for individuals and their beneficiaries. By implementing effective estate planning strategies and working with qualified professionals, individuals can ensure a smooth transition of their assets and minimize the tax burden on their heirs.
Estate executors and fiduciaries play a critical role in navigating the complexities of estate administration. Their responsibilities include managing assets, paying taxes, and distributing the estate to beneficiaries. Effective communication, clear estate planning, and compliance with tax regulations are key to a successful and stress-free estate settlement process.
What is the difference between the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax and the federal estate tax?
+
The Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax is a state-level tax imposed on beneficiaries who inherit property or assets from a deceased Virginia resident. It is distinct from the federal estate tax, which is a federal tax levied on the transfer of a decedent’s estate. The federal estate tax has a higher exemption amount and is applicable to larger estates.
Are there any ways to avoid paying the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax altogether?
+
While complete avoidance may not be possible, there are strategies to minimize the tax burden. These include gifting assets during one’s lifetime, establishing trusts, and making charitable contributions. Working with an estate planning professional can help you explore these options and develop a tailored plan.
What happens if I don’t file the Virginia Estate Inheritance Tax return or pay the tax on time?
+
Failing to file the required tax return or pay the inheritance tax on time can result in penalties, interest, and potential legal consequences. It is important to comply with the tax regulations and seek professional advice if you have any concerns or questions about your obligations.
Can I challenge the validity of a will or trust in Virginia?
+
Yes, it is possible to challenge the validity of a will or trust in Virginia. However, these disputes can be complex and often require legal representation. It is advisable to consult an experienced estate planning or probate attorney if you have concerns about the validity of a will or trust.
How can I ensure a smooth estate administration process and minimize conflicts among beneficiaries?
+
Effective communication and clear estate planning are key to a smooth administration process. Regularly updating your estate plan, ensuring beneficiaries are aware of their rights and obligations, and seeking professional guidance can help minimize potential conflicts. Additionally, considering alternative dispute resolution methods can be beneficial in resolving disagreements.



