Va Personal Property Tax

The Virginia Personal Property Tax is a significant aspect of the state's revenue system, contributing to the overall financial health and development of the Commonwealth. This tax, often referred to as the Personal Property Tax (PPT), is levied on tangible personal property owned by individuals and businesses within the state. While it may be an annual burden for taxpayers, it plays a crucial role in funding various public services and infrastructure projects.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Virginia Personal Property Tax, exploring its history, its current state, and its impact on both taxpayers and the economy. By understanding the PPT, residents and businesses can make more informed decisions about their financial strategies and contributions to the community.
Understanding the Virginia Personal Property Tax

The Personal Property Tax in Virginia is a type of ad valorem tax, which means it is based on the assessed value of the property. This tax is imposed on a wide range of tangible personal property, including vehicles, boats, airplanes, recreational vehicles, and certain types of business equipment. It is an annual tax, typically due by January 31st of each year, and is calculated based on the property’s assessed value as of January 1st.
The PPT is administered by local governments in Virginia, with each county, city, or town setting its own tax rate. This decentralized approach allows for local control and flexibility, enabling communities to tailor the tax to their specific needs and priorities. The revenue generated from the PPT is used to fund essential services such as education, public safety, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
Taxable Property and Assessment
The scope of taxable personal property in Virginia is broad, encompassing various assets owned by individuals and businesses. Here’s a breakdown of the key categories:
- Vehicles: This includes cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other motor vehicles. The tax is based on the vehicle's assessed value, which is typically determined by its make, model, and age.
- Boats and Trailers: Any boat or trailer used for recreational purposes is subject to the PPT. The tax is usually calculated based on the boat's length and age.
- Airplanes: Aircraft, including private jets and small planes, are also taxed based on their assessed value, which takes into account factors like size, make, and model.
- Recreational Vehicles (RVs): RVs, campers, and similar mobile accommodations are taxable. The assessment is often based on the vehicle's size and features.
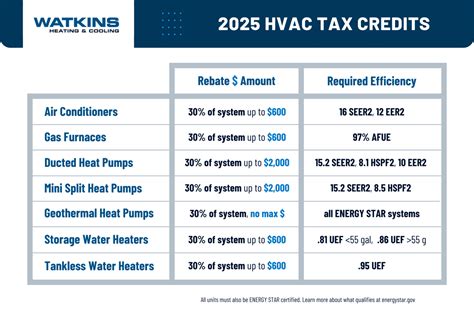
- Business Equipment: Certain types of business equipment, such as computers, machinery, and furniture, are also subject to the PPT. The tax rate and assessment methods may vary depending on the locality and the nature of the business.
The assessment process involves evaluating the property's fair market value, which is then multiplied by the applicable tax rate set by the local government. This results in the tax liability for the property owner. It's important to note that the assessment process and tax rates can vary significantly between different localities in Virginia.
| Property Type | Assessment Method |
|---|---|
| Vehicles | Based on make, model, and age. |
| Boats | Determined by length and age. |
| Airplanes | Consider factors like size, make, and model. |
| Recreational Vehicles | Assessment depends on size and features. |
| Business Equipment | Varies by locality and business type. |

History and Evolution of the PPT

The Personal Property Tax has a long history in Virginia, dating back to the early days of the Commonwealth. Initially, it was implemented as a means to generate revenue for local governments to fund essential services and infrastructure. Over time, the tax has undergone several transformations to keep up with changing economic landscapes and technological advancements.
One of the notable changes occurred in the late 20th century when the state introduced the Personal Property Tax Relief Act. This act provided significant relief to taxpayers by reducing the tax burden on certain types of personal property, particularly vehicles. It aimed to alleviate the financial strain on individuals and businesses while still ensuring a steady revenue stream for local governments.
Recent Developments and Reforms
In recent years, there have been ongoing discussions and efforts to reform the Personal Property Tax in Virginia. These initiatives are driven by a desire to simplify the tax system, reduce administrative burdens, and provide more equitable tax treatment for different types of personal property.
One of the key proposals is the Personal Property Tax Relief and Reform Act, which aims to:
- Standardize tax rates across localities.
- Introduce a uniform assessment methodology.
- Provide additional tax relief for certain property types.
- Enhance transparency and clarity in tax administration.
These reforms are designed to make the PPT more predictable and less burdensome for taxpayers while ensuring that local governments can continue to provide essential services. The proposed changes are still under consideration and may undergo further modifications before implementation.
Impact on Taxpayers and the Economy
The Personal Property Tax has a direct and significant impact on both individual taxpayers and the overall economy of Virginia.
Individual Taxpayers
For individuals, the PPT can be a substantial financial obligation, particularly for those with multiple vehicles or valuable personal property. The tax liability can vary widely depending on the locality and the assessed value of the property. However, it’s important to note that the state offers various exemptions and deductions to ease the tax burden on certain individuals, such as senior citizens and disabled persons.
The tax can also influence purchasing decisions, as individuals may consider the tax implications when acquiring new vehicles or other taxable property. This can impact the timing of purchases and the overall consumer behavior within the state.
Businesses and Economic Development
The PPT also plays a critical role in shaping the business environment and economic development in Virginia. For businesses, the tax can be a significant cost factor, especially for those with extensive equipment or vehicle fleets. It can influence a company’s decision to locate or expand its operations within the state.
However, the tax revenue generated from the PPT is vital for funding infrastructure projects, improving transportation networks, and supporting economic growth. It contributes to the overall business-friendly environment and can attract new investments and businesses to the state.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the PPT allows local governments to tailor their tax policies to attract specific industries or businesses, fostering economic diversification and localized growth.
Future Implications and Considerations
Looking ahead, the future of the Virginia Personal Property Tax is likely to be shaped by ongoing debates and policy decisions. As the state continues to evolve economically and technologically, the tax system will need to adapt to remain effective and equitable.
One key consideration is the potential impact of electric vehicles (EVs) on the PPT. With the increasing popularity of EVs, there is a growing discussion about how to fairly tax these vehicles, which currently face lower fuel tax burdens compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Finding an equitable solution for EV taxation will be crucial to ensure a sustainable revenue stream for local governments.
Additionally, as Virginia continues to prioritize economic development and business growth, the PPT will play a pivotal role in attracting and retaining businesses. The state's ability to offer competitive tax rates and incentives, while still providing adequate funding for public services, will be a key factor in its economic success.
In conclusion, the Virginia Personal Property Tax is a complex yet essential component of the state's tax system. It influences the financial decisions of individuals and businesses while providing crucial revenue for local governments to fund essential services and infrastructure. As the state navigates the challenges and opportunities of the future, the evolution of the PPT will be a key aspect of its economic strategy.
How often do I need to pay the Personal Property Tax in Virginia?
+The Personal Property Tax is an annual tax, typically due by January 31st of each year. It is based on the assessed value of your personal property as of January 1st.
Are there any exemptions or deductions available for the PPT?
+Yes, Virginia offers certain exemptions and deductions to ease the tax burden on specific individuals. For example, senior citizens and disabled persons may qualify for reduced tax rates or exemptions. It’s advisable to consult with your local tax authority or a tax professional to understand the available options.
How can I estimate my Personal Property Tax liability?
+You can estimate your tax liability by multiplying the assessed value of your personal property by the applicable tax rate set by your locality. However, it’s recommended to consult with your local tax office or a tax professional for accurate calculations and to understand any specific assessment methods or exemptions that may apply.