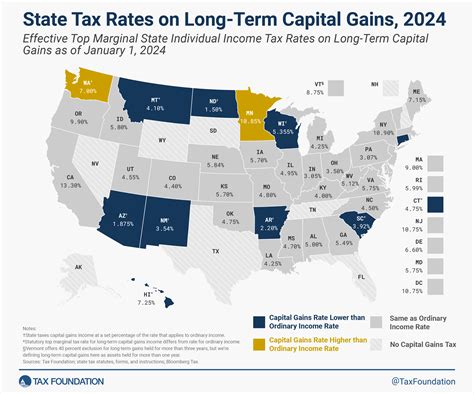
Self Employment Tax Credit

The Self-Employment Tax Credit, often referred to as the Self-Employment Tax Credit for Health Insurance, is a financial incentive designed to support the well-being of self-employed individuals and their families. This tax credit is an essential tool for independent workers, offering a means to offset the costs of health insurance premiums, which can be a significant financial burden. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the Self-Employment Tax Credit, exploring its history, eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and the potential impact it can have on the financial health of self-employed individuals.
The Evolution of the Self-Employment Tax Credit

The concept of providing tax incentives to support health insurance coverage for self-employed individuals is not a new one. The journey towards the establishment of the Self-Employment Tax Credit began with the recognition of the unique challenges faced by those who choose the path of self-employment. Unlike traditional employees, self-employed individuals do not have access to employer-sponsored health plans, making it crucial for them to navigate the complex landscape of individual health insurance markets.
The history of the Self-Employment Tax Credit can be traced back to the early 2000s, when policymakers began to address the growing concern of uninsured self-employed workers. The initial iterations of the credit aimed to provide a modest financial relief, allowing self-employed individuals to deduct a portion of their health insurance premiums from their taxable income. However, it was soon realized that a more substantial incentive was necessary to encourage broader participation and provide adequate support for the diverse needs of the self-employed population.
Over the years, the Self-Employment Tax Credit has undergone significant transformations. The Affordable Care Act (ACA), enacted in 2010, played a pivotal role in reshaping the credit. The ACA not only expanded the eligibility criteria but also increased the potential value of the credit, making it a more attractive option for self-employed individuals. This landmark legislation aimed to improve access to affordable healthcare, and the Self-Employment Tax Credit was a key component in achieving this goal for the self-employed sector.
Understanding Eligibility: Who Qualifies for the Credit?

Determining eligibility for the Self-Employment Tax Credit is a critical step in understanding whether an individual can benefit from this financial incentive. The criteria for qualification are designed to target those who are actively engaged in self-employment and face specific challenges in accessing affordable health insurance.
Key Eligibility Factors
- Self-Employment Status: To be eligible, an individual must be considered self-employed. This includes sole proprietors, independent contractors, and those who operate a business as a single member LLC. It’s important to note that the definition of self-employment may vary based on the tax jurisdiction and specific guidelines.
- Health Insurance Coverage: The Self-Employment Tax Credit is specifically designed for individuals who purchase their own health insurance plans. This includes marketplace plans, private insurance policies, or even COBRA continuation coverage. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the health insurance plan meets the minimum essential coverage requirements as defined by the ACA.
- Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI): The MAGI plays a crucial role in determining eligibility and the amount of the credit. Generally, individuals with a lower MAGI are more likely to qualify for a higher credit amount. The specific MAGI thresholds can vary depending on the tax year and the guidelines set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or the relevant tax authority.
- Household Income: In some cases, the household income may also be considered when determining eligibility. This is particularly relevant for individuals who file taxes jointly with their spouse or partners. The household income threshold can impact the eligibility and the potential credit amount.
Calculating the Self-Employment Tax Credit
The calculation of the Self-Employment Tax Credit involves a series of steps that consider various factors, including the cost of health insurance premiums, the individual’s income, and the applicable tax credit rate. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the calculation process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Determine the eligible premium amount. This is the amount an individual pays for their health insurance premium, including any premiums paid for family members covered under the same plan. |
| 2 | Calculate the household income. For individuals filing taxes jointly, this includes the combined income of the filer and their spouse. For single filers, it's their individual income. |
| 3 | Identify the applicable tax credit rate. The tax credit rate is determined based on the household income and the applicable tax year. The IRS provides guidelines on the specific credit rates for each income bracket. |
| 4 | Multiply the eligible premium amount by the applicable tax credit rate. This calculation provides the preliminary tax credit amount. |
| 5 | Adjust the preliminary credit amount based on any applicable limitations or phase-outs. These adjustments ensure that the credit remains within the allowable range and does not exceed the individual's tax liability. |
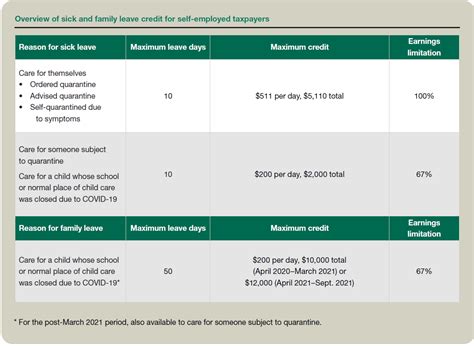
Maximizing the Benefits: Strategies for Self-Employed Individuals
For self-employed individuals, understanding the intricacies of the Self-Employment Tax Credit can be a powerful tool in managing their financial well-being. Here are some strategies and considerations to make the most of this tax incentive:
Explore Health Insurance Options
The first step in maximizing the benefits of the Self-Employment Tax Credit is to carefully evaluate health insurance options. Compare different plans, considering factors such as coverage, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses. Choosing a plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and budget can ensure that you receive the maximum credit.
Understand Income Thresholds
Income plays a significant role in determining the eligibility and amount of the Self-Employment Tax Credit. Stay informed about the income thresholds for your specific tax year. Adjusting your business income or expenses strategically, within legal and ethical boundaries, can help you stay within the eligible income range and maximize your credit.
Utilize Tax Software or Professionals
Calculating the Self-Employment Tax Credit accurately can be complex. Consider using tax preparation software or seeking the assistance of a tax professional. These tools and experts can ensure that you claim the correct amount of credit and avoid potential errors that could lead to audits or penalties.
Stay Updated on Tax Law Changes
Tax laws are subject to change, and the Self-Employment Tax Credit is no exception. Stay informed about any updates or amendments to the tax code that may impact your eligibility or the calculation of the credit. Being aware of these changes can help you plan your financial strategies accordingly.
Impact and Future Outlook
The Self-Employment Tax Credit has had a significant impact on the financial landscape for self-employed individuals. By providing a financial incentive for health insurance coverage, it has encouraged more self-employed workers to access affordable healthcare. This, in turn, has contributed to improved overall health outcomes and financial security for this segment of the workforce.
Looking ahead, the future of the Self-Employment Tax Credit remains closely tied to the broader healthcare and tax policy landscape. As healthcare costs continue to rise, the credit may play an even more critical role in supporting self-employed individuals. Policymakers and tax authorities will need to carefully consider the evolving needs of the self-employed population and ensure that the credit remains an effective tool for promoting access to healthcare and financial stability.
Key Takeaways
- The Self-Employment Tax Credit is a financial incentive designed to support self-employed individuals in accessing affordable health insurance.
- Eligibility criteria include self-employment status, health insurance coverage, and income thresholds.
- The credit amount is calculated based on eligible premium costs and applicable tax credit rates.
- Strategies to maximize the credit include exploring insurance options, understanding income thresholds, and staying updated on tax law changes.
- The future of the credit is tied to healthcare and tax policy, with potential for further expansion to meet the needs of self-employed individuals.
Can I claim the Self-Employment Tax Credit if I’m already receiving health insurance through my spouse’s employer-sponsored plan?
+The eligibility for the Self-Employment Tax Credit is based on your self-employment status and the health insurance coverage you purchase for yourself and your family. If you are not the primary policyholder on the health insurance plan obtained through your spouse’s employer, you may still qualify for the credit. However, it’s important to review the specific guidelines and consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate eligibility determination.
Are there any limitations on the types of health insurance plans that qualify for the Self-Employment Tax Credit?
+The Self-Employment Tax Credit generally applies to a wide range of health insurance plans, including marketplace plans, private insurance policies, and even COBRA continuation coverage. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the plan meets the minimum essential coverage requirements as defined by the Affordable Care Act. Some specialized plans or limited benefit policies may not qualify, so it’s essential to review the plan’s coverage details.
How often can I claim the Self-Employment Tax Credit?
+The Self-Employment Tax Credit is typically claimed annually when filing your tax return. As long as you continue to meet the eligibility criteria and purchase qualifying health insurance plans, you can claim the credit each year. However, it’s important to stay updated on any changes to the tax code or eligibility requirements that may impact your ability to claim the credit in future tax years.