Utah Income Tax Rate
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Utah Income Tax Rate, a critical aspect of personal finance and state revenue systems. Understanding the tax landscape is essential for individuals and businesses operating within Utah, as it directly impacts their financial planning and compliance obligations. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the Utah income tax system, offering clarity and insights to navigate this complex yet crucial financial territory.
Understanding the Utah Income Tax Structure

Utah’s income tax system is a vital component of the state’s revenue generation, contributing significantly to the funding of essential public services and infrastructure. The state employs a progressive tax system, meaning the tax rate increases as income rises, promoting fairness and equitable distribution of financial responsibilities among residents.
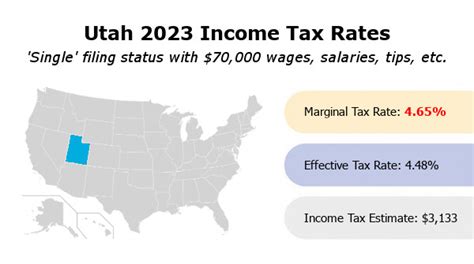
The current income tax structure in Utah consists of seven tax brackets, each with its own tax rate, ranging from 4.75% to 5.30%. This design ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their earnings to the state's coffers. The table below provides a detailed breakdown of these tax brackets, offering a clear view of how the tax system operates.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Applicable Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.75% | $0 - $1,625 |
| 2 | 4.85% | $1,626 - $3,250 |
| 3 | 4.95% | $3,251 - $4,875 |
| 4 | 5.05% | $4,876 - $8,125 |
| 5 | 5.15% | $8,126 - $13,500 |
| 6 | 5.25% | $13,501 - $19,750 |
| 7 | 5.30% | $19,751 and above |
These tax brackets are designed to ensure that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their earnings to the state's revenue, promoting a sense of fiscal responsibility and social equity. The Utah State Tax Commission administers this system, overseeing the collection and allocation of these taxes to support various public services and initiatives.
Impact on Individuals and Businesses
For individuals, understanding the income tax structure is crucial for effective financial planning and budgeting. It allows them to estimate their tax liabilities accurately, plan for tax payments, and explore potential tax-saving strategies. The progressive nature of Utah’s tax system ensures that those with higher incomes contribute proportionally more, aligning with principles of economic fairness.
Businesses operating in Utah also need to be well-versed in the state's income tax regulations. They must ensure compliance with tax laws, file appropriate tax returns, and understand the implications of the tax structure on their financial operations. This includes considerations for business income, payroll taxes, and potential tax incentives or deductions offered by the state.
Tax Exemptions and Deductions in Utah
Utah’s income tax system also offers various exemptions and deductions, which can significantly reduce an individual’s or business’s taxable income. These provisions are designed to encourage certain behaviors or support specific sectors, providing financial relief to taxpayers while also achieving broader societal or economic goals.
Common Exemptions and Deductions
- Standard Deduction: Utah offers a standard deduction that reduces taxable income by a set amount. For the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction is 2,300 for single filers</strong> and <strong>4,600 for married couples filing jointly.
- Personal Exemptions: The state allows a personal exemption for each dependent, reducing taxable income. The amount of the personal exemption varies based on the tax bracket.
- Business Expenses: Businesses can deduct various expenses incurred in the ordinary course of business, such as rent, utilities, supplies, and advertising costs.
- Charitable Contributions: Donations to qualified charitable organizations can be deducted, encouraging philanthropy and supporting non-profit sectors.
- Mortgage Interest: Interest paid on home mortgages is deductible, providing an incentive for homeownership.
Unique Utah Deductions
In addition to the common deductions, Utah offers several unique deductions tailored to the state’s specific needs and priorities.
- Education Deduction: Utah allows taxpayers to deduct qualified education expenses, including tuition, books, and supplies, up to a certain limit.
- Retirement Plan Contributions: Contributions to certain retirement plans, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, can be deducted, encouraging long-term savings and retirement planning.
- Homeownership Incentives: Utah offers deductions for property taxes and mortgage interest, providing financial relief to homeowners and encouraging homeownership.
Filing and Payment Process
The filing and payment process for Utah income taxes is straightforward and accessible, thanks to the state’s online systems and resources. Taxpayers can file their returns electronically, ensuring accuracy and expediting the refund process. The state also provides clear guidelines and resources to assist taxpayers in understanding their obligations and ensuring compliance.
Online Filing and Payment Options
Utah taxpayers have the option to file their returns and make payments online through the Utah State Tax Commission’s website. This platform offers a secure and user-friendly interface, allowing taxpayers to navigate the filing process efficiently. It also provides real-time updates on the status of returns and refunds, enhancing transparency and convenience.
Payment Deadlines and Penalties
The deadline for filing Utah income tax returns is typically April 15th each year, aligning with the federal tax deadline. However, it’s crucial to note that any unpaid taxes or late payments may incur interest and penalties. The state imposes a 0.5% monthly penalty on unpaid taxes, up to a maximum of 25%, and a 10% penalty for late filing.
Tax Relief Programs and Initiatives
Utah recognizes the importance of providing tax relief to certain segments of its population, particularly those facing financial hardships or unique circumstances. The state has implemented several programs and initiatives to ease the tax burden on these individuals, fostering a more inclusive and supportive tax environment.
Low-Income Tax Credits
Utah offers several tax credits specifically targeted at low-income individuals and families. These credits can significantly reduce tax liabilities, providing much-needed financial relief. Some of the notable low-income tax credits include:
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): This federal credit is available to low- and moderate-income workers, providing a refundable tax credit that can reduce tax liabilities or increase refunds.
- Child and Dependent Care Credit: This credit assists working families by offsetting the costs of child and dependent care, making it easier for parents to balance work and family responsibilities.
- Property Tax Refund: Utah provides a property tax refund for homeowners with limited incomes, reducing the financial burden of property taxes and promoting homeownership.
Other Tax Relief Initiatives
Beyond low-income credits, Utah has implemented other tax relief measures to support specific sectors or address unique challenges.
- Senior Citizens Tax Relief: Utah offers a property tax relief program for senior citizens, reducing the property taxes owed by eligible individuals.
- Military and Veterans Benefits: The state provides various tax benefits for active-duty military personnel and veterans, recognizing their service and supporting their transition to civilian life.
- Small Business Incentives: Utah offers tax incentives for small businesses, encouraging entrepreneurship and supporting local economies.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes

As with any tax system, Utah’s income tax structure is subject to potential changes and reforms. These changes can be driven by various factors, including shifts in the economic landscape, political priorities, or emerging societal needs. Understanding these potential changes is crucial for individuals and businesses to stay ahead of the curve and adapt their financial strategies accordingly.
Potential Reforms and Updates
The Utah State Legislature and the Governor regularly review and consider proposals to modify the state’s tax system. These proposals can range from adjusting tax rates and brackets to introducing new deductions or credits. For instance, there have been recent discussions about:
- Income Tax Rate Adjustments: Proposals to either raise or lower the income tax rates to balance the state’s budget or provide tax relief to residents.
- Tax Bracket Updates: Suggestions to revise the income tax brackets to ensure they remain aligned with inflation and changing economic conditions.
- New Deductions or Credits: Initiatives to introduce new deductions or credits to support specific industries, encourage certain behaviors, or provide relief to targeted populations.
Impact of Economic Trends
Economic trends can significantly influence the future of Utah’s income tax system. For example, during periods of economic growth, the state may experience increased revenue, which could lead to discussions about tax cuts or enhanced services. Conversely, economic downturns may prompt considerations of tax increases or temporary measures to boost revenue.
Political and Social Factors
Political ideologies and societal priorities also play a role in shaping the future of Utah’s tax system. Changes in administration or shifts in public opinion can lead to new tax policies or reforms. For instance, there may be proposals to simplify the tax code, enhance transparency, or address specific societal concerns, such as income inequality or environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
The Utah income tax system is a dynamic and essential component of the state’s fiscal framework. It plays a critical role in funding public services, infrastructure, and initiatives that support the well-being and prosperity of Utah’s residents. Understanding this system, its rates, exemptions, and potential changes is vital for individuals and businesses to navigate their financial obligations effectively.
By staying informed about Utah's income tax landscape, taxpayers can make informed decisions about their financial planning, budgeting, and compliance. This knowledge empowers them to leverage the available deductions and credits, plan for potential changes, and contribute constructively to the state's economic and social fabric.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current income tax rate in Utah for the 2023 tax year?
+
The income tax rate in Utah for the 2023 tax year ranges from 4.75% to 5.30%, depending on the tax bracket an individual’s income falls into.
Are there any unique deductions or credits offered by Utah that other states don’t provide?
+
Yes, Utah offers several unique deductions and credits, including an education deduction, retirement plan contributions deduction, and homeownership incentives.
What are the payment deadlines for Utah income taxes, and what penalties apply for late payments or filings?
+
The deadline for filing Utah income tax returns is typically April 15th each year. Late payments or filings may incur a 0.5% monthly penalty on unpaid taxes, up to a maximum of 25%, and a 10% penalty for late filing.
Are there any tax relief programs or initiatives in Utah specifically targeting low-income individuals or families?
+
Yes, Utah offers various tax relief programs for low-income individuals and families, including the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), Child and Dependent Care Credit, and Property Tax Refund.
What are some potential changes or reforms that could impact Utah’s income tax system in the future?
+
Potential changes could include adjustments to income tax rates and brackets, the introduction of new deductions or credits, or reforms driven by economic trends, political ideologies, and societal priorities.



