Tax Loopholes For Small Business

In the world of small business ownership, understanding tax strategies is crucial for financial success. Tax loopholes, when used ethically and within legal boundaries, can provide significant benefits, allowing businesses to optimize their financial operations and overall growth. This article aims to delve into the various tax loopholes available to small businesses, providing an in-depth analysis and practical insights.
Maximizing Tax Deductions: A Key Strategy
One of the primary tax loopholes for small businesses is the strategic use of deductions. By understanding the intricacies of the tax code, businesses can maximize their eligible deductions, reducing their overall taxable income. This strategy is particularly effective for new businesses with higher startup costs and ongoing expenses.
Key Deduction Strategies
One effective approach is to claim deductions for business-related expenses, such as office rent, equipment purchases, and employee salaries. Additionally, small businesses can benefit from deducting specific expenses that are often overlooked, like professional development costs, marketing expenses, and even certain travel costs.
For instance, consider a small business owner who regularly attends industry conferences and workshops to stay updated on the latest trends. These attendance fees, along with travel and accommodation expenses, can be claimed as tax deductions, provided they are directly related to business operations and not purely for personal development.
| Deduction Category | Eligible Expenses |
|---|---|
| Office Expenses | Rent, utilities, office supplies, internet/phone services |
| Equipment/Software | Computers, machinery, software licenses, maintenance costs |
| Marketing & Advertising | Print/digital ads, website development, promotional materials |
| Employee Costs | Salaries, benefits, training expenses, recruitment fees |

It's important to note that the eligibility of certain deductions may vary based on the business structure and industry. Consulting with a tax professional or accountant is highly recommended to ensure compliance and maximize potential deductions.
Capitalizing on Tax Credits

Beyond deductions, small businesses can leverage tax credits to further reduce their tax liability. Tax credits are particularly beneficial as they directly reduce the amount of tax owed, rather than just the taxable income like deductions.
Common Tax Credits for Small Businesses
One widely available credit is the Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit, which encourages innovation by providing a credit for businesses engaged in qualified research activities. This credit can significantly offset tax liabilities, especially for startups and businesses investing in research and development.
Another credit to consider is the Small Business Health Care Tax Credit, which is designed to offset the cost of providing health insurance to employees. This credit can be a substantial benefit for small businesses with fewer than 25 full-time equivalent employees, helping to ease the financial burden of offering health coverage.
Additionally, certain industries may have specific tax credits available. For instance, renewable energy businesses can take advantage of the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and the Production Tax Credit (PTC) for solar and wind energy projects.
| Tax Credit | Eligibility |
|---|---|
| Research & Development (R&D) Credit | Businesses engaged in qualified research activities |
| Small Business Health Care Credit | Small businesses providing health insurance to employees |
| Investment Tax Credit (ITC) | Renewable energy projects (solar, wind, etc.) |
| Production Tax Credit (PTC) | Renewable energy generation (wind, geothermal, etc.) |
It's crucial to stay updated on the availability and requirements of these tax credits, as they can provide significant financial benefits to small businesses.
Strategic Business Structuring
The legal structure of a business can significantly impact its tax obligations and liabilities. Small business owners have several options, each with its own advantages and disadvantages from a tax perspective.
Common Business Structures and Their Tax Implications
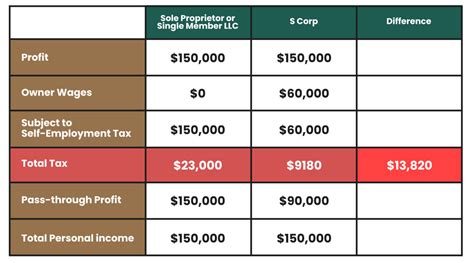
Sole proprietorships are the simplest and most common business structure, offering ease of setup and operation. However, from a tax perspective, they are not a separate entity from the owner, which means business income is taxed as personal income, often at higher rates.
On the other hand, incorporating as an S-Corporation or an LLC (Limited Liability Company) can provide significant tax benefits. These structures allow for the pass-through of business income and losses to the owner's personal tax return, often reducing the overall tax burden. Additionally, they offer liability protection, separating the owner's personal assets from business liabilities.
For instance, consider a small business owner who operates as a sole proprietor and earns $100,000 in profit. This income would be taxed at the owner's personal tax rate, which could be as high as 37% for high-income earners. In contrast, if the business were structured as an S-Corp, the owner could pay themselves a reasonable salary (taxed at personal income tax rates) and distribute the remaining profits as dividends, which are taxed at a lower capital gains rate.
| Business Structure | Tax Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorship | Easy to set up, minimal paperwork | Business and personal finances are intertwined, higher tax rates |
| S-Corporation | Pass-through taxation, lower tax rates, liability protection | More complex setup, strict eligibility criteria |
| LLC (Limited Liability Company) | Flexibility in taxation (pass-through or corporate), liability protection | Varies by state, may require more complex tax filings |
The decision to change the business structure should be made with careful consideration and professional advice, as it can have long-term financial implications.
Conclusion: Navigating Tax Loopholes Ethically
While tax loopholes can provide significant financial benefits to small businesses, it’s crucial to approach them with integrity and within the boundaries of the law. By understanding and ethically utilizing these strategies, small business owners can optimize their financial operations, reduce tax liabilities, and foster long-term growth.
Key Takeaways
- Maximize deductions for business expenses to reduce taxable income.
- Leverage tax credits to directly reduce tax liabilities.
- Strategically structure your business to align with tax benefits and long-term goals.
- Always consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance and maximize benefits.
How can I stay updated on tax law changes that may affect my small business?
+It’s essential to stay informed about tax law changes. Subscribe to reputable tax newsletters or follow tax blogs specific to small businesses. Additionally, consider attending tax seminars or webinars, and consult with your accountant or tax advisor regularly to stay abreast of any changes that may impact your business.
Are there any potential drawbacks to claiming certain deductions or credits?
+While deductions and credits can provide significant benefits, there may be potential drawbacks. For instance, claiming certain deductions or credits may trigger additional scrutiny from tax authorities. It’s crucial to ensure that all deductions and credits claimed are fully supported by accurate records and documentation to avoid any potential penalties or audits.
What are some common mistakes small business owners make regarding taxes?
+Common tax mistakes for small business owners include failing to keep proper records, not understanding the difference between business and personal expenses, and not taking advantage of available tax credits and deductions. It’s important to educate yourself on tax obligations and consult with professionals to avoid these pitfalls.



