Ri Sales Tax

The state of Rhode Island, known for its vibrant culture and rich history, has a unique tax system that impacts its residents and businesses. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the Rhode Island Sales Tax, its rates, applicability, and how it affects the local economy. By understanding the sales tax landscape, we can navigate the state's financial regulations with ease and ensure compliance.
Understanding the Basics of Rhode Island Sales Tax

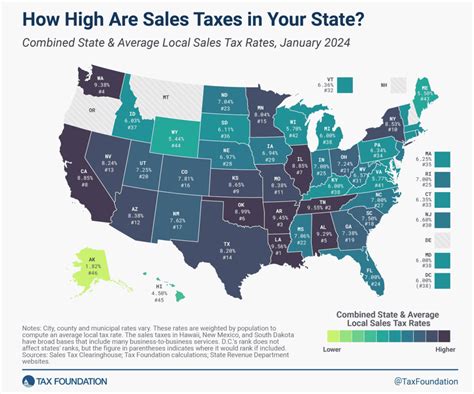
Rhode Island, like many other states, imposes a sales tax on various goods and services sold within its borders. This tax is a crucial source of revenue for the state government, contributing to essential public services and infrastructure development. The sales tax rate in Rhode Island is not a flat percentage but varies based on the type of goods or services being purchased. Understanding these variations is key to managing financial obligations accurately.
The state sales tax rate in Rhode Island currently stands at 7%, which is applicable to most tangible personal property and certain services. However, it's important to note that there are specific categories of items that are exempt from this tax, such as certain food products, prescription drugs, and certain types of manufacturing equipment. These exemptions are designed to encourage specific economic activities and provide relief to certain sectors.
Local Tax Rates and Their Impact
In addition to the state sales tax, Rhode Island also allows municipalities to impose their own local sales taxes. These local taxes are often levied to support local projects and infrastructure, and they can significantly impact the overall sales tax rate a consumer pays. For instance, while the state sales tax rate is a consistent 7%, local tax rates can vary from one city or town to another, resulting in a total sales tax rate that differs across the state.
The impact of these local taxes can be significant, especially for businesses operating in multiple municipalities. It's crucial for businesses to understand these local tax variations to ensure accurate pricing and compliance with local regulations. Mismanagement of these taxes can lead to legal issues and financial penalties.
| City/Town | Local Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Providence | 1% |
| Newport | 1.5% |
| Westerly | 1% |
| Warwick | 1% |
| Bristol | 1% |

Taxable Items and Exemptions
Not all goods and services are subject to the Rhode Island sales tax. The state has a detailed list of items that are considered taxable and those that are exempt. Understanding these categories is crucial for both businesses and consumers to ensure compliance and avoid unnecessary tax burdens.
Taxable Items
The list of taxable items in Rhode Island is extensive and includes most tangible personal property. This includes items like clothing, electronics, furniture, and vehicles. Additionally, certain services, such as repair and installation services, are also subject to sales tax. Here’s a simplified breakdown of some common taxable items:
- Groceries (excluding unprepared food)
- Alcoholic beverages
- Restaurant meals
- Entertainment tickets
- Hotels and lodging
- Vehicles (cars, motorcycles, boats)
- Construction materials
Exemptions and Special Cases
On the other hand, there are several categories of items and services that are exempt from sales tax in Rhode Island. These exemptions are often designed to promote specific economic activities or provide relief to certain sectors. Here are some notable exemptions:
- Prescription drugs
- Certain medical devices
- Non-prepared food items (groceries)
- Manufacturing equipment (under certain conditions)
- Residential electricity and natural gas
- Legal services
It's important to note that these exemptions can be complex and may have specific conditions or limitations. For instance, the exemption for manufacturing equipment often depends on the equipment's primary use and the nature of the manufacturing process.
Sales Tax Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with sales tax regulations is a critical aspect of doing business in Rhode Island. Businesses are responsible for collecting, reporting, and remitting sales tax to the state and local governments. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties and legal issues.
Registration and Permits
Any business selling taxable goods or services in Rhode Island must register with the Rhode Island Division of Taxation and obtain the necessary permits. This registration process ensures that businesses are officially recognized as tax-collecting entities and provides them with the necessary tools to comply with sales tax regulations.
The registration process typically involves providing detailed information about the business, its location(s), and the types of goods or services it offers. This information helps the state understand the business's tax obligations and ensure that the correct tax rates are applied.
Collection and Remittance
Once registered, businesses are responsible for collecting the appropriate sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This tax is typically added to the purchase price and displayed as a separate line item on the sales receipt. It’s important for businesses to accurately calculate and collect this tax to avoid under- or over-collection, both of which can lead to financial and legal issues.
The collected sales tax must then be remitted to the state and local governments on a regular basis. The frequency of these remittances depends on the business's sales volume and can range from monthly to quarterly. Failure to remit sales tax on time can result in penalties and interest charges.
Reporting Requirements
In addition to collecting and remitting sales tax, businesses are also required to file regular sales tax returns. These returns provide detailed information about the business’s sales and the corresponding sales tax collected. The information on these returns helps the state understand the business’s tax obligations and ensure that the correct tax amounts are being remitted.
Sales tax returns typically include details such as the total sales, the sales tax rate applied, and the total sales tax collected. Businesses must maintain accurate records to support these returns, including sales receipts, invoices, and other relevant documentation.
The Impact of Sales Tax on the Rhode Island Economy
The sales tax is a significant contributor to Rhode Island’s economy, providing essential revenue for state and local governments. This revenue is used to fund a wide range of public services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and social programs.
Revenue Generation and Allocation
The sales tax is a reliable source of revenue for the state, as it is levied on a broad base of goods and services. This revenue is crucial for maintaining the state’s fiscal health and ensuring the continuity of public services. The allocation of this revenue is carefully planned to address the state’s priorities and needs.
A portion of the sales tax revenue is allocated to the state's general fund, which is used for a variety of purposes, including funding state agencies, maintaining public safety, and supporting public education. The remaining revenue is often earmarked for specific programs or initiatives, such as infrastructure projects, economic development initiatives, or social welfare programs.
Economic Growth and Consumer Spending
While the sales tax can be seen as a burden by consumers, it also plays a vital role in stimulating economic growth. The tax revenue generated helps fund infrastructure projects, such as road improvements, public transportation, and utility upgrades, which in turn attract businesses and create jobs. Additionally, the sales tax provides an incentive for consumers to make informed purchasing decisions, promoting responsible spending habits.
However, it's important to strike a balance between tax revenue generation and consumer spending. Excessive sales tax rates can discourage consumer spending and negatively impact the economy. Therefore, states like Rhode Island carefully consider the impact of sales tax rates on consumer behavior and the overall economy when making tax policy decisions.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
As with any tax system, the Rhode Island sales tax is subject to potential changes and reforms. These changes can be driven by various factors, including economic conditions, political priorities, and the need to address emerging challenges.
Potential Reforms and Modernization
One of the key areas of focus for sales tax reforms is ensuring that the tax system keeps up with the changing economic landscape. This includes addressing the growth of e-commerce and ensuring that online sales are subject to the same tax obligations as traditional brick-and-mortar stores. Rhode Island, like many other states, is working to modernize its sales tax regulations to adapt to the digital age.
Additionally, there is ongoing discussion about the potential for simplifying the sales tax system, particularly regarding the complexity of local tax rates. Simplifying the system could make it easier for businesses to comply with tax regulations and reduce the administrative burden associated with sales tax collection and remittance.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Any changes to the sales tax system can have significant implications for both businesses and consumers. For businesses, changes in tax rates or regulations can impact pricing strategies, compliance obligations, and overall financial planning. It’s crucial for businesses to stay informed about potential tax reforms and adapt their operations accordingly.
For consumers, changes in sales tax rates can directly impact their purchasing power and spending habits. Higher sales tax rates can make certain goods and services more expensive, potentially influencing consumer choices and behavior. Therefore, it's essential for consumers to be aware of any upcoming tax changes and plan their spending accordingly.
What is the current sales tax rate in Rhode Island for online purchases?
+Rhode Island has implemented a Remote Seller Law, which requires out-of-state sellers to collect and remit sales tax on online purchases made by Rhode Island residents. The sales tax rate for online purchases is the same as the rate for in-store purchases, which is currently 7%.
Are there any special sales tax rates for certain industries in Rhode Island?
+Yes, Rhode Island has specific sales tax rates for certain industries, such as the hospitality industry (hotels and restaurants). These rates can vary depending on the location and the type of service provided. It’s important for businesses in these industries to understand the applicable rates to ensure compliance.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in Rhode Island?
+The frequency of sales tax remittance in Rhode Island depends on the business’s sales volume. Businesses with a monthly sales tax liability of 500 or more must remit sales tax monthly. Those with a liability between 100 and 499 must remit quarterly, and those with a liability under 100 can remit annually. However, it’s recommended to consult with a tax professional for accurate guidance based on your business’s specific circumstances.