Tax Percentage In Wisconsin

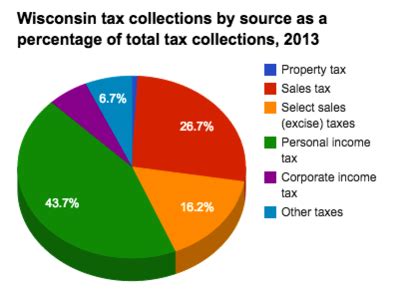
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the tax landscape in Wisconsin, a state known for its vibrant economy, diverse industries, and unique tax structure. As an expert in the field, I aim to provide an in-depth analysis of the tax percentages in Wisconsin, shedding light on the various taxes that residents and businesses encounter. From income taxes to sales taxes and property taxes, we'll delve into the specifics, offering a clear understanding of Wisconsin's tax system and its implications.
Income Tax: A Variable Rate System
Wisconsin operates on a progressive income tax system, which means that the tax percentage increases as an individual’s income rises. This structure ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger proportion of their income to the state’s revenue. The income tax rates in Wisconsin are divided into four brackets, each with its own tax rate:
- Bracket 1 (Up to 12,550):</strong> 3.73% tax rate.</li> <li><strong>Bracket 2 (12,551 - 25,100):</strong> 4.73% tax rate.</li> <li><strong>Bracket 3 (25,101 - 113,200):</strong> 5.98% tax rate.</li> <li><strong>Bracket 4 (Over 113,200): 7.65% tax rate.
For instance, if an individual’s taxable income falls within Bracket 3, they would pay 5.98% on the portion of their income between 25,101 and 113,200, and a lower rate for income below $25,100.
Taxable Income Calculation
Determining taxable income in Wisconsin involves considering various deductions and exemptions. Some common deductions include federal income tax paid, Social Security income, and medical expenses. Additionally, Wisconsin allows for personal exemptions, which reduce taxable income for each eligible individual claimed on the tax return.
Recent Changes
In recent years, Wisconsin has undergone significant tax reforms. Notably, the state implemented a flat tax rate of 4% for S corporations and pass-through entities, a move aimed at attracting and retaining businesses. This flat tax rate provides a simpler and more competitive tax environment for these entities.
Sales and Use Tax: A Variable Rate

Wisconsin’s sales and use tax is a consumption tax applied to the retail sale, lease, and rental of tangible personal property, as well as certain services. The state sales tax rate is 5%, but this can vary at the local level, with some municipalities imposing additional taxes.
| City | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Milwaukee | 5.6% |
| Madison | 5.4% |
| Green Bay | 5.5% |
| Wausau | 5.0% |

Additionally, certain items, such as food, prescription drugs, and some medical devices, are exempt from sales tax, providing relief for essential purchases.
Use Tax
Wisconsin also imposes a use tax, which applies to items purchased from out-of-state vendors and brought into the state. This tax ensures that Wisconsin residents and businesses pay the equivalent of sales tax, even if the purchase was made online or from a retailer outside the state.
Property Tax: A Local Affair
Property taxes in Wisconsin are primarily a local responsibility, with rates and assessments varying widely across the state. These taxes fund local services, including schools, fire departments, and infrastructure maintenance. The tax rate is determined by the local government and can be influenced by factors such as the assessed value of the property and the budget needs of the community.
Assessed Value and Tax Rates
The assessed value of a property is typically a percentage of its fair market value, and this assessment is conducted by local assessors. The tax rate, expressed as a percentage, is then applied to the assessed value to calculate the property tax. For example, if a property is assessed at 200,000 and the tax rate is 1.5%, the annual property tax would be 3,000.
Property Tax Relief Programs
Wisconsin offers several programs aimed at providing property tax relief to eligible residents. These include the Homestead Credit, which provides a credit based on property taxes paid, and the Senior Citizen Property Tax Deferral, which allows qualifying seniors to defer their property taxes until they sell their home or pass away.
Other Taxes in Wisconsin
Wisconsin has a range of other taxes that contribute to its revenue stream. These include:
- Unemployment Insurance Tax: Paid by employers to fund unemployment benefits.
- Franchise Tax: Applicable to corporations and some other entities.
- Excise Taxes: Levied on specific goods and services, such as alcohol and tobacco products.
- Estate and Inheritance Taxes: Taxes on the transfer of property upon death.
Business Tax Climate
Wisconsin has taken steps to improve its business tax climate, with initiatives like the Manufacturing and Agriculture Credit, which provides a tax credit for qualified manufacturing and agricultural businesses. Additionally, the state offers various tax incentives and credits to attract and support business growth.
Conclusion: Navigating Wisconsin’s Tax Landscape

Understanding Wisconsin’s tax structure is essential for individuals and businesses alike. With its progressive income tax, variable sales tax rates, and local property tax assessments, Wisconsin’s tax system can be complex. However, by staying informed and leveraging the available tax incentives and relief programs, taxpayers can navigate this landscape effectively. As Wisconsin continues to evolve its tax policies, staying abreast of changes will be key to optimizing tax strategies and contributing to the state’s economic vitality.
What is the average property tax rate in Wisconsin?
+The average property tax rate in Wisconsin varies widely, ranging from approximately 1.0% to 2.5% depending on the location. The actual rate is determined by local governments and can be influenced by factors like the assessed value of properties and the budget requirements of the community.
Are there any tax incentives for renewable energy projects in Wisconsin?
+Yes, Wisconsin offers several tax incentives for renewable energy projects. These include the Renewable Energy Property Tax Exemption, which exempts renewable energy systems from property taxes, and the Energy Efficiency Tax Credit, which provides a tax credit for investments in energy-efficient equipment.
How does Wisconsin’s income tax compare to other states?
+Wisconsin’s income tax rates are generally on par with or slightly higher than the national average. However, the state’s progressive tax structure ensures that higher-income earners pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes compared to some other states with flatter tax systems.