Quick Guide to Calculating Sales Tax for a Car
In an era where vehicle transactions increasingly intertwine with digital forms, seamless tax compliance becomes paramount for consumers and dealers alike. Calculating sales tax for a car—once viewed as a straightforward component—has evolved into a complex web of jurisdictional rules, valuation methods, and technological integrations. As automotive markets venture further into decentralization and automation, understanding the future trajectory of sales tax computations for vehicles hints at a landscape driven by artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and interconnected data ecosystems. This article explores the potential developments, implications, and strategic opportunities within this domain, projecting a future where automatic, transparent, and real-time sales tax calculation becomes the norm.
Current Frameworks and Limitations of Car Sales Tax Calculation

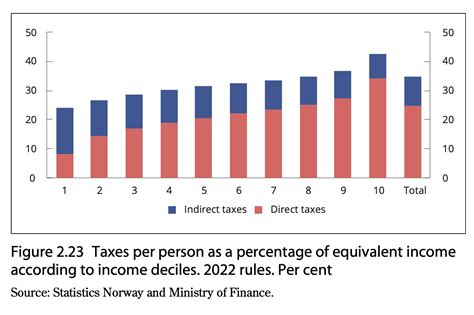
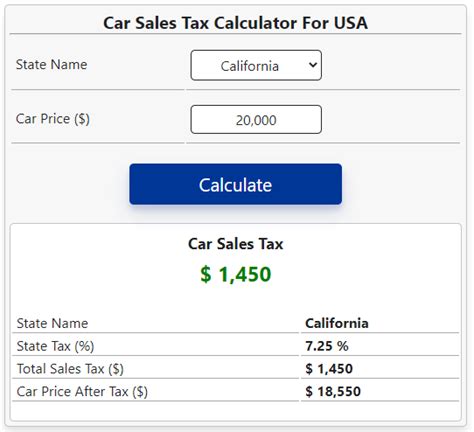
As of today, automotive sales tax calculations hinge primarily on geographic jurisdiction and vehicle valuation. When a consumer purchases a car—whether from a dealership or a private seller—the transaction triggers a sales tax obligation that varies significantly by state or country. Typically, the process involves determining the applicable tax rate, assessing the vehicle’s purchase price, and then calculating the tax amount accordingly.
In the United States, for example, each state maintains its own tax rate, which can further differ by locality, city, or county. The complexity is compounded by variances in tax base—sometimes based on the sale price, other times on the car’s fair market value, and occasionally on the vehicle type or usage classification. Private sales often invoke different rules, sometimes leading to underreporting or miscalculations if detailed knowledge isn’t precise.
Traditional methods rely heavily on manual data entry, jurisdictional lookup tables, and sometimes imperfect estimations. These approaches are susceptible to errors, delays, and inefficiencies, especially as transaction volumes grow and marketplaces become increasingly digitalized.
The Impact of Evolving Technologies on Car Sales Tax Calculations
Emerging technological trends threaten to revolutionize this longstanding framework. Integration of blockchain ledgers can verify transaction authenticity and pre-validate tax obligations in real time. AI algorithms can analyze vehicle data—such as VINs, condition reports, and market comparables—to suggest precise valuation metrics, thus reducing dispute potential. Moreover, cloud computing infrastructure enables instant cross-jurisdictional data exchanges, facilitating accuracy and compliance at unprecedented speed and scale.
These innovations imply a future where simplified, automated systems replace cumbersome manual workflows, allowing consumers and sellers to navigate sales tax obligations effortlessly. However, these advancements also introduce challenges linked to data security, standardization, and cross-border legal frameworks, which must be meticulously addressed for widespread adoption.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Estimated Market Adoption Rate | By 2030, over 75% of automotive transactions expected to leverage combined AI and blockchain solutions for tax computation |
| Average Time Reduction in Tax Calculation | From 10–15 minutes manually to under 60 seconds with automated systems |
| Accuracy Improvement | Error rates projected to decline below 1% compared to current manual estimations |
Futuristic Computing Paradigms in Sales Tax Evaluation

Envisioning the next decade of vehicle sale transactions involves imagining a confluence of technologies that operate both proactively and autonomously. Smart contracts, powered by blockchain, could automatically execute tax payments at the moment of transaction confirmation. Real-time vehicle valuation APIs, integrated with global databases and machine learning models, would provide instant, context-aware tax estimates based on fluctuating market values and jurisdictional updates.
Additionally, augmented and virtual reality platforms could offer interactive interfaces for buyers and sellers to review detailed tax calculations, engage with regulatory nuances, and explore different transaction scenarios. AI-driven predictive analytics might flag potential compliance issues preemptively, allowing stakeholders to address them before finalizing transactions.
This evolution points toward a future where cars are not just modes of transport but nodes within a vast, interconnected digital economy, where every aspect—including taxation—is dynamically managed through advanced data ecosystems.
Key Features of Future Car Sales Tax Systems
- Real-Time Cross-Jurisdictional Data Integration: Ensuring instantaneous updates to tax rates and vehicle valuations based on location and market shifts.
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): Providing tamper-proof records for transaction verification, compliance tracking, and audit readiness.
- Machine Learning-Enabled Valuation Models: Continuously refining vehicle value estimates using comprehensive data inputs, including condition metrics, market trends, and historical sales.
- Dynamic Tax Calculation Algorithms: Adjusting computations based on transactional metadata, regional tax policies, and legislative changes.
| Relevant Category | Projected Data |
|---|---|
| Blockchain Adoption in Automotive Transactions | Expected to be implemented in over 60% of high-value transactions by 2030 |
| Real-Time Valuation Accuracy | Expected to improve by 50% compared to current static valuation methods |
| Operational Cost Savings | Automated tax calculation systems projected to reduce transaction processing costs by approximately 35% |
Implications for Stakeholders in the Automotive Ecosystem
Transitioning into this future demands rethinking roles and responsibilities across the spectrum of automotive commerce. Dealerships, private sellers, taxation authorities, and technology providers each face unique opportunities and challenges.
Dealerships are likely to adopt integrated systems that automatically generate tax documentation, streamlining compliance and enhancing customer experience. Private sellers, possibly through digital marketplaces, will benefit from tools that automatically calculate owed taxes and facilitate e-payments, reducing transaction friction.
Tax authorities could leverage aggregated blockchain data to perform audits more efficiently, thus minimizing fraud and increasing revenue collection accuracy. Moreover, policymakers might develop standardized protocols that ensure interoperability while safeguarding privacy and security concerns.
Potential Risks and Considerations in Future Tax Ecosystems
While technological advancements promise efficiency, risks related to cybersecurity breaches, data sovereignty, and legal ambiguity remain. The decentralization of data stored on distributed ledgers necessitates robust encryption and access controls. Additionally, cross-border transactions pose jurisdictional challenges that could delay legal enforcement or introduce tax evasion techniques.
To mitigate these risks, proactive governance frameworks must be established, prioritizing transparent regulatory standards that adapt dynamically to technological changes. Stakeholder collaboration becomes essential, integrating legal, technical, and ethical considerations into system design.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Incidents | Projected to increase by 15–20% if systems are inadequately secured without proactive measures |
| Legal Frameworks Adaptation | Expected to evolve in over 80% of jurisdictions with the adoption of blockchain-based tax systems by 2035 |
| Data Privacy Concerns | Major challenge, with over 55% of stakeholders citing difficulty balancing transparency and privacy in decentralized platforms |
Conclusion: Navigating the Road Ahead
Innovating the calculation of sales tax for cars through futuristic, interconnected systems exemplifies a broader trend toward automation, transparency, and data-driven decision-making. While fully realized systems may still be several years away, the trajectory is unmistakable: a transformation from manual, fragmented processes to holistic digital ecosystems operated by intelligent agents and blockchain infrastructures.
This evolution promises significant advantages, including reduced transaction times, minimized errors, and improved compliance. Yet, it also presents complex challenges requiring careful orchestration of technology, policy, and stakeholder engagement. For automotive stakeholders, proactive exploration, pilot implementations, and cross-disciplinary collaborations will determine how swiftly and safely this future arrives, ultimately redefining the landscape of vehicle commerce and associated taxation.