State Of Louisiana Taxes
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the tax system in the State of Louisiana. Taxes are an essential aspect of any economy, and understanding how they work is crucial for individuals, businesses, and investors alike. Louisiana, with its unique cultural heritage and diverse economy, has a tax system that reflects its rich history and current economic landscape. This article will delve into the various taxes imposed by the state, providing a comprehensive guide to navigating the Louisiana tax landscape.
Louisiana’s Tax Structure: An Overview
The state of Louisiana imposes a range of taxes to fund its operations and provide services to its residents. These taxes are carefully designed to support the state’s infrastructure, education system, healthcare, and various other public services. Understanding the tax structure is the first step in comprehending the economic landscape of Louisiana.
Louisiana's tax system primarily consists of income taxes, sales taxes, property taxes, and various other fees and levies. Each of these tax categories plays a significant role in the state's fiscal health and contributes to its overall economic stability. Let's explore each of these tax types in detail, understanding their mechanics, rates, and implications.
Income Taxes: A Key Revenue Stream
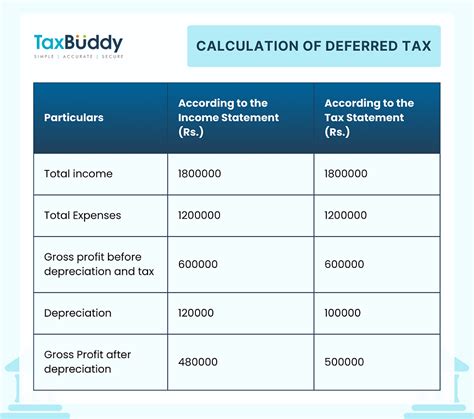
Income taxes are a substantial source of revenue for the state of Louisiana. The state imposes a progressive income tax structure, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at progressively higher rates. This system ensures that individuals and businesses with higher earning capacities contribute a larger share to the state’s coffers.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| First $12,500 | 2% |
| $12,500 - $50,000 | 4% |
| $50,000 - $100,000 | 5% |
| Over $100,000 | 6% |

For instance, consider a resident with an annual income of $75,000. According to the above tax brackets, they would pay 2% on the first $12,500, 4% on the next $37,500, and 5% on the remaining $25,000, totaling an income tax liability of $3,500. This progressive system ensures fairness and allows the state to generate substantial revenue from its higher-earning residents.
Sales Taxes: A Broad-Based Levy
Louisiana also imposes a sales tax on the sale of goods and certain services. This tax is a consumption tax, meaning it is paid by the consumer at the point of purchase. The sales tax rate in Louisiana is set at 4.45%, with additional local taxes often applied on top of this state rate. These local taxes can vary significantly, with some parishes imposing an additional 5% or more, bringing the total sales tax rate in certain areas to over 9%.
For example, if you purchase a $100 item in a parish with a 5% local sales tax, you would pay a total sales tax of $9.45, bringing the final cost of the item to $109.45. This broad-based tax applies to a wide range of goods and services, making it a significant revenue generator for the state and local governments.
Property Taxes: Supporting Local Communities
Property taxes are another crucial component of Louisiana’s tax system. These taxes are imposed on real estate, including land, buildings, and certain personal property. The revenue generated from property taxes primarily supports local governments, including parishes, municipalities, and school districts.
Louisiana's property tax system is based on the assessed value of the property. The assessed value is determined by the local tax assessor's office and is typically a percentage of the property's fair market value. The tax rate, known as the millage rate, is set by the local government and is expressed in mills, with 1 mill equaling $1 of tax for every $1,000 of assessed value.
For instance, if a property has an assessed value of $200,000 and the local millage rate is 100 mills, the annual property tax would amount to $2,000 ($200,000 x 0.0100). This system ensures that property owners contribute to the funding of local services and infrastructure in their communities.
Other Taxes and Fees
In addition to the taxes mentioned above, Louisiana imposes various other taxes and fees to support specific industries and initiatives. These include:
- Franchise Taxes: Businesses operating in Louisiana are subject to a franchise tax, which is based on the capital employed in the state. This tax ensures that businesses contribute to the state's economic development.
- Severance Taxes: Louisiana levies taxes on the extraction of natural resources, such as oil and gas. These severance taxes contribute significantly to the state's revenue and are used to support the environment and local communities impacted by resource extraction.
- Use Taxes: To prevent tax evasion through out-of-state purchases, Louisiana imposes a use tax on certain goods and services used within the state but not subject to sales tax. This ensures fairness and generates additional revenue.
Tax Incentives and Exemptions

Louisiana, like many states, offers a range of tax incentives and exemptions to attract businesses, stimulate economic growth, and support specific industries. These incentives can significantly reduce a company’s tax liability and make Louisiana an attractive location for business operations.
Corporate Tax Incentives
Louisiana provides a range of incentives for corporations, including tax credits, deductions, and exemptions. These incentives are designed to encourage investment, job creation, and economic development. Some of the notable corporate tax incentives include:
- Industrial Tax Exemption Program (ITEP): This program allows eligible manufacturing and industrial businesses to receive a 100% exemption from property taxes for a specified period. The exemption is typically granted for a period of 5 to 10 years, with the potential for renewal.
- Enterprise Zone Tax Credits: Businesses operating in designated Enterprise Zones can qualify for tax credits on their state income tax liability. These credits are based on the number of jobs created and the capital investment made within the zone.
- Research and Development Tax Credits: Louisiana offers tax credits to businesses engaged in research and development activities within the state. These credits can offset a portion of the state's corporate income tax liability.
Individual Tax Incentives
Louisiana also provides tax incentives for individuals, particularly those involved in specific industries or initiatives. Some of the notable individual tax incentives include:
- Homeowner's Rebate Program: This program offers a rebate of up to $750 on state income taxes for eligible homeowners. The rebate is designed to provide relief to homeowners, especially those with limited income.
- Historic Preservation Tax Credits: Individuals or businesses that undertake the rehabilitation of historic buildings can qualify for tax credits. These credits can offset a portion of the cost of the rehabilitation project.
- Film and Digital Media Tax Credits: Louisiana's thriving film and digital media industry benefits from generous tax credits. Individuals and businesses involved in film production can receive tax credits of up to 40% of their qualified production expenses.
Tax Administration and Compliance
Ensuring tax compliance is a critical aspect of Louisiana’s tax system. The state has established various agencies and departments to administer and enforce its tax laws. These entities are responsible for collecting taxes, auditing tax returns, and ensuring that taxpayers comply with the state’s tax regulations.
Louisiana Department of Revenue (LDR)
The Louisiana Department of Revenue is the primary agency responsible for administering and enforcing the state’s tax laws. The LDR collects taxes, provides guidance and assistance to taxpayers, conducts audits, and enforces tax regulations. They also oversee tax incentive programs and ensure that businesses and individuals comply with the requirements for these incentives.
Tax Compliance and Penalties
Louisiana takes tax compliance seriously and imposes penalties for non-compliance. These penalties can include fines, interest charges, and even criminal prosecution for severe cases of tax evasion. It is essential for taxpayers to understand their tax obligations and seek professional advice when necessary to ensure compliance.
Online Filing and Payment Options
Louisiana has embraced technology to streamline the tax filing and payment process. The LDR offers online filing and payment options, making it convenient for taxpayers to fulfill their tax obligations. This digital approach not only simplifies the process but also reduces the potential for errors and delays.
Impact on the Economy and Residents
Louisiana’s tax system has a significant impact on the state’s economy and its residents. The taxes collected fund critical public services, infrastructure development, and initiatives that support the state’s growth and prosperity. Understanding how these taxes are distributed and utilized is essential for evaluating the state’s economic health and future prospects.
Funding Public Services
The revenue generated from taxes is primarily used to fund public services, including education, healthcare, public safety, and infrastructure development. These services are vital for the well-being of Louisiana’s residents and contribute to the state’s overall quality of life.
For instance, income and sales taxes play a significant role in funding Louisiana's renowned higher education system, which includes top universities and colleges. These institutions not only provide quality education but also contribute to the state's research and development efforts, driving innovation and economic growth.
Economic Development and Growth
Louisiana’s tax system, particularly its tax incentives, plays a crucial role in attracting businesses and stimulating economic growth. By offering competitive tax rates and generous incentives, the state creates an attractive business environment, encouraging investment and job creation.
The tax incentives for the film and digital media industry, for example, have transformed Louisiana into a hub for film production. This has not only created thousands of jobs but has also contributed to the state's cultural and economic diversity.
Resident Tax Burden
While taxes are essential for funding public services and supporting economic growth, they also impact the disposable income of Louisiana’s residents. The state’s tax structure, particularly its progressive income tax, ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger share. However, the various tax incentives and exemptions help alleviate the tax burden for certain residents and industries.
For instance, the Homeowner's Rebate Program provides much-needed relief to low- and moderate-income homeowners, helping them manage their tax liabilities and maintain their homes.
Future Implications and Trends
Louisiana’s tax system is subject to ongoing evaluation and adjustment to meet the changing needs of the state and its residents. As the economy evolves, so too must the tax structure to ensure it remains fair, efficient, and effective. Here are some key trends and potential future developments in Louisiana’s tax landscape.
Tax Reform Initiatives
Louisiana has periodically undertaken tax reform initiatives to simplify its tax system, improve efficiency, and promote fairness. These reforms often involve reevaluating tax rates, restructuring tax incentives, and streamlining tax administration processes. Such reforms aim to make the tax system more transparent and easier for taxpayers to navigate.
Economic Shifts and Industry Trends
The state’s tax system must adapt to changing economic conditions and industry trends. As industries evolve and new sectors emerge, Louisiana’s tax policies may need to be adjusted to support these changes. For instance, with the growing importance of renewable energy, the state may consider tax incentives to encourage investment in this sector.
Impact of Federal Tax Changes
Changes in federal tax laws can also have a significant impact on Louisiana’s tax system. Federal tax reforms, such as those implemented in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, can influence the state’s tax policies and revenue streams. Louisiana may need to adjust its tax structure to align with federal changes and ensure its tax system remains competitive.
Budgetary Constraints and Priorities
Louisiana’s tax system must also consider the state’s budgetary constraints and funding priorities. As the state faces fiscal challenges, it may need to carefully manage its tax revenue and consider adjustments to tax rates or incentives to ensure the sustainability of public services.
Technology and Digital Transformation
The continued adoption of technology in tax administration is likely to shape Louisiana’s tax landscape. Digital tools and online platforms can enhance tax compliance, improve efficiency, and reduce administrative burdens. The state may explore further digital transformation to streamline tax processes and improve the taxpayer experience.
Conclusion
Louisiana’s tax system is a complex yet crucial component of the state’s economic landscape. From income taxes to sales taxes and property taxes, each type of tax plays a significant role in funding public services, supporting economic growth, and shaping the state’s future. Understanding this tax system is essential for individuals, businesses, and investors looking to navigate Louisiana’s vibrant economy.
As Louisiana continues to evolve, its tax system will adapt to meet the changing needs of its residents and businesses. By staying informed about tax policies, incentives, and trends, taxpayers can make informed decisions and contribute to the state's prosperity. Louisiana's unique tax landscape, with its blend of traditional taxes and innovative incentives, makes it a fascinating subject for exploration and analysis.
How does Louisiana’s tax system compare to other states in terms of competitiveness?
+Louisiana’s tax system is generally considered competitive compared to other states. Its income tax rates are relatively moderate, and its sales tax structure, while variable, offers flexibility at the local level. However, it’s important to consider other factors, such as the cost of living and business environment, when comparing tax competitiveness.
What are the eligibility criteria for the Industrial Tax Exemption Program (ITEP)?
+The ITEP is available to manufacturing and industrial businesses that meet specific criteria. Eligibility typically requires a minimum capital investment, job creation, and compliance with environmental and other regulations. Businesses should consult the Louisiana Department of Revenue for detailed eligibility guidelines.
How can taxpayers stay updated on tax law changes and incentives in Louisiana?
+Taxpayers can stay informed by regularly visiting the Louisiana Department of Revenue’s website, which provides updates on tax law changes, new incentives, and important deadlines. Additionally, subscribing to their newsletters and following official social media accounts can ensure timely access to tax-related information.
Are there any tax incentives for renewable energy projects in Louisiana?
+Yes, Louisiana offers tax incentives for renewable energy projects, including tax credits and exemptions. These incentives aim to promote the development of renewable energy sources and reduce the state’s reliance on traditional energy sources. Specific incentives may vary, so it’s advisable to consult the LDR for the most current information.