State Of Texas Sales Tax Permit

The State of Texas Sales Tax Permit is a crucial document for businesses operating within the state. It allows businesses to collect and remit sales tax to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts, ensuring compliance with the state's tax laws. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the process of obtaining a Texas Sales Tax Permit, covering everything from eligibility to application procedures and post-issuance responsibilities.
Understanding the Texas Sales Tax Permit

A Texas Sales Tax Permit, officially known as the Sales and Use Tax Permit, is a legal authorization granted by the Texas Comptroller’s office to businesses engaged in selling taxable goods or services within the state. This permit serves as a license to collect sales tax from customers and subsequently remit it to the state government. It is an essential component of doing business in Texas and ensures that the state’s tax revenue is appropriately accounted for and distributed.
The sales tax collected by businesses is a crucial source of revenue for the state, contributing to various public services, infrastructure development, and state operations. By obtaining a Sales Tax Permit, businesses not only fulfill their legal obligations but also contribute to the economic growth and well-being of the state.
Key Responsibilities of Permit Holders
- Sales Tax Collection: Permit holders are required to charge the appropriate sales tax rate on taxable goods and services sold within the state. This rate can vary based on the location of the sale and the type of product or service.
- Tax Rate Calculation: Businesses must accurately calculate the sales tax due on each transaction, ensuring compliance with the applicable tax laws and regulations.
- Record-Keeping: Permit holders must maintain detailed records of all sales transactions, including the amount of sales tax collected. These records are essential for accurate reporting and auditing purposes.
- Periodic Reporting: Businesses are obligated to file sales tax returns on a regular basis, typically quarterly or monthly, depending on their revenue and the Comptroller’s guidelines. These returns detail the sales tax collected and remitted during the specified period.
- Timely Remittance: Sales tax collected must be remitted to the Texas Comptroller’s office within the prescribed deadlines to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Failure to comply with these responsibilities can result in penalties, interest, and even the revocation of the Sales Tax Permit. Therefore, it is imperative for businesses to understand their obligations and ensure timely and accurate compliance.
Eligibility and Requirements for Obtaining a Sales Tax Permit

Not all businesses operating in Texas are required to obtain a Sales Tax Permit. The eligibility criteria and requirements for obtaining a permit are outlined by the Texas Comptroller’s office and vary based on the nature of the business and its operations.
Types of Businesses That Require a Sales Tax Permit
- Retail Businesses: Any business involved in the sale of tangible personal property to the end consumer, such as retail stores, online retailers, and door-to-door salespeople, typically requires a Sales Tax Permit.
- Service Providers: Businesses providing taxable services, such as repair services, consulting services, or entertainment services, are generally required to obtain a permit.
- Wholesalers and Distributors: Wholesalers and distributors who sell goods to other businesses for resale may need a Sales Tax Permit, depending on the nature of their transactions.
- Manufacturers: Manufacturers selling directly to consumers or providing manufacturing services may also be subject to sales tax and require a permit.
Specific Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria for obtaining a Sales Tax Permit can vary based on factors such as the business’s gross receipts, the location of sales, and the type of goods or services sold. For instance, businesses with gross receipts below a certain threshold may be exempt from obtaining a permit, while those with higher revenue are generally required to apply.
Additionally, certain types of transactions are exempt from sales tax, and businesses engaged in these activities may not require a permit. For example, sales of prescription drugs, certain agricultural products, and certain types of professional services are exempt from sales tax in Texas.
Application Process
The application process for a Texas Sales Tax Permit is straightforward and can be completed online through the Comptroller’s website. The application requires businesses to provide detailed information about their operations, including the type of business, location of sales, estimated annual sales, and the nature of goods or services sold.
Businesses must also choose an appropriate tax filing frequency, typically either quarterly or monthly, based on their estimated sales volume and the Comptroller's guidelines. This choice determines the frequency of tax return filings and remittances.
Documents and Information Required
To complete the application, businesses will need to provide the following information and documents:
- Business name, address, and contact information.
- Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or Social Security Number (SSN) for sole proprietors.
- Details of the business activities and the type of goods or services sold.
- Estimated annual sales volume.
- Choice of tax filing frequency (quarterly or monthly).
- Signatures of authorized representatives or owners.
Post-Issuance Responsibilities and Compliance
Once a business obtains a Texas Sales Tax Permit, it assumes several ongoing responsibilities to ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Tax Rate Compliance
Businesses must stay informed about the applicable sales tax rates for their specific location and type of transactions. Texas has a state-wide sales tax rate, but local municipalities may also impose additional sales taxes, known as local option sales taxes. Businesses must calculate and collect the appropriate combined tax rate for each transaction.
Record-Keeping and Reporting
Permit holders are obligated to maintain accurate records of all sales transactions, including the sales amount, the tax rate applied, and the tax collected. These records must be retained for a minimum of three years and made available for audit purposes if required.
Businesses must also file sales tax returns on a regular basis, typically quarterly or monthly, depending on their chosen filing frequency. These returns must be completed accurately and submitted within the prescribed deadlines. Late filing or non-filing can result in penalties and interest charges.
Tax Remittance
Sales tax collected must be remitted to the Texas Comptroller’s office within the designated time frames. The frequency of remittances aligns with the chosen tax filing frequency. Businesses must ensure that the remitted amount matches the tax collected and reported on their tax returns.
Renewal and Updates
Sales Tax Permits are typically valid for an indefinite period, but businesses must ensure that their permit information remains current. Any changes to the business, such as a change of ownership, address, or significant alterations to operations, must be reported to the Comptroller’s office. Failure to do so can result in penalties and compliance issues.
Businesses are also responsible for renewing their Sales Tax Permit if it has been inactive for an extended period. The renewal process involves updating the permit information and ensuring compliance with the latest tax laws and regulations.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with Texas sales tax laws can result in significant penalties and legal consequences for businesses. The Texas Comptroller’s office takes a strict approach to tax enforcement, and businesses must take their tax obligations seriously.
Penalties and Interest Charges
Businesses that fail to obtain a Sales Tax Permit when required, or those that fail to comply with their permit obligations, may face penalties and interest charges. These penalties can be substantial, and interest may accrue on any outstanding tax liabilities.
Legal Action and License Revocation
In cases of severe or repeated non-compliance, the Comptroller’s office may take legal action against the business, including civil or criminal penalties. Additionally, the Sales Tax Permit may be revoked, resulting in the business being unable to legally conduct sales transactions within the state.
Public Record and Reputation Impact
Information about tax non-compliance, including penalties and legal actions, becomes a matter of public record. This can significantly impact a business’s reputation, especially if it is a well-known brand or operates in a competitive market. Potential customers, investors, and partners may view non-compliance as a sign of untrustworthiness or financial instability.
Conclusion
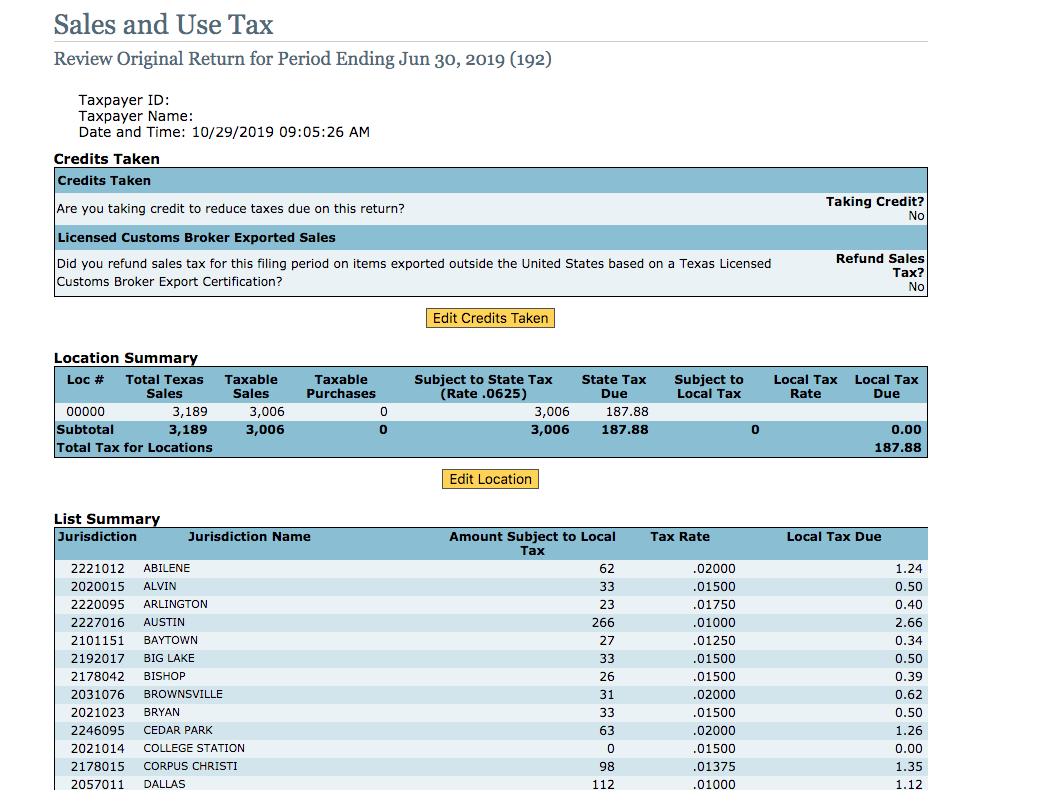
Obtaining and maintaining a Texas Sales Tax Permit is a crucial aspect of doing business in the state. It ensures compliance with tax laws, contributes to the state’s revenue, and protects businesses from legal consequences. By understanding the eligibility criteria, application process, and post-issuance responsibilities, businesses can navigate the process smoothly and ensure ongoing compliance.
The Texas Comptroller's office provides extensive resources and guidance to help businesses understand their tax obligations. By staying informed and diligent in their tax compliance efforts, businesses can operate successfully within the state while contributing to its economic growth and development.
What is the Texas Sales Tax Rate?
+The state-wide sales tax rate in Texas is 6.25% as of [current date]. However, local option sales taxes can increase the total tax rate. It’s important for businesses to stay informed about the applicable tax rates for their specific location.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Texas?
+Yes, Texas offers exemptions for certain transactions, such as sales of prescription drugs, some agricultural products, and certain professional services. It’s crucial for businesses to understand the exemptions that apply to their operations to avoid over-collecting sales tax.
How often do I need to file my sales tax returns in Texas?
+The frequency of filing sales tax returns in Texas depends on your chosen tax filing frequency. You can opt for quarterly or monthly filing. However, the Comptroller’s office may require certain businesses to file more frequently based on their revenue or other factors.



