Payroll Versus Income Tax

In the world of finance and business, understanding the differences between payroll and income tax is crucial for both employers and employees. These two concepts are fundamental to the economic landscape and have a significant impact on personal and business finances. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of payroll and income tax, providing a comprehensive guide to enhance your financial literacy.
Understanding Payroll: A Comprehensive Overview

Payroll is a critical component of any business, as it involves the management of employee compensation, benefits, and deductions. It is the process by which an employer calculates and disburses wages, salaries, bonuses, and other forms of compensation to its employees. Payroll goes beyond just writing checks; it encompasses a range of legal and financial responsibilities that employers must navigate.
Key Components of Payroll
- Gross Pay: This is the total amount earned by an employee before any deductions. It includes regular wages, overtime pay, bonuses, and any other additional earnings.
- Deductions: Payroll deductions include mandatory withholdings such as income tax, Social Security, and Medicare contributions. Additionally, employers may also deduct voluntary contributions like retirement plan contributions and insurance premiums.
- Net Pay: The amount an employee receives after all deductions have been applied is known as net pay. This is the actual amount deposited into the employee’s bank account or paid out in cash.
- Payroll Frequency: Employers can choose between various payroll frequencies, such as weekly, biweekly, semimonthly, or monthly. The frequency impacts the cash flow and financial planning of both the employer and the employee.
Payroll Management
Managing payroll involves a series of complex tasks, including but not limited to:
- Calculating employee earnings accurately, including overtime, bonuses, and commissions.
- Withholding and remitting the appropriate taxes to the government.
- Administering and tracking employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and vacation time.
- Ensuring compliance with federal, state, and local laws regarding payroll and employment taxes.
- Generating and maintaining accurate payroll records for auditing purposes.
Payroll Challenges
Payroll management can be challenging due to the constantly evolving tax laws and regulations. Employers must stay updated to avoid penalties and ensure compliance. Additionally, calculating and processing payroll accurately requires a high level of precision, as errors can lead to financial and legal consequences.
Income Tax: Unraveling the Complexity

Income tax is a crucial aspect of personal finance and government revenue. It is a tax levied on the income earned by individuals or businesses within a jurisdiction. Income tax is a significant source of revenue for governments, which use it to fund public services, infrastructure, and social programs.
How Income Tax Works
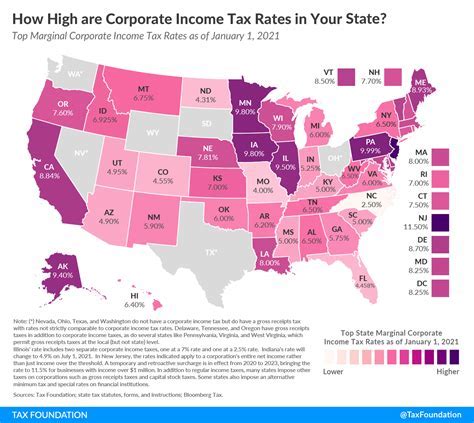
Income tax is typically calculated based on a progressive tax system, where higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. The tax rate increases as income increases, creating a more equitable distribution of tax burden.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $10,000 | 10% |
| $10,001 - $20,000 | 15% |
| $20,001 - $50,000 | 20% |
| Over $50,000 | 25% |
In the above example, an individual earning $25,000 would be taxed at a rate of 20% on their income between $20,001 and $50,000, and at a lower rate of 15% on the first $10,000.
Income Tax Withholding
Employers are responsible for withholding income tax from their employees’ paychecks. The amount withheld is based on the employee’s tax withholding preferences, as indicated on their W-4 form. The withheld tax is then remitted to the appropriate tax authority, usually on a quarterly basis.
Income Tax Filing and Payment
Individuals and businesses must file income tax returns annually to report their income and calculate their tax liability. The due date for filing varies by jurisdiction, but it is typically a fixed date, such as April 15th in the United States. Taxpayers must either pay any outstanding tax liability by the due date or arrange for an extension and a payment plan with the tax authority.
The Relationship Between Payroll and Income Tax
Payroll and income tax are interconnected, as payroll deductions directly impact the income tax liability of employees. Here’s how they relate to each other:
Payroll Deductions for Income Tax
When an employer processes payroll, they withhold a portion of an employee’s earnings as income tax. The amount withheld is based on the employee’s tax withholding preferences and the tax laws in their jurisdiction. This withheld income tax is then remitted to the government by the employer.
Payroll as a Taxable Event
Payroll itself is a taxable event. Employers are required to pay payroll taxes, which include employment taxes like Social Security and Medicare. These taxes are levied on the employer and the employee, with the employer responsible for remitting both portions to the government.
Income Tax Implications for Employers
Employers must ensure that they accurately calculate and withhold income tax from employee paychecks. Failure to do so can result in penalties and legal consequences. Additionally, employers must stay updated on tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid any tax-related issues.
Tips for Navigating Payroll and Income Tax
Understanding payroll and income tax is essential for both employers and employees. Here are some tips to navigate these complex financial aspects effectively:
- Employers should invest in robust payroll software or engage professional payroll services to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Stay updated on tax laws and regulations to avoid penalties and ensure smooth payroll processing.
- Employees should review their W-4 forms annually to ensure their tax withholdings are accurate and aligned with their financial goals.
- Consider seeking professional tax advice for complex financial situations or when starting a business.
Conclusion

Payroll and income tax are integral parts of the financial landscape, impacting both individuals and businesses. By understanding the intricacies of these concepts, employers and employees can make informed financial decisions, navigate tax obligations, and ensure compliance with the law. Staying informed and proactive in managing payroll and income tax is crucial for financial stability and success.
What is the difference between payroll and income tax?
+Payroll refers to the management of employee compensation, benefits, and deductions, while income tax is a tax levied on an individual’s or business’s income. Payroll involves calculating and disbursing wages, whereas income tax is a government-mandated tax on earnings.
How does payroll impact income tax?
+Payroll deductions for income tax directly affect an employee’s tax liability. Employers withhold a portion of an employee’s earnings as income tax, which is then remitted to the government. This reduces the employee’s taxable income and influences their overall tax burden.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with payroll and income tax laws?
+Non-compliance with payroll and income tax laws can result in severe penalties, fines, and legal consequences for both employers and employees. It is crucial to stay updated on tax regulations and seek professional advice to ensure compliance.