State Income Tax Ohio
Ohio, known for its diverse economy and vibrant cities, has a unique approach to state income taxation that sets it apart from many other states in the US. Understanding the specifics of Ohio's income tax system is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within the state. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Ohio's income tax laws, providing an in-depth analysis to help you navigate this essential aspect of financial planning.
The Fundamentals of Ohio’s Income Tax Structure
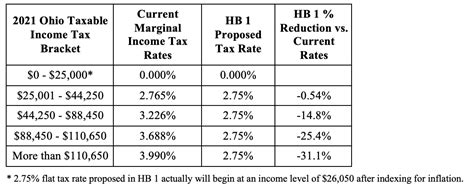
Ohio imposes a graduated income tax on its residents, meaning that the tax rate increases as your income rises. This progressive tax system is designed to ensure that those with higher incomes contribute a greater proportion of their earnings to the state’s revenue. As of 2023, Ohio has four income tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. Here’s a breakdown of these brackets:
| Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $5,700 | 0.479% |
| $5,701 - $11,400 | 1.979% |
| $11,401 - $207,500 | 3.979% |
| Above $207,500 | 4.799% |
It's important to note that these tax rates apply to Ohio residents. Non-residents who work or have income sources within Ohio may also be subject to income tax, but their tax liability is calculated differently. Non-residents are generally taxed at a flat rate of 4.799% on Ohio-sourced income, regardless of their total income.
Exemptions and Deductions
Ohio offers several tax exemptions and deductions that can help reduce your tax liability. For instance, senior citizens aged 65 and above may be eligible for a Senior Citizen Credit, which can reduce their tax bill. Additionally, Ohio provides a School District Income Tax Credit, which offsets the income tax paid to a school district by residents who pay taxes to more than one school district.
Furthermore, Ohio allows itemized deductions for various expenses, including medical and dental costs, charitable contributions, and certain taxes. These deductions can be beneficial for individuals with high out-of-pocket expenses or those who are actively involved in charitable work.
Filing and Payment Procedures

The Ohio Department of Taxation provides a user-friendly online platform for tax filing, known as Ohio Business Gateway. This platform allows individuals and businesses to file their tax returns, make payments, and manage their tax accounts. The deadline for filing Ohio income tax returns is typically aligned with the federal tax deadline, which is usually April 15th of the following year.
For those who owe taxes, Ohio offers various payment options, including electronic payments, credit card payments, and direct bank account withdrawals. It's crucial to ensure that your tax return is accurate and filed on time to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Ohio’s Tax Laws for Businesses
Ohio imposes income tax on businesses operating within the state, with rates varying based on the type of business entity. For instance, C corporations are subject to a 4.799% flat tax rate, while S corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs) are taxed at the individual member’s rate. Partnerships and sole proprietorships are also taxed at the individual’s rate, with the tax liability passed through to the owners.
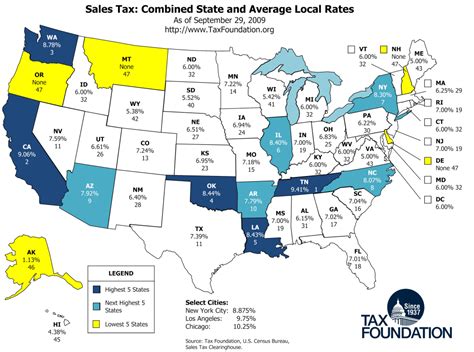
Businesses in Ohio also need to be aware of sales and use taxes, which are levied on the sale of goods and certain services. The state's sales tax rate is currently set at 5.75%, with local jurisdictions allowed to add additional sales tax, resulting in varying rates across the state.
The Impact of Ohio’s Income Tax on the Economy
Ohio’s income tax system plays a crucial role in funding public services and infrastructure projects. The revenue generated from income taxes contributes to education, healthcare, transportation, and other vital sectors. By maintaining a progressive tax structure, Ohio ensures that its tax system remains fair and equitable, allowing for a balanced approach to public spending.
Furthermore, Ohio's tax laws, including its income tax rates, can influence business decisions and investment choices. A well-designed tax system can encourage economic growth, job creation, and business expansion. Conversely, complex or unfavorable tax laws may deter businesses from operating in the state.
Comparative Analysis: Ohio vs. Other States
When compared to other states, Ohio’s income tax rates are relatively moderate. Several states, particularly those with no income tax, may appear more attractive from a tax perspective. However, it’s essential to consider the overall tax burden, including sales tax, property tax, and other levies, when evaluating the tax landscape of a state.
For instance, while Ohio's income tax rates are progressive, its sales tax rate is relatively low compared to some neighboring states. This balance can make Ohio an appealing choice for businesses and individuals seeking a stable and predictable tax environment.
Navigating Ohio’s Tax Landscape: Expert Insights
Understanding and effectively managing your tax obligations is crucial for both individuals and businesses in Ohio. Here are some expert tips to help you navigate the state’s tax system:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with Ohio's tax laws and regulations. The state's tax codes can change annually, so staying informed ensures you're aware of any updates or new deductions that may benefit you.
- Utilize Tax Professionals: Consider working with a certified public accountant (CPA) or tax advisor, especially if you have a complex financial situation. They can provide tailored advice and ensure your tax returns are accurate and optimized.
- Plan Ahead: Tax planning is essential. By understanding your potential tax liability early on, you can make informed financial decisions throughout the year, potentially reducing your overall tax burden.
- Take Advantage of Exemptions and Deductions: Ohio offers a range of tax exemptions and deductions. Make sure you're aware of these and take advantage of them to minimize your tax liability.
In conclusion, Ohio's income tax system, with its graduated rates and various exemptions, provides a balanced approach to state revenue generation. Understanding and effectively managing your tax obligations is key to ensuring compliance and optimizing your financial situation. By staying informed and utilizing the resources available, individuals and businesses can navigate Ohio's tax landscape with confidence.
What are the penalties for late tax filing in Ohio?
+Ohio imposes a penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for every month (or part of a month) that a tax return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest accrues on the unpaid tax at a rate of 5% per year.
Are there any special tax incentives for businesses in Ohio?
+Yes, Ohio offers a range of tax incentives to attract and support businesses. These include job creation tax credits, research and development tax credits, and tax exemptions for certain industries. It’s advisable to consult with a tax professional to understand which incentives your business may qualify for.
How does Ohio’s income tax compare to other states in the Midwest?
+Ohio’s income tax rates are generally on par with other Midwest states. While some states have higher or lower tax rates, the overall tax landscape in the Midwest is relatively similar. However, it’s important to consider the full tax burden, including sales tax and property tax, when comparing states.