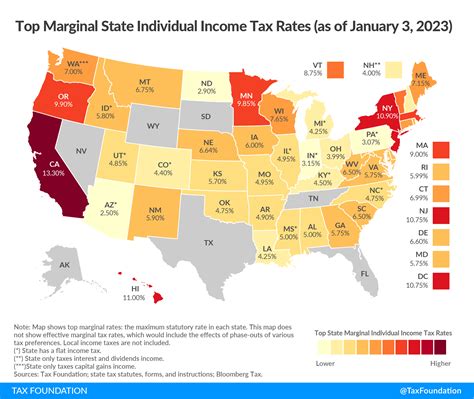
States With State Income Tax Map
Income taxes are a significant source of revenue for many states in the United States, playing a crucial role in funding public services and infrastructure. While the federal government imposes a uniform income tax across the nation, states have the autonomy to establish their own income tax systems, leading to a diverse landscape of tax structures and rates.
The existence of a state income tax can significantly impact an individual's or business's financial planning and overall tax burden. Understanding which states levy income tax and the associated rates is essential for taxpayers, especially when considering residency, business operations, or investment opportunities across different states.
Mapping State Income Taxes

The United States presents a varied landscape when it comes to state income taxes. While some states rely heavily on this revenue stream, others have opted out completely, creating a patchwork of tax policies across the nation.
As of my last update in January 2023, the states that impose an income tax on residents fall into the following categories:
- Progressive Income Tax: These states have a progressive tax system, where higher income brackets are taxed at a higher rate. Examples include California, New York, and Illinois.
- Flat Income Tax: In contrast, some states have adopted a flat income tax rate, applying the same percentage to all income levels. This system is used in states like Colorado, Pennsylvania, and Indiana.
- No Income Tax: Notably, seven states have chosen not to levy an income tax on their residents. These include Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming. While this may be attractive to taxpayers, it's important to note that these states may generate revenue through other means, such as sales taxes or business taxes.
The choice to implement or forgo a state income tax is often a complex decision, influenced by economic factors, political ideologies, and the state's overall fiscal health.
State Income Tax Rates and Brackets
The income tax rates and brackets can vary significantly from state to state. Here's a closer look at some of the states with a progressive income tax system:
California
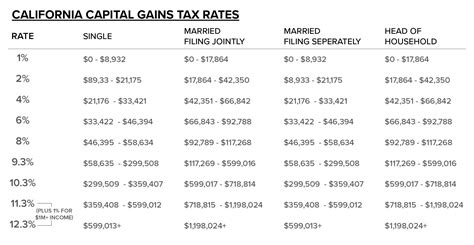
California has some of the highest income tax rates in the nation. The state's income tax brackets and rates for 2022 are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $9,668 | 1% |
| $9,669 - $41,737 | 2% |
| $41,738 - $57,037 | 4% |
| $57,038 - $88,136 | 6% |
| $88,137 - $263,337 | 8% |
| $263,338 - $526,677 | 9.3% |
| $526,678 and above | 10.3% |
These rates can change annually, so it's essential to refer to the California Franchise Tax Board for the most up-to-date information.
New York
New York also has a progressive income tax system with multiple brackets. The 2022 income tax rates are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $11,650 | 4% |
| $11,651 - $22,250 | 4.5% |
| $22,251 - $55,600 | 6% |
| $55,601 - $161,550 | 6.5% |
| $161,551 - $250,000 | 6.85% |
| $250,001 - $500,000 | 7% |
| $500,001 - $2,000,000 | 8.82% |
| $2,000,001 and above | 10.9% |
New York City residents may also be subject to an additional city income tax.
Illinois
Illinois has a progressive income tax system with the following rates for 2022:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $10,000 | 4.95% |
| $10,001 - $100,000 | 4.95% |
| $100,001 - $250,000 | 4.95% |
| $250,001 - $500,000 | 4.95% |
| $500,001 and above | 7.75% |
It's worth noting that Illinois recently implemented a temporary increase in the income tax rate for individuals earning over $250,000 and households earning over $500,000. This increase is set to expire in 2025.
The Impact of State Income Taxes
State income taxes can have a significant influence on an individual's or business's financial decisions. For instance, a state with high income tax rates might encourage residents to seek out tax planning strategies or consider moving to states with more favorable tax environments.
From a business perspective, the income tax structure of a state can impact investment decisions, business growth, and overall profitability. Companies might choose to locate their operations in states with lower income tax rates to reduce their tax liabilities.
Strategies for Taxpayers
Taxpayers have various strategies to mitigate the impact of state income taxes. These include:
- Tax Planning: Working with tax professionals to optimize income distribution and take advantage of deductions and credits.
- Business Structuring: Choosing the right business entity can impact tax liabilities. For instance, an S-corporation might be favored over a sole proprietorship in certain states.
- Residency Planning: For high-income individuals, considering part-year residency or establishing residency in a state with no income tax can be a strategy to reduce tax burdens.
However, it's crucial to consult with tax advisors before making significant decisions based on tax considerations, as each individual's situation is unique.
Future Implications
The landscape of state income taxes is constantly evolving. Some states are considering reforms to their tax systems, while others are exploring ways to reduce or eliminate income taxes altogether. These changes can be influenced by economic factors, political shifts, and public opinion.
For instance, there have been discussions in several states about implementing a flat income tax rate, which proponents argue could simplify the tax system and make it more equitable. On the other hand, critics argue that a flat tax may not provide sufficient revenue for essential public services.
The future of state income taxes will continue to be a topic of debate and policy reform, with potential implications for taxpayers, businesses, and the overall economic health of states.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between state and federal income tax?
+
State income tax is imposed by individual states, while federal income tax is a uniform tax applied across the United States. State income taxes can vary significantly, with some states having progressive rates, flat rates, or no income tax at all. In contrast, the federal income tax has a progressive structure with different tax brackets for individuals and married couples.
How do state income taxes impact my federal tax return?
+
State income taxes paid during the year may be deductible on your federal tax return. However, there are limitations, and the deduction is subject to the overall limitations on state and local tax deductions. It’s recommended to consult a tax professional to understand the impact on your specific situation.
Can I avoid state income tax by moving to another state?
+
Moving to a state with no income tax can reduce your state tax liability. However, it’s important to consider the overall tax burden of the new state, including sales tax, property tax, and other taxes. Additionally, establishing residency in a new state can have legal and financial implications, so it’s advisable to seek professional guidance.
What are some strategies to reduce my state income tax burden?
+
There are several strategies to consider. Maximizing deductions and credits allowed by your state’s tax laws can help reduce your taxable income. Some states also offer tax incentives for specific industries or activities. Additionally, tax planning and consulting with a professional can provide tailored strategies based on your circumstances.
Are there any states with unique tax structures I should be aware of?
+
Yes, some states have unique tax systems. For example, Tennessee and New Hampshire only tax dividend and interest income, while Texas and Florida have no income tax but impose high sales taxes. Understanding these unique structures is crucial when considering business operations or residency in these states.