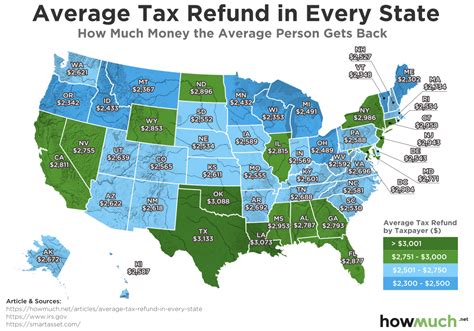
State Of Ohio Income Tax Rate
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the State of Ohio's income tax rate. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of Ohio's tax system, exploring the current tax rates, historical changes, and the impact on individuals and businesses within the state. Understanding the income tax landscape is crucial for both residents and businesses operating in Ohio, as it directly affects financial planning and decision-making. Let's navigate through the intricacies of Ohio's tax structure and uncover valuable insights.
Understanding Ohio’s Income Tax Structure

Ohio, like many other states, imposes an income tax on its residents and businesses. The state’s tax system is designed to generate revenue to fund essential services and infrastructure projects. The income tax rate in Ohio is progressive, meaning that the tax rate increases as taxable income rises. This structure ensures that individuals and entities with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their income to the state’s revenue.
The Ohio Department of Taxation oversees the collection and administration of income taxes. The department ensures compliance with state tax laws and provides resources and guidance to taxpayers. It is important for individuals and businesses to stay updated with the latest tax regulations and deadlines to avoid any penalties or legal issues.
Ohio's income tax system is designed to be fair and equitable. The state offers various deductions, credits, and exemptions to reduce the tax burden on individuals and promote economic growth. These incentives encourage investment, support small businesses, and provide relief to low- and middle-income earners.
Current Income Tax Rates in Ohio
As of my last update in January 2023, the State of Ohio imposes a flat income tax rate of 4.75% on individuals, trusts, and estates. This rate applies to taxable income earned within the state, regardless of the filer’s residency status. Ohio’s flat tax rate simplifies the tax calculation process and provides consistency for taxpayers.
It is important to note that Ohio's income tax rate is subject to change. The state's legislature has the authority to modify tax rates to address budgetary needs or economic conditions. Therefore, it is advisable to stay informed about any potential tax rate adjustments to ensure accurate financial planning.
| Tax Rate | Applicable To |
|---|---|
| 4.75% | Individuals, Trusts, and Estates |
Taxable Income and Deductions
When calculating taxable income in Ohio, individuals and businesses must consider various deductions and exemptions. Ohio allows taxpayers to deduct certain expenses, such as business costs, charitable contributions, and certain medical expenses, to reduce their taxable income. These deductions can significantly impact the overall tax liability and provide relief to taxpayers.
Additionally, Ohio offers tax credits for specific activities or investments. For instance, the state provides tax credits for research and development activities, job creation, and investment in renewable energy projects. These credits incentivize businesses to engage in economically beneficial activities and contribute to Ohio's growth and development.
Individuals should also be aware of personal exemptions and deductions available to them. Ohio allows a standard deduction or the option to itemize deductions, depending on the taxpayer's circumstances. These deductions can include expenses related to mortgage interest, state and local taxes, and certain personal property taxes.
Historical Perspective on Ohio’s Income Tax Rates

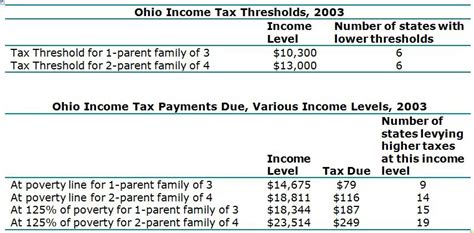
Ohio’s income tax rates have undergone changes over the years, reflecting the state’s fiscal policies and economic conditions. In the early 2000s, Ohio implemented a tax reform that reduced the income tax rate from 5.75% to 4.5%. This reform aimed to stimulate economic growth and make Ohio more competitive in attracting businesses and talent.
However, in recent years, Ohio has experienced budget challenges, leading to discussions about tax rate adjustments. In 2015, the state considered proposals to increase the income tax rate to address revenue shortfalls. These proposals sparked debates among policymakers and taxpayers, highlighting the delicate balance between generating sufficient revenue and maintaining a competitive tax environment.
Despite the discussions, Ohio has maintained its flat tax rate of 4.75% since 2013. This stability provides predictability for taxpayers and allows individuals and businesses to plan their finances effectively. The state's commitment to a consistent tax rate fosters a sense of certainty and encourages long-term investment and economic development.
Impact on Individuals and Businesses
Ohio’s income tax rate directly affects individuals and businesses operating within the state. For individuals, the tax rate impacts their disposable income and overall financial well-being. A lower tax rate can provide more disposable income, allowing individuals to save, invest, or spend more freely. Conversely, a higher tax rate may result in a reduced disposable income, impacting an individual’s financial planning and lifestyle choices.
Businesses, on the other hand, consider the income tax rate as a critical factor when deciding on their location and expansion plans. A competitive tax rate can attract businesses to Ohio, leading to job creation, economic growth, and increased tax revenue. On the contrary, an uncompetitive tax rate may deter businesses from investing in the state, hindering economic development and potentially resulting in job losses.
Ohio's tax structure aims to strike a balance between generating sufficient revenue and maintaining a business-friendly environment. The state offers various incentives and tax credits to encourage business growth and investment, ultimately contributing to a thriving economy.
Comparative Analysis: Ohio vs. Other States
To gain a broader perspective, let’s compare Ohio’s income tax rate with that of other states. While a flat tax rate of 4.75% is relatively competitive, it is important to consider the overall tax environment and the state’s fiscal policies.
Some states, like Texas and Florida, have no income tax, making them attractive destinations for businesses and individuals seeking tax advantages. However, these states may have other forms of taxation, such as sales tax or property tax, to generate revenue. On the other hand, states like California and New York have higher income tax rates, ranging from 1% to 13.3%, depending on the taxpayer's income level.
Ohio's tax rate positions the state in the middle ground, offering a balanced approach to taxation. The state's tax structure aims to attract businesses and individuals while ensuring sufficient revenue to fund essential services and infrastructure. This balance is crucial for maintaining a healthy economic ecosystem and promoting long-term growth.
Tax Incentives and Business Climate
Ohio understands the importance of a favorable business climate to attract and retain businesses. In addition to its competitive tax rate, the state offers various tax incentives and programs to support business growth and expansion.
The Ohio Development Services Agency plays a vital role in promoting economic development and business attraction. The agency offers tax incentives such as the Job Creation Tax Credit, which provides a credit against corporate franchise or income taxes for companies creating new jobs in the state. This incentive encourages businesses to invest in Ohio and create employment opportunities.
Ohio also provides tax credits for research and development activities, energy efficiency improvements, and investments in renewable energy. These incentives promote innovation, sustainability, and a transition to a greener economy. By offering such incentives, Ohio aims to foster a business-friendly environment and position itself as a leader in technological advancements and environmental sustainability.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
As Ohio continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic conditions, the state’s income tax rate may undergo further adjustments in the future. While the current flat tax rate of 4.75% provides stability and predictability, economic factors, budgetary needs, and political considerations may influence future tax policies.
Ohio's leaders and policymakers must carefully evaluate the impact of tax rate changes on the state's economy and residents. Striking the right balance between generating revenue and maintaining a competitive tax environment is crucial for long-term economic growth and prosperity. Any proposed tax rate modifications should be thoroughly analyzed and discussed to ensure they align with the state's fiscal goals and the best interests of its citizens.
Additionally, Ohio's tax system may need to adapt to emerging trends and technological advancements. With the rise of remote work and the gig economy, the state may need to consider tax policies that address the changing nature of employment and income generation. Ensuring fairness and compliance in an evolving economic landscape will be a key challenge for Ohio's tax authorities.
Staying informed about potential tax changes and their implications is essential for individuals and businesses operating in Ohio. Regularly reviewing tax guidelines and seeking professional advice can help taxpayers navigate any adjustments and make informed financial decisions.
Conclusion
Ohio’s income tax rate of 4.75% provides a stable and competitive tax environment for individuals and businesses. The state’s tax system offers various deductions, credits, and incentives to reduce the tax burden and promote economic growth. However, taxpayers must stay vigilant and informed about potential changes in tax policies to ensure compliance and effective financial planning.
As Ohio continues to navigate economic challenges and opportunities, its tax rate may evolve to meet the changing needs of its residents and businesses. Understanding the state's tax landscape and staying updated with any adjustments is crucial for making informed decisions and contributing to Ohio's economic success.
What are the income tax rates for businesses in Ohio?
+
Ohio imposes a flat tax rate of 4.75% on businesses, including corporations and partnerships. This rate applies to net income earned within the state.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Ohio?
+
Yes, Ohio offers various tax incentives to attract and support businesses. These include the Job Creation Tax Credit, Research and Development Tax Credit, and Energy Efficiency Tax Credit. These incentives provide tax savings and encourage investment in the state.
How does Ohio’s income tax rate compare to other states?
+
Ohio’s flat tax rate of 4.75% is relatively competitive compared to other states. Some states have no income tax, while others have higher rates. Ohio’s rate strikes a balance between attracting businesses and generating revenue for essential services.